📌 相关文章
- C#多态性(1)
- C++中的多态性(1)
- C++中的多态性
- C++多态性(1)
- Python中的多态性(1)
- python中的多态性(1)
- Python中的多态性
- 多态性javascript(1)
- Java多态性
- Java多态性(1)
- Java中的多态性
- Java中的多态性(1)
- php中的多态性(1)
- python代码示例中的多态性
- 多态性javascript代码示例
- php代码示例中的多态性
- R 编程中的多态性(1)
- R 编程中的多态性
- Ruby 中的多态性(1)
- Ruby 中的多态性
- GoLang 中的多态性
- Kotlin 中的多态性
- Kotlin 中的多态性(1)
- 什么是运行时多态性 (1)
- Java的接口和多态性
- Java的接口和多态性(1)
- java中的多态性与覆盖(1)
- Solidity – 多态性
- php 多态性 - PHP 代码示例
📜 C++多态性
📅 最后修改于: 2020-10-16 07:04:31 🧑 作者: Mango
C++多态
术语“多态”是“多” +“变形”的组合,表示多种形式。这是一个希腊词。在面向对象的编程中,我们使用3个主要概念:继承,封装和多态。
多态性的现实例子
让我们考虑一个现实生活中的多态性示例。一位女士的行为就像教室里的老师,家里的母亲或女儿以及市场上的客户一样。在这里,一个人的行为会根据情况而有所不同。
C++中有两种类型的多态性:
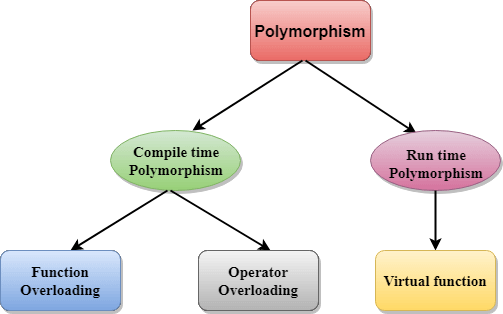
- 编译时多态性:通过匹配参数的类型和数量来调用重载函数。该信息在编译时可用,因此,编译器在编译时选择适当的函数。它是通过函数重载和运算符重载来实现的,也称为静态绑定或早期绑定。现在,让我们考虑一下函数名称和原型相同的情况。
class A // base class declaration.
{
int a;
public:
void display()
{
cout<< "Class A ";
}
};
class B : public A // derived class declaration.
{
int b;
public:
void display()
{
cout<<"Class B";
}
};
在上述情况下,在基类和派生类中,display()函数的原型都是相同的。因此,不能应用静态绑定。如果在运行时选择了适当的函数,那就太好了。这称为运行时多态。
- 运行时多态性:运行时多态性是在运行时而不是编译时调用对象的方法时实现的。它是通过方法覆盖(也称为动态绑定或后期绑定)来实现的。
黑白差异编译时间和运行时多态性。
| Compile time polymorphism | Run time polymorphism |
|---|---|
| The function to be invoked is known at the compile time. | The function to be invoked is known at the run time. |
| It is also known as overloading, early binding and static binding. | It is also known as overriding, Dynamic binding and late binding. |
| Overloading is a compile time polymorphism where more than one method is having the same name but with the different number of parameters or the type of the parameters. | Overriding is a run time polymorphism where more than one method is having the same name, number of parameters and the type of the parameters. |
| It is achieved by function overloading and operator overloading. | It is achieved by virtual functions and pointers. |
| It provides fast execution as it is known at the compile time. | It provides slow execution as it is known at the run time. |
| It is less flexible as mainly all the things execute at the compile time. | It is more flexible as all the things execute at the run time. |
C++运行时多态示例
让我们看一个简单的C++运行时多态性示例。
//没有virtual关键字的示例。
#include
using namespace std;
class Animal {
public:
void eat(){
cout<<"Eating...";
}
};
class Dog: public Animal
{
public:
void eat()
{ cout<<"Eating bread...";
}
};
int main(void) {
Dog d = Dog();
d.eat();
return 0;
}
输出:
Eating bread...
C++运行时多态示例:通过使用两个派生类
让我们看一下C++中运行时多态的另一个示例,其中有两个派生类。
//一个带有虚拟关键字的示例。
#include
using namespace std;
class Shape { // base class
public:
virtual void draw(){ // virtual function
cout<<"drawing..."<draw();
s=&rec;
s->draw();
s=?
s->draw();
}
输出:
drawing...
drawing rectangle...
drawing circle...
数据成员的运行时多态
运行时多态可以通过C++中的数据成员来实现。让我们看一个例子,其中我们通过引用变量访问字段,引用变量引用派生类的实例。
#include
using namespace std;
class Animal { // base class declaration.
public:
string color = "Black";
};
class Dog: public Animal // inheriting Animal class.
{
public:
string color = "Grey";
};
int main(void) {
Animal d= Dog();
cout< 输出:
Black