类型转换基本上是从一种类型到另一种类型的转换。类型转换有两种类型:
- 隐式类型转换
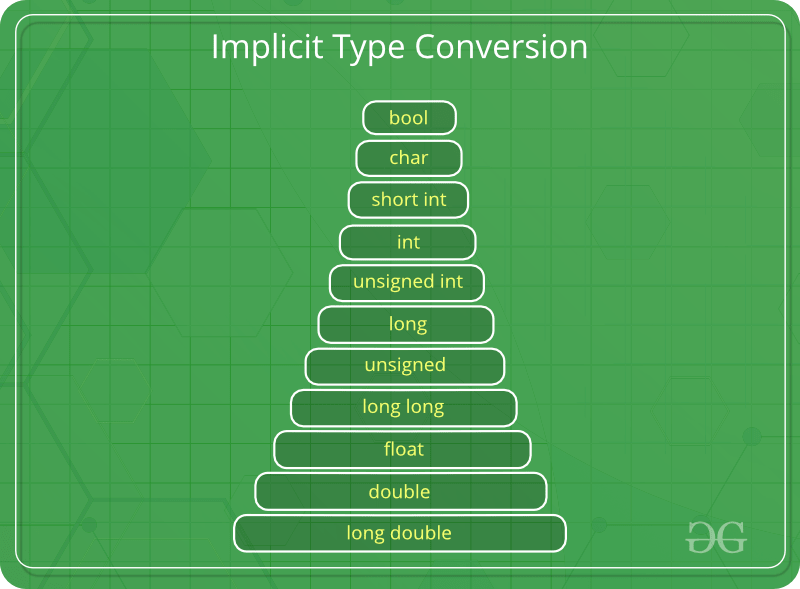
也称为“自动类型转换”。
- 由编译器自行完成,而无需用户的任何外部触发。
- 通常在表达式中存在多个数据类型时发生。在这种情况下,将进行类型转换(类型提升)以避免数据丢失。
- 变量的所有数据类型都将升级为具有最大数据类型的变量的数据类型。
bool -> char -> short int -> int -> unsigned int -> long -> unsigned -> long long -> float -> double -> long double - 隐式转换可能会丢失信息,符号可能会丢失(将符号隐式转换为无符号),并且会发生溢出(当long long被隐式转换为float时)。
类型隐式转换的示例:
// An example of implicit conversion #includeint main() { int x = 10; // integer x char y = 'a'; // character c // y implicitly converted to int. ASCII // value of 'a' is 97 x = x + y; // x is implicitly converted to float float z = x + 1.0; printf("x = %d, z = %f", x, z); return 0; } 输出:
x = 107, z = 108.000000
- 显式类型转换–
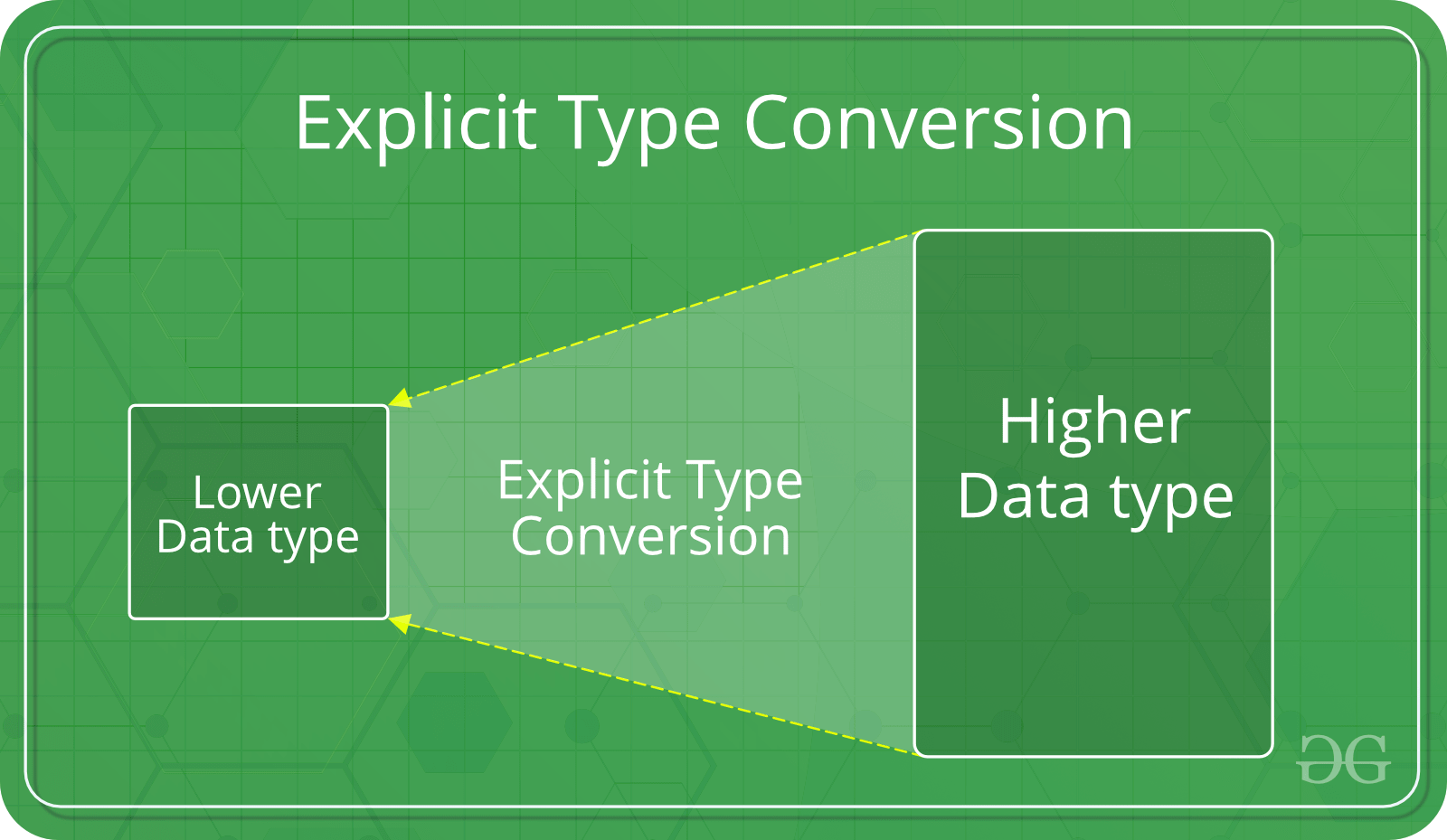
此过程也称为类型转换,它是用户定义的。用户可以在此处键入强制转换结果以使其具有特定的数据类型。
C语言中的语法:
(type) expression类型表示最终结果将转换为的数据类型。
// C program to demonstrate explicit type casting #includeint main() { double x = 1.2; // Explicit conversion from double to int int sum = (int)x + 1; printf("sum = %d", sum); return 0; } 输出:
sum = 2类型转换的优点
- 这样做是为了利用类型层次结构或类型表示形式的某些功能。
- 它有助于我们计算包含不同数据类型变量的表达式。
想要从精选的最佳视频中学习和练习问题,请查看《基础知识到高级C的C基础课程》。