在本文中,我们将讨论C++中未格式化的输入/输出操作。由于运算符>>和<<的重载可以识别所有基本的C++类型,因此可以将对象cin和cout用于各种类型的数据的输入和输出。运算符>>在istream的类重载和运算符<<在ostream的类重载。
从键盘读取数据的一般格式:
cin >> var1 >> var2 >> …. >> var_n;
- 在这里, var 1 , var 2 ,……, var n是已经声明的变量名。
- 输入数据必须用空格字符分隔,并且用户输入的数据类型必须与程序中声明的变量的数据类型相似。
- 运算符通过>>字符读取数据字符,并将其分配到指定的位置。
- 当出现空格或出现与目标类型不匹配的字符类型时,变量的读取将终止。
程序1:
C++
// C++ program to illustrate the
// input and output of the data
// enterred by user
#include
using namespace std;
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int data;
char val;
// Input the data
cin >> data;
cin >> val;
// Print the data
cout << data << " " << val;
return 0;
} C++
// C++ program to illustrate the
// input and output of data using
// get() and puts()
#include
using namespace std;
// Driver Code
int main()
{
char data;
int count = 0;
cout << "Enter Data: ";
// Get the data
cin.get(data);
while (data != '\n') {
// Print the data
cout.put(data);
count++;
// Get the data again
cin.get(data);
}
return 0;
} C++
// C++ program to illustrate the
// input and output of file using
// getline() and write() function
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// Driver Code
int main()
{
char line[100];
// Get the input
cin.getline(line, 10);
// Print the data
cout.write(line, 5);
cout << endl;
// Print the data
cout.write(line, 20);
cout << endl;
return 0;
} 输出:
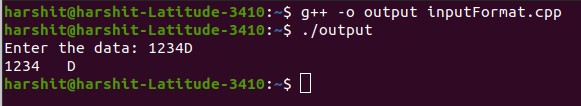
说明:在上面的程序中, 123存储在integer的变量val中, B传递到下一个cin对象并存储在字符的数据变量中。
put()和get()函数:
istream和ostream类具有预定义的函数get()和put(),以处理单个字符的输入和输出操作。函数get()方法可以有两种方式,如GET(字符*),并得到(无效)获取字符,包括空格,换行字符,标签中使用。函数get(char *)将值分配给一个变量,而get(void)将其返回给字符的值。
句法:
char data;
// get() return the character value and assign to data variable
data = cin.get();
// Display the value stored in data variable
cout.put(data);
例子:
char c;
// directly assign value to c
cin.get(c);
// Display the value stored in c variable
cout.put()
程式2:
C++
// C++ program to illustrate the
// input and output of data using
// get() and puts()
#include
using namespace std;
// Driver Code
int main()
{
char data;
int count = 0;
cout << "Enter Data: ";
// Get the data
cin.get(data);
while (data != '\n') {
// Print the data
cout.put(data);
count++;
// Get the data again
cin.get(data);
}
return 0;
}
输出:
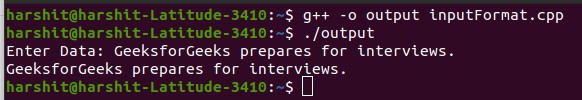
getline()和write()函数:
在C++中,函数getline()和write()提供了一种更有效的方式来处理面向行的输入和输出。函数getline()函数读取文本的完整产品线与新行字符结束。可以使用cin对象调用此函数。
句法:
cin.getline(variable_to_store_line, size);
读数以‘\ n’字符终止。该函数会读取新字符,但不会显示该新字符,而是将其替换为NULL字符。阅读特定字符串后,CIN在字符串的结束会自动添加字符。
write()函数可一次性显示整行,其语法与getline()函数。
句法:
cin.write(variable_to_store_line, size);
要记住的关键点是,当出现NULL字符时, write()函数不会自动停止显示字符串。如果大小大于行的长度,则write()函数显示在行的边界之外。
程序3:
C++
// C++ program to illustrate the
// input and output of file using
// getline() and write() function
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// Driver Code
int main()
{
char line[100];
// Get the input
cin.getline(line, 10);
// Print the data
cout.write(line, 5);
cout << endl;
// Print the data
cout.write(line, 20);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
输出:
