Java Java类
Java .io.CharArrayReader类使用字符数组创建字符缓冲区。
宣言:
public class CharArrayReader
extends Reader构造函数:
- CharArrayReader(char[] char_array) :从指定的字符数组创建一个 CharArrayReader。
- CharArrayReader(char[] char_array, int offset, int maxlen) :从字符数组的指定部分创建一个 CharArrayReader。
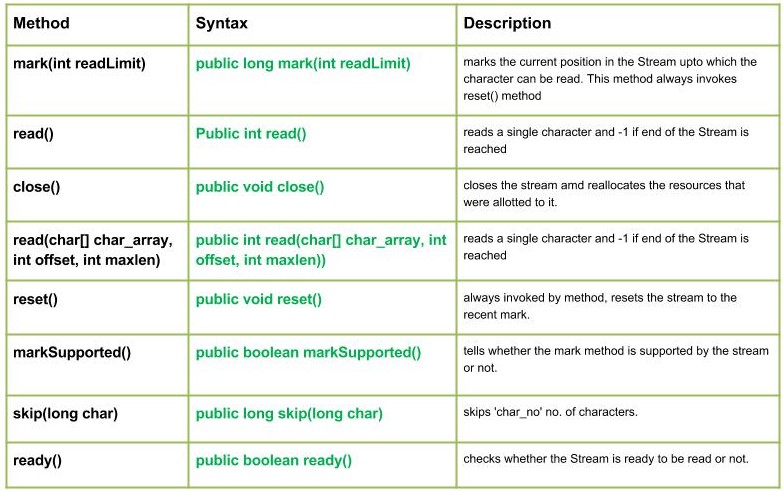
方法:
- read() : Java.io.CharArrayReader.read()读取单个字符并在到达 Stream 末尾时返回 -1。
句法 :
public int read()
Parameters :
-----------
Return :
Returns read character as an integer ranging from range 0 to 65535.
-1 : when end of file is reached.- read(char[] char_array, int offset, int maxlen) : Java.io.CharArrayReader.read(char[] char_array, int offset, int maxlen))读取单个字符并在到达 Stream 末尾时返回 -1
句法 :
public int read(char[] char_array, int offset, int maxlen))
Parameters :
char_array : destination array
offset : starting position from where to store characters
maxlen : maximum no. of characters to be read
Return :
Returns all the characters read
-1 : when end of file is reached.- ready() : Java.io.CharArrayReader.ready()检查 Stream 是否准备好被读取。
CharArrayReader 始终准备好被读取。
句法 :
public boolean ready()
Parameters :
-----------
Return :
true if CharArrayReader is ready to be read.- skip(long char) : Java.io.CharArrayReader.skip(long char_no)跳过'char_no' no。字符。如果 n 为负数,则此方法不执行任何操作并返回 0。
句法 :
public long skip(long char)
Parameters :
char_no : char no. of characters to be skipped
Return :
no. of characters skipped
Exception :
IOException : In case of I/O error occursJava
// Java program illustrating the working of CharArrayReader class methods
// read(), skip(), ready()
// read(char[] char_array, int offset, int maxlen)
import java.io.*;
public class NewClass
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
// Initializing the character array
char[] geek = {'G', 'E', 'E', 'K', 'S'};
// Initializing the char_array
CharArrayReader char_array1 = new CharArrayReader(geek);
CharArrayReader char_array2 = new CharArrayReader(geek);
// Use of ready() method
boolean check1 = char_array1.ready();
if(check1 ==true)
System.out.println("char_array1 is ready");
else
System.out.println("char_array1 is not ready");
int a = 0;
System.out.print("Use of read() method : ");
// Use of read() method : reading each character one by one
while((a = char_array1.read()) != -1)
{
char c1 = (char)a;
System.out.println(c1);
// Use of skip() method
long char_no = char_array1.skip(1);
System.out.println("Characters Skipped : "+(c1+1));
}
System.out.println("");
// Use of ready() method
boolean check2 = char_array2.ready();
if(check2 ==true)
System.out.println("char_array2 is ready");
else
System.out.println("char_array2 is not ready");
// Use of read(char[] char_array, int offset, int maxlen) : reading a part of array
char_array2.read(geek, 1, 2);
int b = 0;
System.out.print("Use of read(char[] char_array, int offset, int maxlen) method : ");
while((b = char_array2.read()) != -1)
{
char c2 = (char)b;
System.out.print(c2);
}
}
}Java
// Java program illustrating the working of FilterInputStream method
// mark(), reset()
// markSupported(), close()
import java.io.*;
public class NewClass
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
// Initializing CharArrayReader
CharArrayReader char_array = null;
char[] geek = {'H', 'E', 'L', 'L', 'O', 'G', 'E', 'E', 'K', 'S'};
try
{
char_array = new CharArrayReader(geek);
// read() method : reading and printing Characters
// one by one
System.out.println("Char : "+(char)char_array.read());
System.out.println("Char : "+(char)char_array.read());
System.out.println("Char : "+(char)char_array.read());
// mark() : read limiting the 'geek' input stream
char_array.mark(0);
System.out.println("mark() method comes to play");
System.out.println("Char : "+(char)char_array.read());
System.out.println("Char : "+(char)char_array.read());
System.out.println("Char : "+(char)char_array.read());
// Use of markSupported() :
boolean check = char_array.markSupported();
if (check == true )
System.out.println("mark() supported\n");
if (char_array.markSupported())
{
// reset() method : repositioning the stream to
// marked positions.
char_array.reset();
System.out.println("reset() invoked");
System.out.println("Char : "+(char)char_array.read());
System.out.println("Char : "+(char)char_array.read());
}
else
System.out.println("mark() method not supported.");
}
catch(Exception excpt)
{
// in case of I/O error
excpt.printStackTrace();
}
finally
{
// Use of close() : releasing the resources back to the
// GarbageCollector when closes
if(char_array != null)
char_array.close();
}
}
}输出 :
char_array1 is ready
Use of read() method : G
Characters Skipped : 72
E
Characters Skipped : 70
S
Characters Skipped : 84
char_array2 is ready
Use of read(char[] char_array, int offset, int maxlen) method : EKS- mark(int readLimit) : Java.io.CharArrayReader.mark(int readLimit)标记 Stream 中可以读取字符的当前位置。此方法始终调用 reset() 方法。对 reset() 的后续调用会将流重新定位到该点。
句法 :
public long mark(int readLimit)
Parameters :
readLimit : No. of characters that can be read up to the mark
Return :
void
Exception :
IOException : In case of I/O error occurs- markSupported() : Java.io.CharArrayReader.markSupported()告诉流是否支持标记方法。
句法 :
public boolean markSupported()
Parameters :
-------
Return :
true if the mark method is supported by the stream
Exception :
IOException : In case of I/O error occurs- reset() : Java.io.CharArrayReader.reset()将流重置为最近的标记,如果从未标记,则重置为开头。
句法 :
public void reset()
Parameters :
-------
Return :
void
Exception :
IOException : In case of I/O error occurs- close() : Java.io.CharArrayReader.close()关闭流并重新分配分配给它的资源。
句法 :
public void close()
Parameters :
-------
Return :
void
Exception :
IOException : In case of I/O error occursJava
// Java program illustrating the working of FilterInputStream method
// mark(), reset()
// markSupported(), close()
import java.io.*;
public class NewClass
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
// Initializing CharArrayReader
CharArrayReader char_array = null;
char[] geek = {'H', 'E', 'L', 'L', 'O', 'G', 'E', 'E', 'K', 'S'};
try
{
char_array = new CharArrayReader(geek);
// read() method : reading and printing Characters
// one by one
System.out.println("Char : "+(char)char_array.read());
System.out.println("Char : "+(char)char_array.read());
System.out.println("Char : "+(char)char_array.read());
// mark() : read limiting the 'geek' input stream
char_array.mark(0);
System.out.println("mark() method comes to play");
System.out.println("Char : "+(char)char_array.read());
System.out.println("Char : "+(char)char_array.read());
System.out.println("Char : "+(char)char_array.read());
// Use of markSupported() :
boolean check = char_array.markSupported();
if (check == true )
System.out.println("mark() supported\n");
if (char_array.markSupported())
{
// reset() method : repositioning the stream to
// marked positions.
char_array.reset();
System.out.println("reset() invoked");
System.out.println("Char : "+(char)char_array.read());
System.out.println("Char : "+(char)char_array.read());
}
else
System.out.println("mark() method not supported.");
}
catch(Exception excpt)
{
// in case of I/O error
excpt.printStackTrace();
}
finally
{
// Use of close() : releasing the resources back to the
// GarbageCollector when closes
if(char_array != null)
char_array.close();
}
}
}
输出 :
Char : H
Char : E
Char : L
mark() method comes to play
Char : L
Char : O
Char : G
mark() supported
reset() invoked
Char : L
Char : O