多线程中的条件等待和信号是什么?
说明:当您要使线程休眠时,可以使用条件变量。在Linux下的C中,有一个函数pthread_cond_wait()可以等待或进入睡眠状态。
另一方面,有一个函数pthread_cond_signal()来唤醒睡眠或等待线程。
线程可以等待条件变量。
先决条件:多线程
pthread_cond_wait()的语法:
int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond,
pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex);
范围 :
cond : condition variable
mutex : is mutex lock
返回值:
On success, 0 is returned ; otherwise, an error
number shall be returned to indicate the error.
pthread_cond_wait()释放互斥锁指定的锁,并等待条件cond变量。
pthread_cond_signal()的语法:
int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond);
范围 :
cond : condition variable
返回值:
On success, 0 is returned ; otherwise, an error number
shall be returned to indicate the error.
pthread_cond_signal()唤醒线程,等待条件变量。
注意:以上两个功能可以同时使用。
以下是条件,等待和信号功能的实现。
// C program to implement cond(), signal()
// and wait() functions
#include
#include
#include
// Declaration of thread condition variable
pthread_cond_t cond1 = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
// declaring mutex
pthread_mutex_t lock = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
int done = 1;
// Thread function
void* foo()
{
// acquire a lock
pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
if (done == 1) {
// let's wait on conition variable cond1
done = 2;
printf("Waiting on condition variable cond1\n");
pthread_cond_wait(&cond1, &lock);
}
else {
// Let's signal condition variable cond1
printf("Signaling condition variable cond1\n");
pthread_cond_signal(&cond1);
}
// release lock
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
printf("Returning thread\n");
return NULL;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
pthread_t tid1, tid2;
// Create thread 1
pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, foo, NULL);
// sleep for 1 sec so that thread 1
// would get a chance to run first
sleep(1);
// Create thread 2
pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, foo, NULL);
// wait for the completion of thread 2
pthread_join(tid2, NULL);
return 0;
}
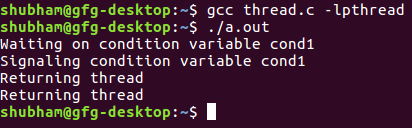
输出 :
想要从精选的最佳视频中学习和练习问题,请查看《基础知识到高级C的C基础课程》。