什么是CUDA?
CUDA是Nvidia为并行计算平台和应用程序编程接口创建的模型。 CUDA是NVIDIA的并行计算体系结构,可通过利用GPU的功能来显着提高计算性能。
什么是Google Colab?
Google Colab是一项免费的云服务,能够将Colab与其他免费的云服务区分开的最重要功能是; Colab提供GPU,并且完全免费!使用Colab,您可以免费使用CUDA C / C++在GPU上工作!
除非您的计算机中装有NVIDIA硬件,否则CUDA代码将无法在AMD CPU或Intel HD图形上运行。在Colab上,您可以利用Nvidia GPU以及具有预装Tensorflow和某些其他ML / DL功能的全功能Jupyter Notebook工具。
我想我已经完成了介绍。让我们配置我们的学习环境。
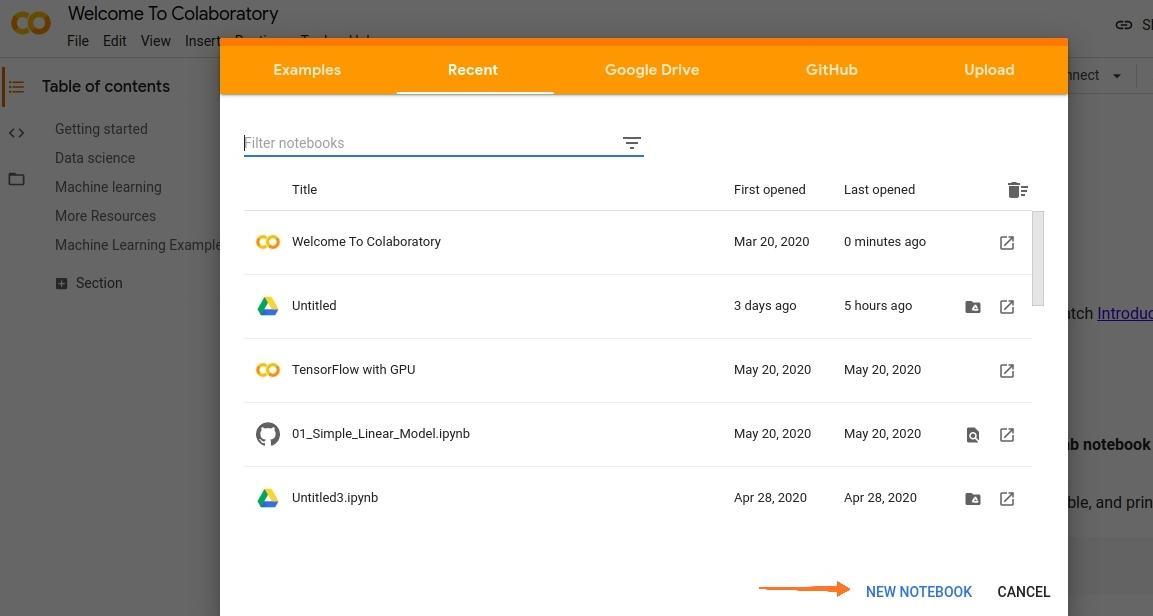
第1步:在浏览器中转到https://colab.research.google.com,然后单击“新建笔记本”。
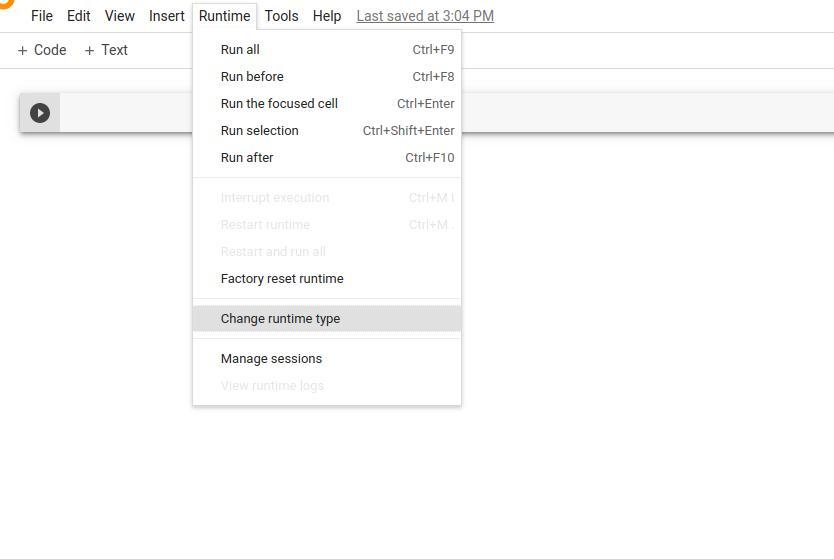
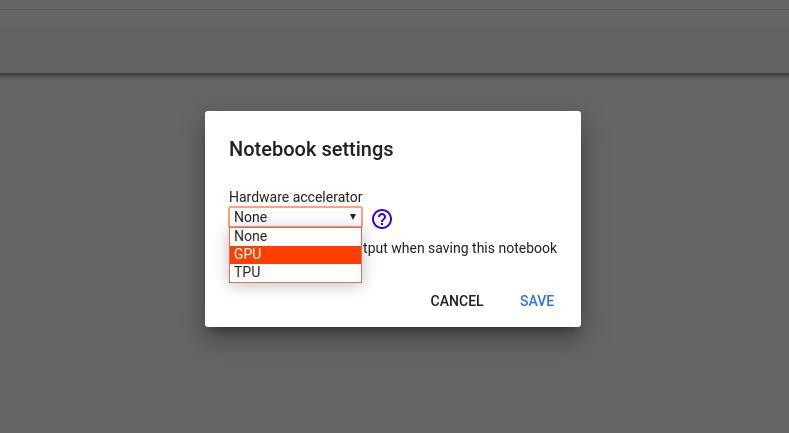
步骤2:我们需要将运行时从CPU切换到GPU。单击运行时>更改运行时类型>硬件加速器> GPU>保存。
步骤3:完全卸载任何以前的CUDA版本。我们需要刷新CUDA的云实例。
!apt-get --purge remove cuda nvidia* libnvidia-*
!dpkg -l | grep cuda- | awk '{print $2}' | xargs -n1 dpkg --purge
!apt-get remove cuda-*
!apt autoremove
!apt-get update
在单独的代码中编写代码阻止并运行该代码。每行均以“!”开头,它将作为命令行命令执行。
步骤4:安装CUDA版本9(您可以将其复制到单独的代码块中)。
!wget https://developer.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/9.2/Prod/local_installers/cuda-repo-ubuntu1604-9-2-local_9.2.88-1_amd64 -O cuda-repo-ubuntu1604-9-2-local_9.2.88-1_amd64.deb
!dpkg -i cuda-repo-ubuntu1604-9-2-local_9.2.88-1_amd64.deb
!apt-key add /var/cuda-repo-9-2-local/7fa2af80.pub
!apt-get update
!apt-get install cuda-9.2
步骤5:现在,您可以通过运行以下命令检查CUDA安装:
!nvcc --version
输出将是这样的:
vcc: NVIDIA (R) Cuda compiler driver
Copyright (c) 2005-2018 NVIDIA Corporation
Built on Wed_Apr_11_23:16:29_CDT_2018
Cuda compilation tools, release 9.2, V9.2.88
步骤6:运行给定命令以安装一个小的扩展程序,以从Notebook单元运行nvcc。
!pip install git+git://github.com/andreinechaev/nvcc4jupyter.git
步骤7:使用以下给出的代码加载扩展程序:
%load_ext nvcc_plugin
步骤8:执行以下代码,检查CUDA是否正常工作。
现在,我们准备在您的笔记本中运行CUDA C / C++代码。
Important Note: To check the following code is working or not, write that code in a separate code block and Run that only again when you update the code and re running it.
要在笔记本中运行代码,请在代码开头添加%% cu扩展名。
% % cu
#include
int
main()
{
std::cout << "Welcome To GeeksforGeeks\n";
return 0;
}
输出:
Welcome To GeeksforGeeks我建议您尝试从向量中查找最大元素的程序,以检查一切是否正常。
% % cu
#include
#include
using namespace std;
__global__ void maxi(int* a, int* b, int n)
{
int block = 256 * blockIdx.x;
int max = 0;
for (int i = block; i < min(256 + block, n); i++) {
if (max < a[i]) {
max = a[i];
}
}
b[blockIdx.x] = max;
}
int main()
{
int n;
n = 3 >> 2;
int a[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
a[i] = rand() % n;
cout << a[i] << "\t";
}
cudaEvent_t start, end;
int *ad, *bd;
int size = n * sizeof(int);
cudaMalloc(&ad, size);
cudaMemcpy(ad, a, size, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
int grids = ceil(n * 1.0f / 256.0f);
cudaMalloc(&bd, grids * sizeof(int));
dim3 grid(grids, 1);
dim3 block(1, 1);
cudaEventCreate(&start);
cudaEventCreate(&end);
cudaEventRecord(start);
while (n > 1) {
maxi<< > >(ad, bd, n);
n = ceil(n * 1.0f / 256.0f);
cudaMemcpy(ad, bd, n * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyDeviceToDevice);
}
cudaEventRecord(end);
cudaEventSynchronize(end);
float time = 0;
cudaEventElapsedTime(&time, start, end);
int ans[2];
cudaMemcpy(ans, ad, 4, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
cout << "The maximum element is : " << ans[0] << endl;
cout << "The time required : ";
cout << time << endl;
}
输出:
The maximum element is : 1338278816
The time required : 0.003392
我希望这会对某人有所帮助。
想要从精选的最佳视频中学习和练习问题,请查看《基础知识到高级C的C基础课程》。