给定一个二叉树,任务是在每次操作期间删除二叉树的叶节点并打印计数。
例子:
Input:
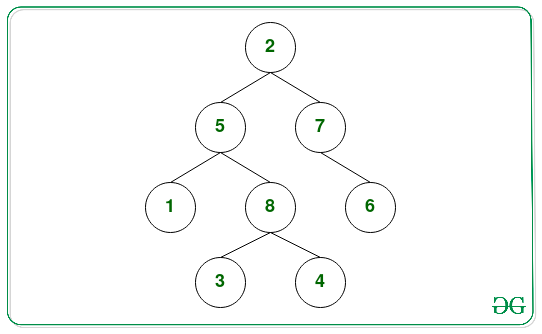
Output: 4 2 1 1
Explanation:
In the 1st operation removing the leaf nodes { 1, 3, 4, 6 } from the binary tree.
In the 2nd operation removing the leaf nodes { 8, 7 }
In the 3rd operation removing the leaf nodes { 5 }
In the 4th operation removing the leaf nodes { 2 }
Therefore, the count of leaf nodes removed in each operation 4 2 1 1.
Input:
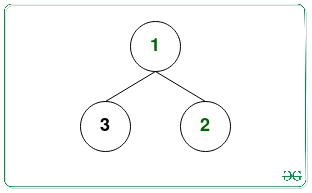
Output: 2 1
天真的方法:解决此问题的最简单方法是为每个操作重复遍历树并打印当前在二叉树中存在的叶节点的数量,并从二叉树中删除所有叶节点。
时间复杂度: O(N 2 )
辅助空间: O(1)
高效方法:为了优化上述方法,我们的想法是观察到,除非已删除其两个子节点,否则不会删除该节点。因此,可以确定节点将在哪一步被删除,这将等于1 +从该节点到以该节点为根的子树中的任何叶节点的最大路径长度。请按照以下步骤解决此问题:
- 初始化一个Map,例如M ,以在每次删除树时存储叶子节点。
- 请按照以下步骤在给定的二叉树上执行DFS遍历:
- 检查给定的节点是否为NULL 。如果发现为真,则返回0 。
- 否则,递归调用的左边和右边的节点和存储从它返回的值。
- 在每个节点的上述步骤中,找到每个节点将成为叶节点时的最大高度,例如maxHeight ((1 +左右递归调用返回的值的最大值)) 。
- 将当前节点插入地图M的maxHeight键处。
- 完成上述步骤后,在每次删除后打印存储在Map中的叶节点数。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Structure of a
// Binary Tree Node
struct Node {
int data;
Node *left, *right;
};
// Function to allocate
// a new tree node
Node* newNode(int data)
{
Node* node = new Node;
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
// Function to find the maximum height
// from leaf in the subtree rooted at
// current node and add that to hashmap
int maxHeightToLeafUTIL(
Node* curr, map >& mp)
{
if (curr == NULL) {
return 0;
}
// Max height to leaf in left subtree
int leftLeaf
= maxHeightToLeafUTIL(curr->left, mp);
// Max height to leaf in right subtree
int rightLeaf
= maxHeightToLeafUTIL(curr->right, mp);
// Max height to leaf in current subtree
int maxHeightSubtree
= 1 + max(leftLeaf, rightLeaf);
// Adding current node to the Map
mp[maxHeightSubtree].push_back(
curr->data);
return maxHeightSubtree;
}
// Function to find the count of leaf nodes
// by repeatedly removing the leaf nodes
void printAndDelete(Node* root)
{
// Stores the leaf deletion with
// each iteration
map > mp;
// Function Call to find the order
// of deletion of nodes
maxHeightToLeafUTIL(root, mp);
// Printing the map values
for (auto step : mp) {
cout << mp[step.first].size() << " ";
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Given Binary Tree
Node* root = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(7);
root->right->right = newNode(6);
root->left = newNode(5);
root->left->left = newNode(1);
root->left->right = newNode(8);
root->left->right->left = newNode(3);
root->left->right->right = newNode(4);
/*
Input :
2
/ \
5 7
/ \ \
1 8 6
/ \
3 4
*/
// Function Call
printAndDelete(root);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by pragup Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
// A binary tree node
class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class GFG
{
Node root;
// Function to find the maximum height
// from leaf in the subtree rooted at
// current node and add that to hashmap
static int maxHeightToLeafUTIL(
Node curr, Map > mp)
{
if (curr == null)
{
return 0;
}
// Max height to leaf in left subtree
int leftLeaf
= maxHeightToLeafUTIL(curr.left, mp);
// Max height to leaf in right subtree
int rightLeaf
= maxHeightToLeafUTIL(curr.right, mp);
// Max height to leaf in current subtree
int maxHeightSubtree
= 1 + Math.max(leftLeaf, rightLeaf);
// Adding current node to the Map
if(!mp.containsKey(maxHeightSubtree))
{
mp.put(maxHeightSubtree, new ArrayList<>());
}
mp.get(maxHeightSubtree).add(curr.data);
return maxHeightSubtree;
}
// Function to find the count of leaf nodes
// by repeatedly removing the leaf nodes
static void printAndDelete(Node root)
{
// Stores the leaf deletion with
// each iteration
Map > mp=new HashMap<>();
// Function Call to find the order
// of deletion of nodes
maxHeightToLeafUTIL(root, mp);
// Printing the map values
for (Map.Entry> k:mp.entrySet())
{
System.out.print(k.getValue().size() + " ");
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
GFG tree = new GFG();
tree.root = new Node(2);
tree.root.left = new Node(5);
tree.root.right = new Node(7);
tree.root.right.right = new Node(6);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(1);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(8);
tree.root.left.right.left = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.right.right = new Node(4);
/*
Input :
2
/ \
5 7
/ \ \
1 8 6
/ \
3 4
*/
// Function Call
printAndDelete(tree.root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by offbeat Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# Tree node structure used in the program
class Node:
def __init__(self, x):
self.data = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Function to find the maximum height
# from leaf in the subtree rooted at
# current node and add that to hashmap
def maxHeightToLeafUTIL(curr):
global mp
if (curr == None):
return 0
# Max height to leaf in left subtree
leftLeaf = maxHeightToLeafUTIL(curr.left)
# Max height to leaf in right subtree
rightLeaf = maxHeightToLeafUTIL(curr.right)
# Max height to leaf in current subtree
maxHeightSubtree = 1 + max(leftLeaf, rightLeaf)
# Adding current node to the Map
mp[maxHeightSubtree].append(curr.data)
return maxHeightSubtree
# Function to find the count of leaf nodes
# by repeatedly removing the leaf nodes
def printAndDelete(root):
global mp
# Function Call to find the order
# of deletion of nodes
maxHeightToLeafUTIL(root)
for step in mp:
if len(step):
print(len(step), end = " ")
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
mp = [[] for i in range(1000)]
# Given Binary Tree
root = Node(2)
root.right = Node(7)
root.right.right = Node(6)
root.left = Node(5)
root.left.left = Node(1)
root.left.right = Node(8)
root.left.right.left = Node(3)
root.left.right.right = Node(4)
#
#
# Input :
# 2
# / \
# 5 7
# / \ \
# 1 8 6
# / \
# 3 4
# Function Call
printAndDelete(root)
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29输出:
4 2 1 1时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)