1.消息切换:
在这种技术中,整个消息从一个节点到另一个节点的传输没有中断。它首先存储然后转发需要更多时间的信息。因此,增加了访问时间。在发送方和接收方之间不存在直接链接。
消息切换示例– 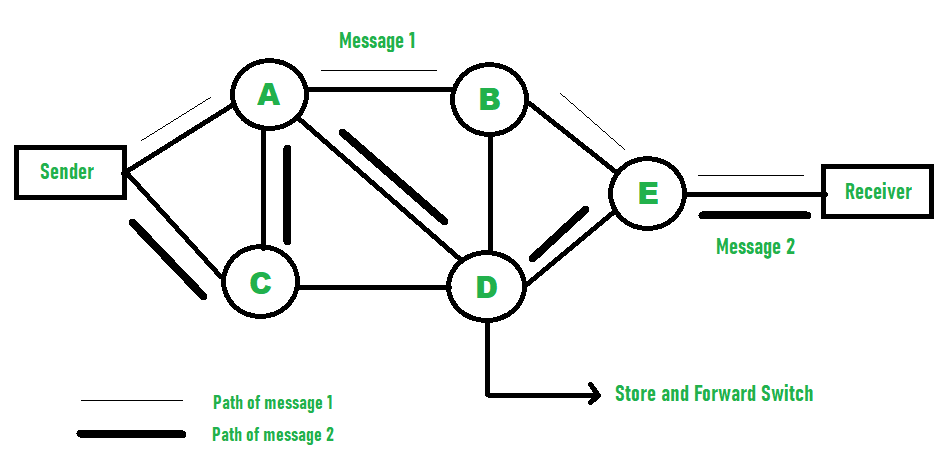
2.分组交换:
在数据包交换中,信息以数据包的形式在发送方和接收方之间传输。这些数据包从发送方一路转发到接收方。每个数据包都与一个报头相关联。然后,这些数据包然后重新组合为原始消息。由于减少了访问数据包所需的时间,因此提高了性能。因此,网络的整体性能得以提高。
分组交换的例子– 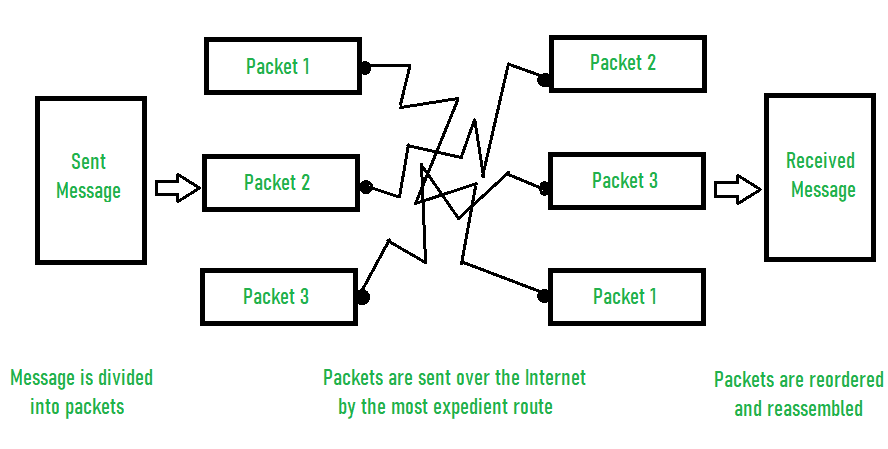
消息和分组交换之间的区别:
| Message Switching | Packet Switching |
|---|---|
| A complete message is passed across a network. | Message is broken into smaller units known as Packets. |
| In this, computer language used is ASCII, baudot, morse. | In packet switching, binary type is used. |
| In message switching there is no limit on block size. | Packet switching places a tight upper limit on block size. |
| Message exist only in one location in the network. | Parts i.e. packets of the message exist in many places in the network. |
| Example: Hop-by-hop Telex forwarding and UUCP(UNIX-to-UNIX Copy Protocol) | Example: Frame Relay, IP, and X. 25 |
| Physical links are allocated dynamically. | Virtual links are made simultaneously. |
| Access time is reduced due to increase in performance as packets are stored in disk. | Packets are stored in main memory. |