Java中的静态关键字
Java中的static关键字主要用于内存管理。 Java中的 static 关键字用于共享给定类的相同变量或方法。用户可以将静态关键字应用于变量、方法、块和嵌套类。 static关键字属于类而不是类的实例。 static 关键字用于常量变量或类的每个实例都相同的方法。
static关键字是 Java 中的Java访问修饰符,适用于以下情况:
- 块
- 变量
- 方法
- 课程
Note: To create a static member(block, variable, method, nested class), precede its declaration with the keyword static.
当一个成员被声明为静态时,它可以在其类的任何对象被创建之前被访问,并且不引用任何对象。例如,在下面的Java程序中,我们访问静态方法m1()而不创建Test类的任何对象。
Java
// Java program to demonstrate that a static member
// can be accessed before instantiating a class
class Test
{
// static method
static void m1()
{
System.out.println("from m1");
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// calling m1 without creating
// any object of class Test
m1();
}
}Java
// Java program to demonstrate use of static blocks
class Test
{
// static variable
static int a = 10;
static int b;
// static block
static {
System.out.println("Static block initialized.");
b = a * 4;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("from main");
System.out.println("Value of a : "+a);
System.out.println("Value of b : "+b);
}
}Java
// Java program to demonstrate execution
// of static blocks and variables
class Test
{
// static variable
static int a = m1();
// static block
static {
System.out.println("Inside static block");
}
// static method
static int m1() {
System.out.println("from m1");
return 20;
}
// static method(main !!)
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("Value of a : "+a);
System.out.println("from main");
}
}Java
// Java program to demonstrate restriction on static methods
class Test
{
// static variable
static int a = 10;
// instance variable
int b = 20;
// static method
static void m1()
{
a = 20;
System.out.println("from m1");
// Cannot make a static reference to the non-static field b
b = 10; // compilation error
// Cannot make a static reference to the
// non-static method m2() from the type Test
m2(); // compilation error
// Cannot use super in a static context
System.out.println(super.a); // compiler error
}
// instance method
void m2()
{
System.out.println("from m2");
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// main method
}
}Java
// A java program to demonstrate use of
// static keyword with methods and variables
// Student class
class Student {
String name;
int rollNo;
// static variable
static String cllgName;
// static counter to set unique roll no
static int counter = 0;
public Student(String name)
{
this.name = name;
this.rollNo = setRollNo();
}
// getting unique rollNo
// through static variable(counter)
static int setRollNo()
{
counter++;
return counter;
}
// static method
static void setCllg(String name) { cllgName = name; }
// instance method
void getStudentInfo()
{
System.out.println("name : " + this.name);
System.out.println("rollNo : " + this.rollNo);
// accessing static variable
System.out.println("cllgName : " + cllgName);
}
}
// Driver class
public class StaticDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// calling static method
// without instantiating Student class
Student.setCllg("XYZ");
Student s1 = new Student("Alice");
Student s2 = new Student("Bob");
s1.getStudentInfo();
s2.getStudentInfo();
}
}Java
// A java program to demonstrate use
// of static keyword with Classes
import java.io.*;
public class GFG {
private static String str = "GeeksforGeeks";
// Static class
static class MyNestedClass {
// non-static method
public void disp(){
System.out.println(str);
}
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
GFG.MyNestedClass obj
= new GFG.MyNestedClass();
obj.disp();
}
}from m1静态块
如果您需要进行计算以初始化您的静态变量,您可以声明一个静态块,该块在类首次加载时只执行一次。
考虑以下演示静态块使用的Java程序。
Java
// Java program to demonstrate use of static blocks
class Test
{
// static variable
static int a = 10;
static int b;
// static block
static {
System.out.println("Static block initialized.");
b = a * 4;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("from main");
System.out.println("Value of a : "+a);
System.out.println("Value of b : "+b);
}
}
Static block initialized.
from main
Value of a : 10
Value of b : 40有关静态块的详细文章,请参阅静态块
静态变量
当一个变量被声明为静态变量时,该变量的一个副本被创建并在类级别的所有对象之间共享。静态变量本质上是全局变量。类的所有实例共享相同的静态变量。
静态变量的要点:
- 我们只能在类级别创建静态变量。看这里
- 静态块和静态变量按照它们在程序中出现的顺序执行。
下面是演示静态块和静态变量按照它们在程序中出现的顺序执行的Java程序。
Java
// Java program to demonstrate execution
// of static blocks and variables
class Test
{
// static variable
static int a = m1();
// static block
static {
System.out.println("Inside static block");
}
// static method
static int m1() {
System.out.println("from m1");
return 20;
}
// static method(main !!)
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("Value of a : "+a);
System.out.println("from main");
}
}
from m1
Inside static block
Value of a : 20
from main静态方法
当使用static关键字声明方法时,它被称为静态方法。最常见的静态方法示例是main()方法。如上所述,可以在创建其类的任何对象之前访问任何静态成员,并且无需引用任何对象。声明为静态的方法有几个限制:
- 它们只能直接调用其他静态方法。
- 他们只能直接访问静态数据。
- 他们不能以任何方式引用 this 或 super。
下面是演示静态方法限制的Java程序。
Java
// Java program to demonstrate restriction on static methods
class Test
{
// static variable
static int a = 10;
// instance variable
int b = 20;
// static method
static void m1()
{
a = 20;
System.out.println("from m1");
// Cannot make a static reference to the non-static field b
b = 10; // compilation error
// Cannot make a static reference to the
// non-static method m2() from the type Test
m2(); // compilation error
// Cannot use super in a static context
System.out.println(super.a); // compiler error
}
// instance method
void m2()
{
System.out.println("from m2");
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// main method
}
}
输出:
prog.java:18: error: non-static variable b cannot be referenced from a static context
b = 10; // compilation error
^
prog.java:22: error: non-static method m2() cannot be referenced from a static context
m2(); // compilation error
^
prog.java:25: error: non-static variable super cannot be referenced from a static context
System.out.println(super.a); // compiler error
^
prog.java:25: error: cannot find symbol
System.out.println(super.a); // compiler error
^
symbol: variable a
4 errors何时使用静态变量和方法?
为所有对象共有的属性使用静态变量。例如,在学生班级中,所有学生共享相同的大学名称。使用静态方法更改静态变量。
考虑下面的Java程序,它说明了静态关键字与变量和方法的使用。
Java
// A java program to demonstrate use of
// static keyword with methods and variables
// Student class
class Student {
String name;
int rollNo;
// static variable
static String cllgName;
// static counter to set unique roll no
static int counter = 0;
public Student(String name)
{
this.name = name;
this.rollNo = setRollNo();
}
// getting unique rollNo
// through static variable(counter)
static int setRollNo()
{
counter++;
return counter;
}
// static method
static void setCllg(String name) { cllgName = name; }
// instance method
void getStudentInfo()
{
System.out.println("name : " + this.name);
System.out.println("rollNo : " + this.rollNo);
// accessing static variable
System.out.println("cllgName : " + cllgName);
}
}
// Driver class
public class StaticDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// calling static method
// without instantiating Student class
Student.setCllg("XYZ");
Student s1 = new Student("Alice");
Student s2 = new Student("Bob");
s1.getStudentInfo();
s2.getStudentInfo();
}
}
name : Alice
rollNo : 1
cllgName : XYZ
name : Bob
rollNo : 2
cllgName : XYZ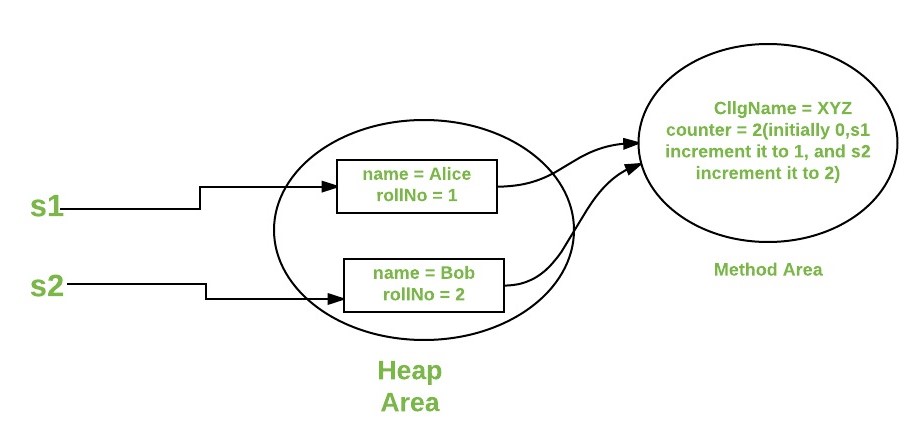
静态类
只有当一个类是嵌套类时,它才能被设为静态。我们不能用静态修饰符声明顶级类,但可以将嵌套类声明为静态。这种类型的类称为嵌套静态类。嵌套静态类不需要外部类的引用。在这种情况下,静态类不能访问 Outer 类的非静态成员。
Note: For static nested class, see a static nested class in java
执行:
Java
// A java program to demonstrate use
// of static keyword with Classes
import java.io.*;
public class GFG {
private static String str = "GeeksforGeeks";
// Static class
static class MyNestedClass {
// non-static method
public void disp(){
System.out.println(str);
}
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
GFG.MyNestedClass obj
= new GFG.MyNestedClass();
obj.disp();
}
}
GeeksforGeeks