问题是使用pthread库同步n个线程。这个想法是获取线程数并在第一个线程中打印1,在第二个线程中打印2,在第三个线程中打印3,…..在第n个线程中打印n,然后从线程1无限重复。
先决条件:多线程
例子 :
Input : Thread count
Output : 1 2 3 ... thread count 1 2 3 ... thread
count 1 2 3 ... thread count ....
Input : 5
Output : 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5
1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 ....
下面是实现:
CPP
// C code to synchronize threads
#include
#include
#include
#include
pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
pthread_cond_t* cond = NULL;
int threads;
volatile int cnt = 0;
// function to synchronize threads
void* foo(void* arg)
{
// turn is a basically to identify a thread
int turn = *(int*)arg;
while (1) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
// cnt is used to determne which thread should
// enter into critical section(printf() statement)
if (turn != cnt) {
// put all thread except one thread in waiting
// state
pthread_cond_wait(&cond[turn], &mutex);
}
// it's a time to print turn can have
// values starting from 0. Hence + 1
printf("%d ", turn + 1);
// detemine which thread need to be scheduled now
if (cnt < threads - 1) {
cnt++;
}
else {
cnt = 0;
}
// weak up next thread
pthread_cond_signal(&cond[cnt]);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
return NULL;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
pthread_t* tid;
volatile int i;
int* arr;
printf("\nEnter number of threads: ");
scanf("%d", &threads);
// allocate memory to cond (conditional variable),
// thread id's and array of size threads
cond = (pthread_cond_t*)malloc(sizeof(pthread_cond_t)
* threads);
tid = (pthread_t*)malloc(sizeof(pthread_t) * threads);
arr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * threads);
// Initialize cond (conditional variable)
for (int i = 0; i < threads; i++) {
if (pthread_cond_init(&cond[i], NULL) != 0) {
perror("pthread_cond_init() error");
exit(1);
}
}
// create threads
for (i = 0; i < threads; i++) {
arr[i] = i;
pthread_create(&tid[i], NULL, foo, (void*)&arr[i]);
}
// waiting for thread
for (i = 0; i < threads; i++) {
pthread_join(tid[i], NULL);
}
return 0;
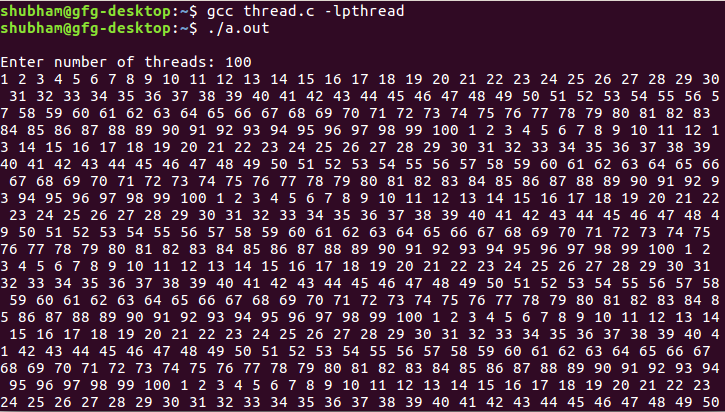
} 输出 :
想要从精选的最佳视频中学习和练习问题,请查看《基础知识到高级C的C基础课程》。