什么是构造函数?
构造函数是类的成员函数,用于初始化类的对象。在C++中,创建对象(类的实例)时会自动调用Constructor。它是该类的特殊成员函数。
构造函数与普通成员函数有何不同?
构造函数与普通函数在以下方面有所不同:
- 构造函数与类本身具有相同的名称
- 构造函数没有返回类型
- 创建对象时会自动调用构造函数。
- 如果我们不指定构造函数,则C++编译器会为我们生成一个默认构造函数(不带参数,并且具有空主体)。
让我们通过一个真实的例子来了解C++中构造函数的类型。假设您去商店买了一个记号笔。当您想购买标记笔时,有哪些选择?第一个你去商店说要给我一个记号笔。因此,只说给我一个标记就意味着您没有设置哪个品牌名称和哪种颜色,也没有提及任何事情,只是说您想要一个标记。因此,当我们说我只想要一个记号笔时,无论市场上还是他的商店中经常出售的记号笔,他都将简单地交出。这就是默认的构造函数!第二种方法是您去商店说我要一个标记为红色和XYZ品牌的标记。所以您提到这件事,他会给您这个标记。因此,在这种情况下,您已经给出了参数。这就是参数化的构造函数!然后是第三个,您去商店说我要这样的记号笔(您手上的记号笔)。因此,店主将看到该标记。好的,他会为您提供一个新标记。因此,复制该标记。这就是复制构造函数!
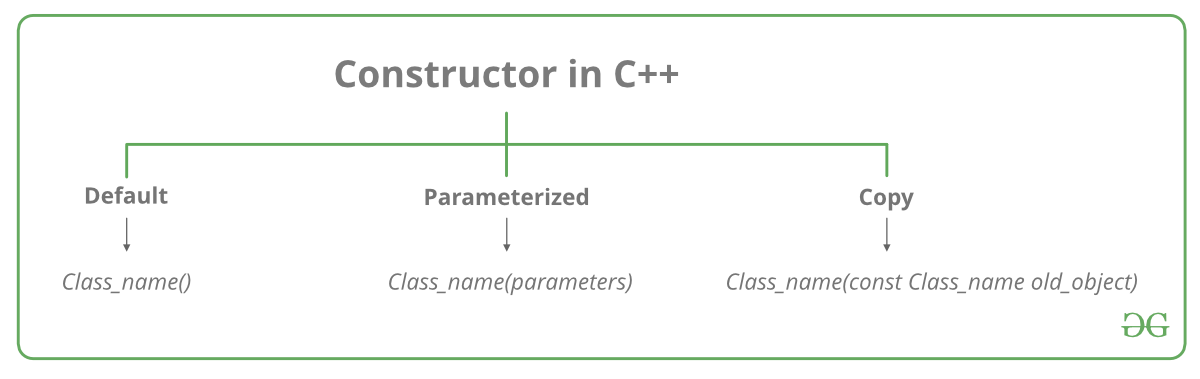
构造函数的类型
1.默认构造函数:默认构造函数是不带任何参数的构造函数。它没有参数。
CPP
// Cpp program to illustrate the
// concept of Constructors
#include
using namespace std;
class construct
{
public:
int a, b;
// Default Constructor
construct()
{
a = 10;
b = 20;
}
};
int main()
{
// Default constructor called automatically
// when the object is created
construct c;
cout << "a: " << c.a << endl
<< "b: " << c.b;
return 1;
} CPP
// CPP program to illustrate
// parameterized constructors
#include
using namespace std;
class Point
{
private:
int x, y;
public:
// Parameterized Constructor
Point(int x1, int y1)
{
x = x1;
y = y1;
}
int getX()
{
return x;
}
int getY()
{
return y;
}
};
int main()
{
// Constructor called
Point p1(10, 15);
// Access values assigned by constructor
cout << "p1.x = " << p1.getX() << ", p1.y = " << p1.getY();
return 0;
} CPP
// Illustration
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
class point
{
private:
double x, y;
public:
// Non-default Constructor &
// default Constructor
point (double px, double py)
{
x = px, y = py;
}
};
int main(void)
{
// Define an array of size
// 10 & of type point
// This line will cause error
point a[10];
// Remove above line and program
// will compile without error
point b = point(5, 6);
}输出:
a: 10
b: 20注意:即使我们没有显式定义任何构造函数,编译器也会自动隐式提供默认的构造函数。
2.参数化的构造函数:可以将参数传递给构造函数。通常,这些参数有助于在创建对象时初始化对象。要创建参数化的构造函数,只需像对其他任何函数那样向其添加参数即可。定义构造函数的主体时,请使用参数初始化对象。
CPP
// CPP program to illustrate
// parameterized constructors
#include
using namespace std;
class Point
{
private:
int x, y;
public:
// Parameterized Constructor
Point(int x1, int y1)
{
x = x1;
y = y1;
}
int getX()
{
return x;
}
int getY()
{
return y;
}
};
int main()
{
// Constructor called
Point p1(10, 15);
// Access values assigned by constructor
cout << "p1.x = " << p1.getX() << ", p1.y = " << p1.getY();
return 0;
}
输出:
p1.x = 10, p1.y = 15在参数化构造函数中声明对象时,必须将初始值作为参数传递给构造函数。对象声明的常规方法可能不起作用。构造函数可以显式或隐式调用。
Example e = Example(0, 50); // Explicit call
Example e(0, 50); // Implicit call- 参数化构造函数的用途:
- 创建对象时,使用它来初始化具有不同值的不同对象的各种数据元素。
- 它用于重载构造函数。
- 一个类中可以有多个构造函数吗?
是的,这称为构造函数重载。
3.复制构造函数:复制构造函数是一个成员函数,它使用同一类的另一个对象初始化一个对象。有关复制构造函数的详细文章。
每当我们为一个类定义一个或多个非默认构造函数(带有参数)时,也应显式定义一个默认构造函数(不带参数),因为在这种情况下编译器将不提供默认构造函数。但是,没有必要,但是始终定义默认构造函数被认为是最佳实践。
CPP
// Illustration
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
class point
{
private:
double x, y;
public:
// Non-default Constructor &
// default Constructor
point (double px, double py)
{
x = px, y = py;
}
};
int main(void)
{
// Define an array of size
// 10 & of type point
// This line will cause error
point a[10];
// Remove above line and program
// will compile without error
point b = point(5, 6);
}
输出:
Error: point (double px, double py): expects 2 arguments, 0 provided相关文章 :
- C++中的析构函数
- C++中的构造函数测验
- C++程序的输出|一组26(构造函数)
- C++程序的输出|第27集(构造函数和析构函数)