可逆和不可逆过程之间的区别
热力学的整个研究都建立在三个概念上,即热力学第一、第二和第三定律。这些热力学定律仅适用于系统处于平衡状态或从一种平衡状态移动到另一种平衡状态的情况。这些法律纯粹是根据人类经验得出的,没有任何这些法律的理论证据。尽管如此,这些法律的有效性得到了这样一个事实的支持,即与这些法律相悖的微不足道的事实已经被长期植入,并且没有预料到任何相反的事情。
Significance of Thermodynamics –
- It helps us to prognosticate whether any contributed chemical reaction can come about under the contributed set of conditions
- It helps in prognosticating the termination of reaction before the equilibrium is achieved.
- It helps to conclude some consequential laws like the Law of chemical equilibrium, Distribution law, etc.
热力学第一定律
热力学第一定律完全是能量守恒定律,它指出——
Energy can neither be created nor destroyed although it may be proselytized from one form to another. This implies that the whole energy of the universe ( i.e., the system and the surroundings) remains constant, although it may experience transfiguration from one form to the other.
简而言之,可以说孤立系统的能量是恒定的。
热力学第二定律
存在热力学第一定律的限制,它不能预测过程的自发性。有助于预测过程自发性的后效应称为第二定律。它指出,在任何自发过程中,宇宙(系统和环境)的熵总是增加的。其他一些定义是所有自发过程在热力学上都是不可逆的,或者在没有外部机构的帮助下,自发过程无法逆转。总结第二定律最普通的陈述,让我们重新讨论随后的自发过程。
- 冷却一杯茶
- 一滴墨水在水中的扩散
- 山下的水流。
- 两种气体的混合
热力学第二定律可以描述如下——
All spontaneous processes (or naturally occurring processes) are thermodynamically irreversible.
上述程序仍然可以通过一些偶然机构的操作反其道而行之,例如,可以用电动机制造水向上坡,可以通过加热再次加热茶。因此,第二定律可以替代地概述如下——
Without the help of an external agency, a spontaneous process cannot be reversed, example heat cannot by itself flow from a colder to a hotter body.
热力学第三定律
众所周知,绝对物质的熵随着温度的升高而增加,因为分子运动(即平移、振动和旋转)随着温度的升高而增加。同样,熵随着温度的下降而减少。 Nernst 提出了关于绝对零时无可挑剔的结晶物质的熵的后续观察,并提出了一个被称为热力学第三定律的观察概念,
The entropy of perfectly crystalline solid approaches zeroes the temperature approaches absolute zero.
不同的说法,
The entropy of all ideally crystalline solids may be taken as zero at the absolute zero of temperature.
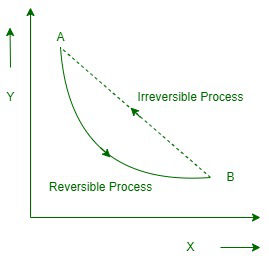
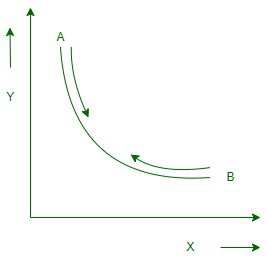
可逆过程
The process in which the system and the surroundings can be rebuilt from the final state to the original state without any change in the thermodynamic properties of the universe is called a reversible process.
Reversible Process
让我们假设系统经历了从状态 A 到状态 B 的修改。但是,如果宇宙没有变化,如果系统可以从状态 B 恢复到状态 A,则该过程表示为可逆过程。可逆过程可以完全逆转,并且没有留下任何痕迹来证明系统经历了热力学变化。为了使系统维持可逆变化,它必须无限缓慢。
在可逆过程中发生的所有状态波动都处于热力学平衡状态。因此,执行可逆过程有两个随之而来的意外情况。基本上,该过程必须发生在无限短的路径中,其次,系统的所有原始状态和最终状态必须相互平衡。
但是,如果系统的热含量在可逆过程中保持不变。这是一个绝热过程,这个过程也是一个各向同性的过程,即系统的熵保持不变。
可逆过程
可逆过程的类型
有两种类型的可逆过程,如下所示 -
- 内部可逆过程:如果在系统终止内没有发生不可逆,则说明一个过程是内部可逆的。在这些过程中,一个系统会经历一系列的平衡状态,当这个过程逆转时,系统也会经历相似的平衡状态,取代原来的状态。
- 外部可逆过程:在外部可逆过程中,过程中不会出现系统边界之外的不可逆性。例如,如果系统与力的接触面处于相同温度,则力与系统之间的热传递也是一个外部可逆过程。
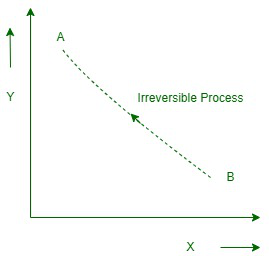
不可逆过程
Irreversible processes are correspondingly called innate processes because all the actions that take place in nature are irreversible processes. The natural process is due to the finite gradient between the two states of the system. For example, the temperature gradient between two bodies causes heat to flow between two bodies; This is actually the natural flow of heat.
此外,水从高位流向低位,电流从高位溢出到低位等。系统和环境的原始状态无法在不可逆的过程中从最终状态重建。
在不可逆过程中,系统的有色状态在从原始状态到最终状态的修改路径上彼此不平衡。在不可逆过程中,系统的熵显着增加,无法降级回其最临界值。
不可逆过程
不可逆过程的类型
有两种类型的不可逆过程,如下所示 -
- 内部不可逆性:在这种内部不可逆性中,破坏作用存在于工作流体中。
- 外部不可逆性:在这种外部不可逆性中,耗散器存在于可移动的工作流体之外。由外部来源引起的机械摩擦示例。
可逆和不可逆过程之间的区别
Reversible Process | Irreversible Process |
| The process is carried out infinitesimally slowly, i.e., the difference between the driving force and the opposing force is very very small. | This process is not carried out infinitesimally slowly but is carried out rapidly, i.e., the difference between the driving force and the opposing force is quite large. |
| At any stage during the process, equilibrium is not disturbed. | Equilibrium may exist only after the completion of the process. |
| It takes infinite time for completion. | It takes a finite time for completion. |
| It is only imaginary and cannot be achieved in actual practice. | These processes actually occur in nature. |
| Work obtained in this process is maximum. | Work obtained in this process is not the maximum. |
示例问题
问题 1:水分解每摩尔吸收 286.2 kJ 电能。当H 2和O 2 结合形成一摩尔H 2 O时,会产生286.2 kJ的热量。证明了哪条定律?从中得出什么法律声明?
回答:
Law of conservation of energy (or 1st law of thermodynamics) is proved here. According to which the energy can neither be created or destroyed, although it may be converted from one form to another.
问题2:可以借助泵将水提升到位于房屋顶部的水箱中。那为什么不认为是自发的呢?
回答:
A spontaneous process should continue to happen on its own after initiation. But in the given case it is not so as long as the pump is working the water will go up.
问题3:我们正在消耗大量的电能、太阳能等。因此,您是否认为宇宙的能量在不断减少?解释。还有哪些热力学量在不断增加或减少?
回答:
No, the energy of the universe remains constant (law of conservation of energy). The entropy of the universe is constantly increasing.
问题4:解释为什么纯晶体物质的熵在0K时为零?提及它所依据的法律。执行这项法律?
回答:
At 0 K, the constituent particles of a pure crystalline substance have an orderly arrangement and no disorder. Therefore, its entropy is taken to be zero. This statement is based on the third law of thermodynamics. The law is applied to find the absolute entropy of a substance in any given state at any given temperature.
问题5:可逆过程和不可逆过程有什么区别?
回答:
Following are the differences between Reversible Processes and Irreversible Processes: Reversible Process Irreversible ProcessThe process is carried out infinitesimally slowly, i.e., the difference between the driving force and the opposing force is very very small. This process is not carried out infinitesimally slowly but is carried out rapidly, i.e., the difference between the driving force and the opposing force is quite large. At any stage during the process, equilibrium is not disturbed. Equilibrium may exist only after the completion of the process. It takes infinite time for completion. It takes a finite time for completion. It is only imaginary and cannot be achieved in actual practice. These processes actually occur in nature. Work obtained in this process is maximum. Work obtained in this process is not the maximum.