确定字符串中给定索引处的 Unicode 代码点的Java程序
ASCII 是一种将英文字母转换为数字的代码,因为数字可以转换为我们的计算机可以理解的汇编语言。为此,我们为每个字符分配了一个从 0 到 127 的数字。字母区分大小写,大写字母的处理方式不同。可以解释完整的 ASCII 值表,但最好坚持下图中的表,无需在表中倾斜完整的 ASCII 值。端点分配如下,以便通过记住完整的表格来正确猜测 Unicode 值。使用此表,您可以提取所有字母 Unicode,无论是大写还是小写。
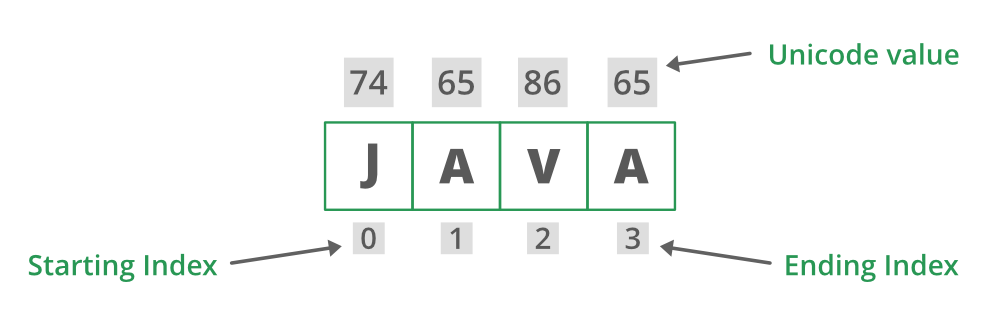
插图:S.No Must remember cases Unicode Value 1 Lowercase starting of alphabets 65 2 Lowercase ending of alphabets 90 3 Uppercase starting of alphabets 97 4 Uppercase ending of alphabets 122
由此,可以得到其他值的 Unicode,例如 b 是 66,因为小写开头是 a,如上表所示,其 65。对于 'B',它是 98。类似地,对于 'G' 的 Unicode,是 71, 'E' 是 69,'K' 是 75,依此类推。
代码点() 内置方法用于用户想要返回特定索引处的字符。索引指的是字符值(Unicode 单位),范围从 0 到 length()-1
定义:这是一个内置函数,用于返回特定索引处的字符(Unicode 点)。索引指的是字符值(Unicode 单位),范围从 0 到 length()-1。
句法:
java.lang.String.codePointAt();参数:字符值的索引。
返回类型:此方法返回指定索引处的 Unicode 值。索引指的是字符值(Unicode 代码单元),范围从 0 到 [ length() -1]。简单来说,在外行语言中,索引处字符的代码点值。
实现:考虑到此函数涉及异常的情况和另一个简单地描述函数的内部使用的情况,为了清楚地理解,讨论了两个示例。
示例 1:在这种异常处理的边缘情况下,不考虑上述哪个方法会抛出。
Java
// Importing Files and Classes
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Considering random string for input
String str = "GEEKS";
// Unicode at index 0
// Input is a small string
int result_1 = str.codePointAt(0);
int result_2 = str.codePointAt(1);
int result_3 = str.codePointAt(2);
int result_4 = str.codePointAt(3);
int result_5 = str.codePointAt(4);
// Printing the input string
System.out.println("Original String : " + str);
// Prints unicode character at index 0 to 4
// in above input string
// to show usage of codePointAt()
System.out.println("unicode point at 0 = "
+ result_1);
System.out.println("unicode point at 1 = "
+ result_2);
System.out.println("unicode point at 2 = "
+ result_3);
System.out.println("unicode point at 3 = "
+ result_4);
System.out.println("unicode point at 4 = "
+ result_5);
}
}Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Try block to check exceptions
try {
// Input string
String str = "Geeksforgeeks";
// unicode at index 0
// Storing it in integer variable
int result_1 = str.codePointAt(0);
// unicode at index 4
int result_2 = str.codePointAt(-4);
// Printing input/original string
System.out.println("Original String : " + str);
// Prints unicode character at index 1 in string
System.out.println("Character(unicode point) = "
+ result_1);
// Prints unicode character at index 4 in string
System.out.println("Character(unicode point) = "
+ result_2);
}
// Catch block to handle exception
catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
// Message printed if exception occurs
System.out.println("Exception thrown :" + e);
}
}
}输出:
Original String : GEEKS
unicode point at 0 = 71
unicode point at 1 = 69
unicode point at 2 = 69
unicode point at 3 = 75
unicode point at 4 = 83上述代码的时间复杂度为 O(n) 。
现在考虑这里的异常概念,异常只是在运行时出现的一个问题,会破坏程序的正常流程。它们可以是受检异常和非受检异常两种类型。 Checked 可以被我们的编译器检测到,其中 unchecked 异常无法被编译器检测到。为此, Java中的异常处理技术处理相同。现在处理函数中的异常。有时一个 异常时抛出 正在尝试访问超出内存的索引。下面是有关codePointAt( ) 方法中异常的概念细节。同样,讨论 索引出站 异常缺点并为了处理它 尝试捕捉技术。
示例 2:抛出 IndexOutOfBoundsException以指示某种索引(例如指向数组、指向字符串或指向向量)超出范围,如下所示。下面是说明 codeAtPoint() 抛出异常的示例。
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Try block to check exceptions
try {
// Input string
String str = "Geeksforgeeks";
// unicode at index 0
// Storing it in integer variable
int result_1 = str.codePointAt(0);
// unicode at index 4
int result_2 = str.codePointAt(-4);
// Printing input/original string
System.out.println("Original String : " + str);
// Prints unicode character at index 1 in string
System.out.println("Character(unicode point) = "
+ result_1);
// Prints unicode character at index 4 in string
System.out.println("Character(unicode point) = "
+ result_2);
}
// Catch block to handle exception
catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
// Message printed if exception occurs
System.out.println("Exception thrown :" + e);
}
}
}
Exception thrown :java.lang.StringIndexOutOfBoundsException: index -4,length 13