Java中的数组列表
ArrayList 是集合框架的一部分,存在于Java.util 包中。它为我们提供了Java中的动态数组。虽然,它可能比标准数组慢,但在需要对数组进行大量操作的程序中很有帮助。此类位于Java.util包中。

插图:
示例:以下实现演示了如何创建和使用 ArrayList。
Java
// Java program to demonstrate the
// working of ArrayList in Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class ArrayListExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Size of the
// ArrayList
int n = 5;
// Declaring the ArrayList with
// initial size n
ArrayList arrli
= new ArrayList(n);
// Appending new elements at
// the end of the list
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
arrli.add(i);
// Printing elements
System.out.println(arrli);
// Remove element at index 3
arrli.remove(3);
// Displaying the ArrayList
// after deletion
System.out.println(arrli);
// Printing elements one by one
for (int i = 0; i < arrli.size(); i++)
System.out.print(arrli.get(i) + " ");
}
} Java
// Java Program to Add elements to An ArrayList
// Importing all utility classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating an Array of string type
ArrayList al = new ArrayList<>();
// Adding elements to ArrayList
// Custom inputs
al.add("Geeks");
al.add("Geeks");
// Here we are mentioning the index
// at which it is to be added
al.add(1, "For");
// Printing all the elements in an ArrayList
System.out.println(al);
}
} Java
// Java Program to Change elements in ArrayList
// Importing all utility classes
import java.util.*;
// main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating an Arraylist object of string type
ArrayList al = new ArrayList<>();
// Adding elements to Arraylist
// Custom input elements
al.add("Geeks");
al.add("Geeks");
// Adding specifying the index to be added
al.add(1, "Geeks");
// Printing the Arraylist elements
System.out.println("Initial ArrayList " + al);
// Setting element at 1st index
al.set(1, "For");
// Printing the updated Arraylist
System.out.println("Updated ArrayList " + al);
}
} Java
// Java program to Remove Elements in ArrayList
// Importing all utility classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating an object of arraylist class
ArrayList al = new ArrayList<>();
// Adding elements to ArrayList
// Custom addition
al.add("Geeks");
al.add("Geeks");
// Adding element at specific index
al.add(1, "For");
// Printing all elements of ArrayList
System.out.println("Initial ArrayList " + al);
// Removing element from above ArrayList
al.remove(1);
// Printing the updated Arraylist elements
System.out.println("After the Index Removal " + al);
// Removing this word element in ArrayList
al.remove("Geeks");
// Now printing updated ArrayList
System.out.println("After the Object Removal "
+ al);
}
} Java
// Java program to Iterate the elements
// in an ArrayList
// Importing all utility classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating an Arraylist of string type
ArrayList al = new ArrayList<>();
// Adding elements to ArrayList
// using standard add() method
al.add("Geeks");
al.add("Geeks");
al.add(1, "For");
// Using the Get method and the
// for loop
for (int i = 0; i < al.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(al.get(i) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
// Using the for each loop
for (String str : al)
System.out.print(str + " ");
}
} [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
[1, 2, 3, 5]
1 2 3 5 由于 ArrayList 是一个动态数组,我们在创建它时不必指定大小,所以当我们动态添加和删除项目时,数组的大小会自动增加。尽管实际的库实现可能更复杂,但以下是一个非常基本的想法,解释了当数组变满时数组的工作以及我们尝试添加项目时:
- 在堆内存上创建更大的内存(例如双倍大小的内存)。
- 将当前内存元素复制到新内存。
- 现在添加了新项目,因为现在有更大的内存可用。
- 删除旧记忆。
重要特点:
- ArrayList 继承 AbstractList 类并实现 List 接口。
- ArrayList 由大小初始化。但是,如果从集合中删除对象,则如果集合增长或缩小,则大小会自动增加。
- Java ArrayList 允许我们随机访问列表。
- ArrayList 不能用于原始类型,如 int、char 等。对于这种情况,我们需要一个包装类。
- Java中的 ArrayList 可以看作 C++ 中的向量。
- ArrayList 未同步。它在Java中的等价同步类是 Vector。
让我们深入了解Java ArrayList 。看下图:
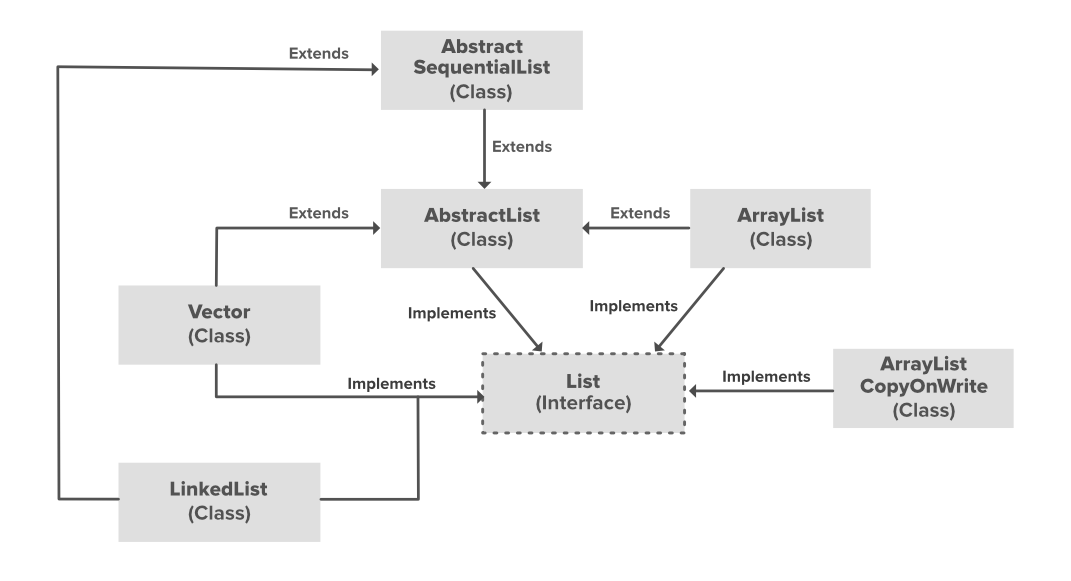
在上图中,AbstractList、CopyOnWriteArrayList 和 AbstractSequentialList 是实现列表接口的类。在每个提到的类中都实现了一个单独的功能。他们是:
- AbstractList:该类用于实现一个不可修改的列表,只需要扩展这个AbstractList类,实现get()和size()方法即可。
- CopyOnWriteArrayList:该类实现列表接口。它是 ArrayList 的增强版本,其中所有修改(添加、设置、删除等)都是通过制作列表的新副本来实现的。
- AbstractSequentialList:这个类实现了 Collection 接口和 AbstractCollection 类。该类用于实现一个不可修改的列表,只需要扩展这个 AbstractList 类并实现get()和size()方法即可。
ArrayList 中的构造函数
为了创建一个 ArrayList,我们需要创建一个 ArrayList 类的对象。 ArrayList 类由各种构造函数组成,这些构造函数允许创建数组列表。以下是此类中可用的构造函数:
1. ArrayList():该构造函数用于构建一个空数组列表。如果我们希望创建一个名为arr的空 ArrayList,则可以将其创建为:
ArrayList arr = new ArrayList();
2. ArrayList(Collection c):此构造函数用于构建一个数组列表,该数组列表使用集合 c 中的元素进行初始化。假设,我们希望创建一个 ArrayList arr,其中包含集合 c 中存在的元素,那么它可以创建为:
ArrayList arr = new ArrayList(c);
3. ArrayList(int capacity):该构造函数用于构建指定初始容量的数组列表。假设我们希望创建一个初始大小为 N 的 ArrayList,那么它可以创建为:
ArrayList arr = new ArrayList(N);
Java ArrayList 中的方法
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| add(int index, Object element) | This method is used to insert a specific element at a specific position index in a list. |
| add(Object o) | This method is used to append a specific element to the end of a list. |
| addAll(Collection C) | This method is used to append all the elements from a specific collection to the end of the mentioned list, in such an order that the values are returned by the specified collection’s iterator. |
| addAll(int index, Collection C) | Used to insert all of the elements starting at the specified position from a specific collection into the mentioned list. |
| clear() | This method is used to remove all the elements from any list. |
| clone() | This method is used to return a shallow copy of an ArrayList. |
| contains?(Object o) | Returns true if this list contains the specified element. |
| ensureCapacity?(int minCapacity) | Increases the capacity of this ArrayList instance, if necessary, to ensure that it can hold at least the number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument. |
| forEach?(Consumer action) | Performs the given action for each element of the Iterable until all elements have been processed or the action throws an exception. |
| get?(int index) | Returns the element at the specified position in this list. |
| indexOf(Object O) | The index the first occurrence of a specific element is either returned, or -1 in case the element is not in the list. |
| isEmpty?() | Returns true if this list contains no elements. |
| lastIndexOf(Object O) | The index of the last occurrence of a specific element is either returned or -1 in case the element is not in the list. |
| listIterator?() | Returns a list iterator over the elements in this list (in proper sequence). |
| listIterator?(int index) | Returns a list iterator over the elements in this list (in proper sequence), starting at the specified position in the list. |
| remove?(int index) | Removes the element at the specified position in this list. |
| remove?(Object o) | Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list, if it is present. |
| removeAll?(Collection c) | Removes from this list all of its elements that are contained in the specified collection. |
| removeIf?(Predicate filter) | Removes all of the elements of this collection that satisfy the given predicate. |
| removeRange?(int fromIndex, int toIndex) | Removes from this list all of the elements whose index is between fromIndex, inclusive, and toIndex, exclusive. |
| retainAll?(Collection c) | Retains only the elements in this list that are contained in the specified collection. |
| set?(int index, E element) | Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with the specified element. |
| size?() | Returns the number of elements in this list. |
| spliterator?() | Creates a late-binding and fail-fast Spliterator over the elements in this list. |
| subList?(int fromIndex, int toIndex) | Returns a view of the portion of this list between the specified fromIndex, inclusive, and toIndex, exclusive. |
| toArray() | This method is used to return an array containing all of the elements in the list in the correct order. |
| toArray(Object[] O) | It is also used to return an array containing all of the elements in this list in the correct order same as the previous method. |
| trimToSize() | This method is used to trim the capacity of the instance of the ArrayList to the list’s current size. |
Note: You can also create a generic ArrayList:
让我们看看如何在列出的 ArrayList 上执行一些基本操作,我们将在实现每个操作的同时进一步讨论这些操作。
- 将元素添加到列表
- 改变元素
- 移除元素
- 迭代元素
操作 1:添加元素
为了向 ArrayList 添加元素,我们可以使用 add() 方法。该方法被重载以根据不同的参数执行多个操作。它们如下:
- add(Object):此方法用于在 ArrayList 的末尾添加一个元素。
- add(int index, Object):此方法用于在 ArrayList 中的特定索引处添加元素。
例子:
Java
// Creating generic integer ArrayList
ArrayList arrli = new ArrayList(); // Java Program to Add elements to An ArrayList
// Importing all utility classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating an Array of string type
ArrayList al = new ArrayList<>();
// Adding elements to ArrayList
// Custom inputs
al.add("Geeks");
al.add("Geeks");
// Here we are mentioning the index
// at which it is to be added
al.add(1, "For");
// Printing all the elements in an ArrayList
System.out.println(al);
}
}
操作 2:更改元素
添加元素后,如果我们希望更改元素,可以使用 set() 方法完成。由于 ArrayList 是索引的,因此我们希望更改的元素由元素的索引引用。因此,此方法采用索引和需要在该索引处插入的更新元素。
例子
Java
[Geeks, For, Geeks]// Java Program to Change elements in ArrayList
// Importing all utility classes
import java.util.*;
// main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating an Arraylist object of string type
ArrayList al = new ArrayList<>();
// Adding elements to Arraylist
// Custom input elements
al.add("Geeks");
al.add("Geeks");
// Adding specifying the index to be added
al.add(1, "Geeks");
// Printing the Arraylist elements
System.out.println("Initial ArrayList " + al);
// Setting element at 1st index
al.set(1, "For");
// Printing the updated Arraylist
System.out.println("Updated ArrayList " + al);
}
}
操作 3:移除元素
为了从 ArrayList 中删除元素,我们可以使用 remove() 方法。该方法被重载以根据不同的参数执行多个操作。它们如下:
- remove(Object):此方法用于简单地从 ArrayList 中删除一个对象。如果有多个这样的对象,则删除第一次出现的对象。
- remove(int index):由于 ArrayList 是索引的,因此此方法采用一个整数值,该值仅删除 ArrayList 中该特定索引处存在的元素。删除元素后,所有元素都向左移动以填充空间并更新对象的索引。
例子
Java
Initial ArrayList [Geeks, Geeks, Geeks]
Updated ArrayList [Geeks, For, Geeks]// Java program to Remove Elements in ArrayList
// Importing all utility classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating an object of arraylist class
ArrayList al = new ArrayList<>();
// Adding elements to ArrayList
// Custom addition
al.add("Geeks");
al.add("Geeks");
// Adding element at specific index
al.add(1, "For");
// Printing all elements of ArrayList
System.out.println("Initial ArrayList " + al);
// Removing element from above ArrayList
al.remove(1);
// Printing the updated Arraylist elements
System.out.println("After the Index Removal " + al);
// Removing this word element in ArrayList
al.remove("Geeks");
// Now printing updated ArrayList
System.out.println("After the Object Removal "
+ al);
}
}
操作 4:迭代 ArrayList
有多种方法可以遍历 ArrayList。最著名的方法是使用基本的 for 循环和 get() 方法来获取特定索引处的元素和高级 for 循环。
例子
Java
Initial ArrayList [Geeks, For, Geeks]
After the Index Removal [Geeks, Geeks]
After the Object Removal [Geeks]// Java program to Iterate the elements
// in an ArrayList
// Importing all utility classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating an Arraylist of string type
ArrayList al = new ArrayList<>();
// Adding elements to ArrayList
// using standard add() method
al.add("Geeks");
al.add("Geeks");
al.add(1, "For");
// Using the Get method and the
// for loop
for (int i = 0; i < al.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(al.get(i) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
// Using the for each loop
for (String str : al)
System.out.print(str + " ");
}
}
必读: Java中的 Array 与 ArrayList