电动马达
用于以旋转形式产生机械动力的电动机。我们来看一个例子:你家的电风扇的用途是什么?当开关打开时它开始旋转,并通过旋转其叶片开始吹气。那么,如果有人问起它的工作原理,答案会是什么?是因为电吗?不,电是启动电风扇的方法,就是将电能转化为机械能。但是电能如何转化为机械能呢?电动机内部会发生什么?让我们讨论一下。
什么是电动机?
电动机是用于将电能转换为机械能的机器。当载流导体放置在磁场中时,它会经历一些有助于轴或轴旋转的力。
电动机是一种将电能转换为机械能的机械。例如,搅拌机有旋转叶片,可将原料捣碎和混合。输入混合器的电能转化为叶片旋转的机械能,从而产生所需的作用。
电动机原理
- 电机根据电流磁效应原理运行。当载流导体在其周围产生磁场时,当载流导体垂直于磁场放置时,力会作用在载流导体上。
- 当将矩形线圈置于磁场中并通过它传输电流时,一个力作用在线圈上,使其不断旋转。
- 考虑两个相互面对的条形磁铁的磁极,由一个狭窄的花坛隔开。一小段导线形成一个环并放置在磁铁之间的间隙中,使其处于磁铁产生的磁场中。当环路的末端连接到电池端子时,环路开始旋转。这是由于磁铁的磁场干扰了流入导体的电流。由于在圆中感应出磁极,感应的南极被吸引到北极,反之亦然。当圆圈中的电流反向时,引起的南极变成北极并被吸引到磁铁的南极。这导致圆圈无限旋转。
弗莱明的左手定则
左手的食指、中指和拇指应相互垂直伸展,食指代表磁场方向,中指代表导体中电流的方向,根据弗莱明的左手定则,拇指指示导体的运动方向。
电动机的构造
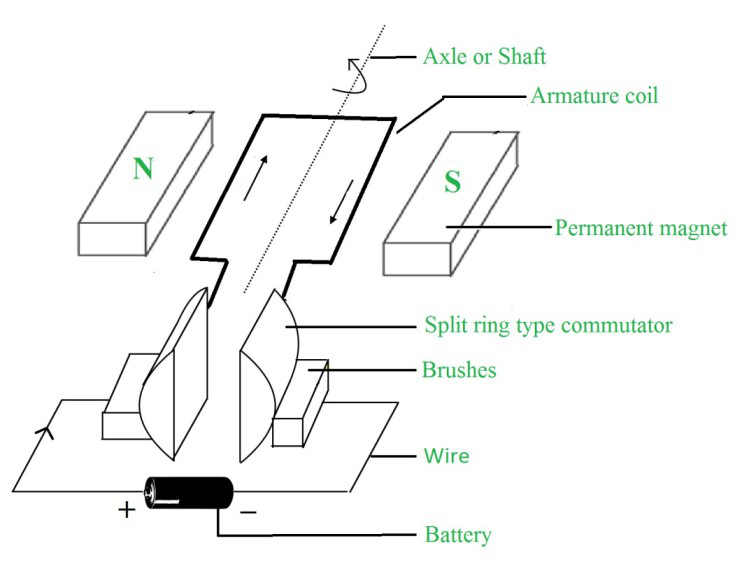
电动机的构造
以下是上图所示电机的主要部件,以及它们各自的功能:
- 电池:电池是经常连接到基本电机的直流电源。它为电枢线圈提供直流电流。
- 电刷:电动机中有两个碳刷,用作换向器和电池端子之间的连接。
- 永磁体:产生强磁场。
- 裂环式换向器:电枢线圈中的电流反转是在换向器的帮助下发生的。它由两个金属环半部分组成。电枢线圈的两端连接到这两半的金属环上。
- 电枢铁芯:电枢线圈由电枢铁芯固定到位,并为线圈提供机械支撑。
- 电枢线圈:由单个或多个矩形绝缘铜线线圈组成。
- 轴或轴:它是发生机械动力交换的地方。电枢铁心和换向器安装在轴上。
电动机的工作
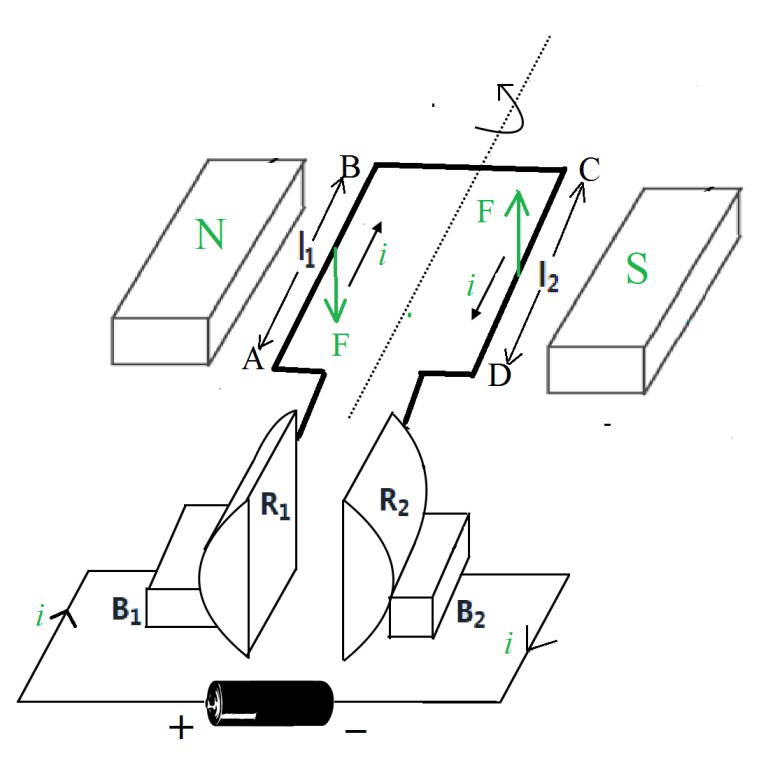
电动机的工作
- 最初,电刷B 1与换向器半环R 1接触,而电刷B 2与换向器半环R 2接触。电流沿矩形线圈 ABCD 的线圈边 l 1从 A 流向 B,并沿线圈边 l 2从 C 流向 D。磁场从磁铁的北极指向其南极。
- 根据弗莱明左手定则,线圈的线圈侧 l 1上的力F是向下的方向,但线圈的线圈侧 l 2上的力F是向上的方向。结果,线圈的l 1侧被拉下,而其l 2侧被向上推。这导致线圈 ABCD 逆时针旋转。
- 当线圈在旋转的同时到达垂直位置时,电刷将接触两个换向环之间的间隙,从而切断线圈中电流i的流动。尽管线圈的电流i在到达确切的垂直位置时被切断,但线圈继续旋转,因为它具有动量并且已经超出了垂直位置。
- 半圈后线圈超出垂直位置时,线圈侧l 2向左移动,而线圈侧l 1向右移动,两个换向器半环自动将接触位置从一个电刷变为另一个即电刷B 1与换向器半环R 2接触,而电刷B 2与换向器半环R 1接触。这使得线圈的电流i向另一个方向流动。
- 现在,当电流i方向反转时,作用在线圈 l 1和 l 2侧的力也反转了。线圈的侧 l 2现在在左侧,施加向下的力F ,而侧侧 l 1现在在右侧,施加向上的力F。结果,线圈侧l 2被拉下并且线圈侧l 1被向上推。这导致线圈逆时针旋转。
- 每转半圈,线圈中的电流就会反转,只要电池的电流通过线圈,线圈就会继续旋转。
Uses of an Electric Motor
Electric motors are utilized for a wide range of purposes. The following is a list of some of them.
- Electric cars: Electric cars used in traveling. and it is pollution-free.
- Rolling mills: Rolling mills used to decrease the width of the hard material like metals.
- Electric cranes: Electric cranes used to lift heavy objects.
- Lifts: Basically used in big buildings.
- Drilling machine: A drilling machine used to make a hole in the walls or woods
- Fan: Fans are used for blowing air.
- Hairdryers: Hairdryers used to dry wet hair.
- Tape recorder: A tape recorder used to record the audio or video.
- Washing machine: The washing machine is the wash the clothes.
- Mixers: Mixers are used to mash and mix things.
The efficiency of a motor to be roughly about 70 – 85% as the remaining energy is wasted in heat production and sounds emitted.
示例问题
问题 1:State Fleming 的左手定则。
解决方案:
Fleming’s left-hand rule state that the first finger, middle finger, and thumb of your left hand should be stretched perpendicular to each other in such a way that the first finger represents the direction of the magnetic field, the middle finger represents the direction of the current in the conductor, and the thumb indicates the direction of motion of the conductor, according to Fleming’s left-hand rule.
问题2:电动机的原理是什么?
解决方案:
A motor operates on the principle of the current magnetic effect. When a current-carrying conductor generates a magnetic field around it then a force acts on a current-carrying conductor when it is placed perpendicular to the magnetic field.
问题3:开口环在电动机中的作用是什么?
解决方案:
The reversal of current in the armature coil takes place with the help of the commutator. It is made up of two metallic ring halves. The armature coil’s two ends are connected to these two halves metallic ring.
问题 4:如何找出载流导体产生的磁场方向?
解决方案:
Maxwell’s right-hand thumb rule is used to determine the direction of the magnetic field lines created by a straight wire carrying electricity. Imagine that the current-carrying wire is in the right hand, with the thumb pointing in the direction of the current, and the direction in which the fingers encircle the wire determines the direction of magnetic lines of force around the wire.
问题5:条形磁铁和电磁铁有什么区别。
解决方案:
Following are the difference between a bar magnet and an electromagnet: Bar Magnet Electromagnet 1. It is a permanent magnet. It is a temporary magnet. 2. It generates a relatively weak attracting force. It generates a powerful magnetic field. 3. A bar magnet’s strength cannot be altered. An electromagnet’s strength can be altered by altering the number of turns in its coil or the current flowing through it. 4. A bar magnet’s polarity is set and cannot be changed. Changing the direction of current in an electromagnet’s coil can change its polarity.