Android中的服务是一个特殊组件,可促进应用程序在后台运行以执行长时间运行的操作任务。服务的主要目的是确保应用程序在后台保持活动状态,以便用户可以同时操作多个应用程序。用户界面不是android服务所需要的,因为它旨在运行长时间运行的进程而无需任何用户干预。即使关闭了应用程序或用户切换到另一个应用程序,服务也可以在后台连续运行。此外,应用程序组件可以将自身绑定到服务以执行进程间通信(IPC) 。 android服务和线程之间的主要区别是,两者之间一定不要混淆。线程是操作系统提供的一项功能,允许用户在后台执行操作。而service是一个Android组件,它执行长时间运行的操作,由于它没有UI,因此用户可能不知道该操作。
Android服务类型
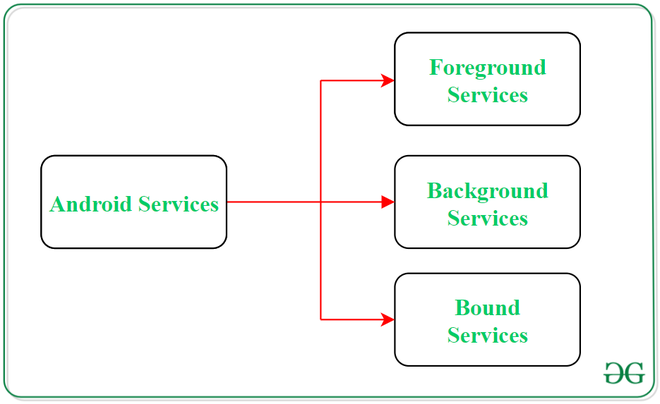
1.前台服务:
通知用户其正在进行的操作的服务称为“前台服务”。用户可以通过提供的有关正在进行的任务的通知与服务进行交互。例如在下载文件时,用户可以跟踪下载进度,也可以暂停和继续该过程。
2.后台服务:
后台服务不需要任何用户干预。这些服务不会将正在进行的后台任务通知用户,并且用户也无法访问它们。数据的计划同步或数据存储之类的过程属于此服务。
3.绑定服务:
这种类型的android服务允许活动之类的应用程序组件与其自身绑定。只要绑定了任何应用程序组件,绑定服务便会执行其任务。一次允许多个组件将自己与服务绑定。为了将应用程序组件与服务绑定,使用bindService()方法。
Android服务的生命周期
在android中,服务有2条可能的路径来完成其生命周期,即Started和Bounded 。
1.启动服务(无限制服务):
通过遵循此路径,服务将在应用程序组件调用startService()方法时启动。一旦启动,即使销毁了启动服务的组件,该服务也可以在后台连续运行。有两个选项可用来停止服务的执行:
- 通过调用stopService()方法,
- 该服务可以使用stopSelf()方法自行停止。
2.有限服务:
可以将其视为客户端-服务器界面中的服务器。通过遵循此路径,Android应用程序组件可以将请求发送到服务并获取结果。当应用程序组件通过调用bindService()方法将自身与服务绑定时,该服务被称为有界。要停止执行此服务,所有组件都必须使用unbindService()方法将自身与服务解除绑定。
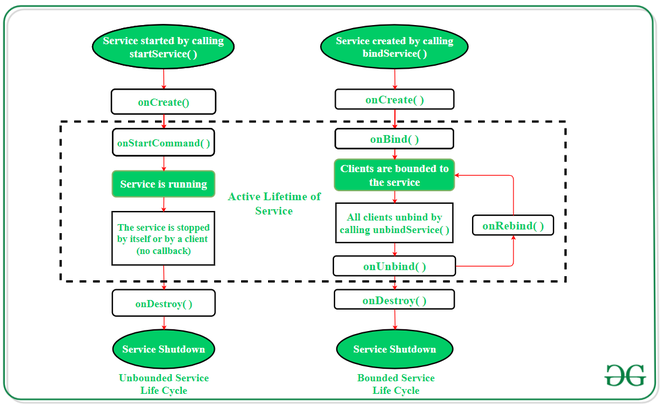
To carry out a downloading task in the background, the startService() method will be called. Whereas to get information regarding the download progress and to pause or resume the process while the application is still in the background, the service must be bounded with a component which can perform these tasks.
Android服务基础
可以通过扩展类Service的普通类来创建用户定义的服务。此外,要在应用程序上执行服务操作,需要重写某些回调方法。以下是Android Services的一些重要方法:
|
Methods |
Description |
|---|---|
| onStartCommand() |
The Android service calls this method when a component(eg: activity) requests to start a service using startService(). Once the service is started, it can be stopped explicitly using stopService() or stopSelf() methods. |
| onBind() |
This method is mandatory to implement in android service and is invoked whenever an application component calls the bindService() method in order to bind itself with a service. User-interface is also provided to communicate with the service effectively by returning an IBinder object. If the binding of service is not required then the method must return null. |
| onUnbind() |
The Android system invokes this method when all the clients get disconnected from a particular service interface. |
| onRebind() |
Once all clients are disconnected from the particular interface of service and there is a need to connect the service with new clients, the system calls this method. |
| onCreate() |
Whenever a service is created either using onStartCommand() or onBind(), the android system calls this method. This method is necessary to perform a one-time-set-up. |
| onDestroy() |
When a service is no longer in use, the system invokes this method just before the service destroys as a final clean up call. Services must implement this method in order to clean up resources like registered listeners, threads, receivers, etc. |
Android服务示例
在后台播放音乐是android服务中非常常见的示例。从用户启动服务之时起,即使用户切换到另一个应用程序,音乐也会在后台连续播放。用户必须明确停止服务才能暂停音乐。以下是使用一些回调方法对该Android服务的完整分步实施。
Note: Following steps are performed on Android Studio version 4.0
步骤1:创建一个新项目
- 单击文件,然后单击新建=>新建项目。
- 选择清空活动
- 选择语言作为Java/科特林
- 根据需要选择最小的SDK。
步骤2:修改字符串.xml文件
此文件中列出了活动中使用的所有字符串。
XML
Services_In_Android
Services In Android
Start the Service
Stop the Service
XML
Java
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.media.MediaPlayer;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.provider.Settings;
import androidx.annotation.Nullable;
public class NewService extends Service {
// declaring object of MediaPlayer
private MediaPlayer player;
@Override
// execution of service will start
// on calling this method
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
// creating a media player which
// will play the audio of Default
// ringtone in android device
player = MediaPlayer.create( this, Settings.System.DEFAULT_RINGTONE_URI );
// providing the boolean
// value as true to play
// the audio on loop
player.setLooping( true );
// starting the process
player.start();
// returns the status
// of the program
return START_STICKY;
}
@Override
// execution of the service will
// stop on calling this method
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
// stopping the process
player.stop();
}
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return null;
}
}Kotlin
import android.app.Service
import android.content.Intent
import android.media.MediaPlayer
import android.os.IBinder
import android.provider.Settings
class NewService : Service() {
// declaring object of MediaPlayer
private lateinit var player:MediaPlayer
// execution of service will start
// on calling this method
override fun onStartCommand(intent: Intent, flags: Int, startId: Int): Int {
// creating a media player which
// will play the audio of Default
// ringtone in android device
player = MediaPlayer.create(this, Settings.System.DEFAULT_RINGTONE_URI)
// providing the boolean
// value as true to play
// the audio on loop
player.setLooping(true)
// starting the process
player.start()
// returns the status
// of the program
return START_STICKY
}
// execution of the service will
// stop on calling this method
override fun onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy()
// stopping the process
player.stop()
}
override fun onBind(intent: Intent): IBinder? {
return null
}
}Java
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {
// declaring objects of Button class
private Button start, stop;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate( savedInstanceState );
setContentView( R.layout.activity_main );
// assigning ID of startButton
// to the object start
start = (Button) findViewById( R.id.startButton );
// assigning ID of stopButton
// to the object stop
stop = (Button) findViewById( R.id.stopButton );
// declaring listeners for the
// buttons to make them respond
// correctly according to the process
start.setOnClickListener( this );
stop.setOnClickListener( this );
}
public void onClick(View view) {
// process to be performed
// if start button is clicked
if(view == start){
// starting the service
startService(new Intent( this, NewService.class ) );
}
// process to be performed
// if stop button is clicked
else if (view == stop){
// stopping the service
stopService(new Intent( this, NewService.class ) );
}
}
}Kotlin
import android.content.Intent
import android.os.Bundle
import android.view.View
import android.widget.Button
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity(), View.OnClickListener {
// declaring objects of Button class
private var start: Button? = null
private var stop: Button? = null
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
// assigning ID of startButton
// to the object start
start = findViewById(R.id.startButton) as Button
// assigning ID of stopButton
// to the object stop
stop = findViewById(R.id.stopButton) as Button
// declaring listeners for the
// buttons to make them respond
// correctly according to the process
start!!.setOnClickListener(this)
stop!!.setOnClickListener(this)
}
override fun onClick(view: View) {
// process to be performed
// if start button is clicked
if (view === start) {
// starting the service
startService(Intent(this, NewService::class.java))
}
// process to be performed
// if stop button is clicked
else if (view === stop) {
// stopping the service
stopService(Intent(this, NewService::class.java))
}
}
} XML
步骤3:使用activity_main.xml文件
打开activity_main.xml文件,并在其中添加2个按钮,这些按钮将启动和停止服务。以下是用于设计适当活动布局的代码。
XML格式
步骤4:创建定制服务类
将在MainActivity类所在的同一目录中创建一个自定义服务类,并且该类将扩展Service类。回调方法用于启动和销毁服务。要播放音乐,请使用MediaPlayer对象。下面是执行此任务的代码。
Java
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.media.MediaPlayer;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.provider.Settings;
import androidx.annotation.Nullable;
public class NewService extends Service {
// declaring object of MediaPlayer
private MediaPlayer player;
@Override
// execution of service will start
// on calling this method
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
// creating a media player which
// will play the audio of Default
// ringtone in android device
player = MediaPlayer.create( this, Settings.System.DEFAULT_RINGTONE_URI );
// providing the boolean
// value as true to play
// the audio on loop
player.setLooping( true );
// starting the process
player.start();
// returns the status
// of the program
return START_STICKY;
}
@Override
// execution of the service will
// stop on calling this method
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
// stopping the process
player.stop();
}
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return null;
}
}
科特林
import android.app.Service
import android.content.Intent
import android.media.MediaPlayer
import android.os.IBinder
import android.provider.Settings
class NewService : Service() {
// declaring object of MediaPlayer
private lateinit var player:MediaPlayer
// execution of service will start
// on calling this method
override fun onStartCommand(intent: Intent, flags: Int, startId: Int): Int {
// creating a media player which
// will play the audio of Default
// ringtone in android device
player = MediaPlayer.create(this, Settings.System.DEFAULT_RINGTONE_URI)
// providing the boolean
// value as true to play
// the audio on loop
player.setLooping(true)
// starting the process
player.start()
// returns the status
// of the program
return START_STICKY
}
// execution of the service will
// stop on calling this method
override fun onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy()
// stopping the process
player.stop()
}
override fun onBind(intent: Intent): IBinder? {
return null
}
}
步骤5:使用MainActivity文件
现在,将声明按钮对象,并在MainActivity类中定义单击这些按钮时要执行的过程。下面是实现此步骤的代码。
Java
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {
// declaring objects of Button class
private Button start, stop;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate( savedInstanceState );
setContentView( R.layout.activity_main );
// assigning ID of startButton
// to the object start
start = (Button) findViewById( R.id.startButton );
// assigning ID of stopButton
// to the object stop
stop = (Button) findViewById( R.id.stopButton );
// declaring listeners for the
// buttons to make them respond
// correctly according to the process
start.setOnClickListener( this );
stop.setOnClickListener( this );
}
public void onClick(View view) {
// process to be performed
// if start button is clicked
if(view == start){
// starting the service
startService(new Intent( this, NewService.class ) );
}
// process to be performed
// if stop button is clicked
else if (view == stop){
// stopping the service
stopService(new Intent( this, NewService.class ) );
}
}
}
科特林
import android.content.Intent
import android.os.Bundle
import android.view.View
import android.widget.Button
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity(), View.OnClickListener {
// declaring objects of Button class
private var start: Button? = null
private var stop: Button? = null
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
// assigning ID of startButton
// to the object start
start = findViewById(R.id.startButton) as Button
// assigning ID of stopButton
// to the object stop
stop = findViewById(R.id.stopButton) as Button
// declaring listeners for the
// buttons to make them respond
// correctly according to the process
start!!.setOnClickListener(this)
stop!!.setOnClickListener(this)
}
override fun onClick(view: View) {
// process to be performed
// if start button is clicked
if (view === start) {
// starting the service
startService(Intent(this, NewService::class.java))
}
// process to be performed
// if stop button is clicked
else if (view === stop) {
// stopping the service
stopService(Intent(this, NewService::class.java))
}
}
}
步骤6:修改AndroidManifest.xml文件
要在任何android设备上成功实现服务,必须在AndroidManifest.xml文件中提及创建的服务。如果此文件中未提及,则服务无法执行其任务。服务名称在应用程序标记中提到。
XML格式