- c 中的标识符 (1)
- C标识符(1)
- C标识符
- java中的标识符(1)
- Java标识符(1)
- Java标识符(1)
- Java标识符
- Java标识符
- c 中的标识符 - 任何代码示例
- java代码示例中的标识符
- java代码示例中的标识符
- js 中的标识符 - Javascript (1)
- Scala 标识符(1)
- Scala 标识符
- js 中的标识符 - Javascript 代码示例
- C#关键字和标识符(1)
- C关键字和标识符(1)
- C#关键字和标识符
- C关键字和标识符
- C中标识符和变量的区别(1)
- C中标识符和变量的区别
- Python关键字和标识符
- Python关键字和标识符
- Python关键字和标识符
- Python关键字和标识符(1)
- Python关键字和标识符(1)
- 关键字和标识符的区别(1)
- 关键字和标识符的区别
- C中标识符和变量之间的区别(1)
📅 最后修改于: 2020-10-16 06:21:28 🧑 作者: Mango
C++标识符
程序中的C++标识符用于引用程序员创建的变量,函数,数组或其他用户定义的数据类型的名称。它们是任何语言的基本要求。每种语言都有自己的标识符命名规则。
简而言之,我们可以说C++标识符表示程序中的基本元素,如下所示:
- 常数
- 变数
- 功能
- 标签
- 定义的数据类型
一些命名规则在C和C++中很常见。它们如下:
- 仅允许使用字母字符,数字和下划线。
- 标识符名称不能以数字开头,即首字母应为字母。在第一个字母之后,我们可以使用字母,数字或下划线。
- 在C++中,大写字母和小写字母是不同的。因此,可以说C++标识符区分大小写。
- 声明的关键字不能用作变量名。
例如,假设我们有两个标识符,分别名为“ FirstName”和“ Firstname”。两种标识符的首字母大写都与字母“ N”不同,而第二字母则小写。因此,证明标识符是区分大小写的。
有效标识符
以下是有效标识符的示例:
Result
Test2
_sum
power
无效的标识符
以下是无效标识符的示例:
Sum-1 // containing special character '-'.
2data // the first letter is a digit.
break // use of a keyword.
注意:标识符不能用作关键字。它可能不会与关键字冲突,但是强烈建议不要将关键字用作标识符名称。您应该始终使用一致的方式来命名标识符,以使您的代码更具可读性和可维护性。
C和C++之间的主要区别在于变量名称长度的限制。 ANSI C++仅考虑名称的前32个字符,而ANSI C++对名称的长度没有限制。
常数是引用固定值的标识符,在程序执行期间不会更改。 C和C++都支持各种字面量常量,并且它们确实具有任何内存位置。例如,123、12.34、037、0X2等是字面量常量。
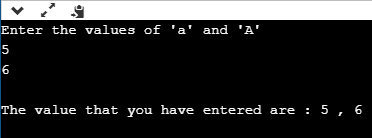
让我们看一个简单的示例,以了解标识符的概念。
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a;
int A;
cout<<"Enter the values of 'a' and 'A'";
cin>>a;
cin>>A;
cout<<"\nThe values that you have entered are : "< 在上面的代码中,我们声明了两个变量“ a”和“ A”。这两个字母是相同的,但是它们将表现为不同的标识符。我们知道标识符是区分大小写的,因此两个标识符将具有不同的存储位置。
输出量
关键字是什么?
关键字是保留字,对编译器有特殊含义。它们被保留用于特殊目的,不能用作标识符。例如,“ for”,“ break”,“ while”,“ if”,“ else”等是预定义的单词,其中预定义的单词是含义已经被编译器知道的单词。而标识符是程序员定义的程序元素,例如变量,函数,数组,对象,类的名称。
标识符和关键字之间的区别
以下是标识符和关键字之间的区别列表:
| Identifiers | Keywords |
|---|---|
| Identifiers are the names defined by the programmer to the basic elements of a program. | Keywords are the reserved words whose meaning is known by the compiler. |
| It is used to identify the name of the variable. | It is used to specify the type of entity. |
| It can consist of letters, digits, and underscore. | It contains only letters. |
| It can use both lowercase and uppercase letters. | It uses only lowercase letters. |
| No special character can be used except the underscore. | It cannot contain any special character. |
| The starting letter of identifiers can be lowercase, uppercase or underscore. | It can be started only with the lowercase letter. |
| It can be classified as internal and external identifiers. | It cannot be further classified. |
| Examples are test, result, sum, power, etc. | Examples are ‘for’, ‘if’, ‘else’, ‘break’, etc. |