关于Java中递增和递减运算符的有趣事实
增量运算符用于将值递增 1。增量运算符有两种:
- Post-Increment:值首先用于计算结果,然后递增。
- Pre-Increment:先增加值,然后计算结果。
减量运算符用于将值减 1。减量运算符有两种。
- 后递减:值首先用于计算结果,然后递减。
- 预递减:先递减值,然后计算结果。
现在让我们做一些关于增量和减量运算符的有趣事实:
- 只能应用于变量
- 不允许嵌套两个运算符
- 它们不是对最终变量进行操作
- 增量和减量运算符不能应用于布尔值。
让我们讨论上面列出的这 4 个事实,并按如下方式实现它们:
事实 1:只能应用于变量
我们只能将 ++ 和 —运算符应用于变量,但不能应用于常量值。如果我们尝试在常量值上应用 ++ 和 —运算符,那么我们将得到一个编译时错误,我们将在下面的示例之后的示例 1B 中看到该错误,如下所示:
示例 1:
Java
// Java program to illustrate Increment
// and Decrement Operators
// Can be Applied to Variables Only
// Main class
public class GFG {
// main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a = 10;
int b = ++a;
// Printing value inside variable
System.out.println(b);
}
}Java
// Java program to Illustrate Increment and Decrement
// operators Can be applied to variables only
// Main class
public class GFG {
// main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Declaring and initializing variable
int a = 10;
int b = ++a;
// This is change made in above program
// which reflects error during compilation
b = 10 ++;
// Printing its value
System.out.println(b);
}
}Java
// Java program to Illustrate Nesting Can Not be Applied
// to Increment and Decrement Operators
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a = 10;
int b = ++(++a);
// Printing the value inside variable
System.out.println(b);
}
}Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Increment and Decrement
// Operators Can not be applied to final variables
// Main class
public class GFG {
// MAin driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Declaring and initializing final variable
final int a = 10;
int b = ++a;
// Trying to print the updated value inside variable
System.out.println(b);
}
}Java
// Java program to Illustrate Increment and Decrement
// Operators Can not be applied boolean data type
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Initially declaring boolean as false
boolean b = false;
b++;
// Trying printing the bool value
System.out.println(b);
}
}输出
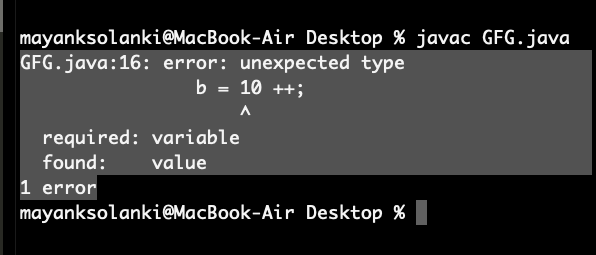
11示例 2:
Java
// Java program to Illustrate Increment and Decrement
// operators Can be applied to variables only
// Main class
public class GFG {
// main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Declaring and initializing variable
int a = 10;
int b = ++a;
// This is change made in above program
// which reflects error during compilation
b = 10 ++;
// Printing its value
System.out.println(b);
}
}
输出:
事实 2:不允许嵌套 ++ 和 —运算符
例子
Java
// Java program to Illustrate Nesting Can Not be Applied
// to Increment and Decrement Operators
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a = 10;
int b = ++(++a);
// Printing the value inside variable
System.out.println(b);
}
}
输出:

事实 3:最终变量不能应用增量和减量运算符
递增和递减运算符不能应用于最终变量,原因很简单,因为它们的值不能改变。
例子
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Increment and Decrement
// Operators Can not be applied to final variables
// Main class
public class GFG {
// MAin driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Declaring and initializing final variable
final int a = 10;
int b = ++a;
// Trying to print the updated value inside variable
System.out.println(b);
}
}
输出:

事实 4:增量和减量运算符不能应用于布尔值
我们可以对除布尔类型以外的所有原始数据类型应用 ++ 和 —运算符,因为它只有 true 和 false,这听起来甚至不切实际。
例子
Java
// Java program to Illustrate Increment and Decrement
// Operators Can not be applied boolean data type
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Initially declaring boolean as false
boolean b = false;
b++;
// Trying printing the bool value
System.out.println(b);
}
}
输出:
