给定一个由编号为[0, N-1]的N个顶点和E 条边组成的无向图,任务是计算循环的数量,使得循环的任何顶点子集都不会形成另一个循环。
例子:
Input: N = 2, E = 2, edges = [{0, 1}, {1, 0}]
Output: 1
Explanation:
Only one cycle exists between the two vertices.

Input: N = 6, E = 9, edges = [{0, 1}, {1, 2}, {0, 2}, {3, 0}, {3, 2}, {4, 1}, {4, 2}, {5, 1}, {5, 0}]
Output: 4
Explanation:
The possible cycles are shown in the diagram below:
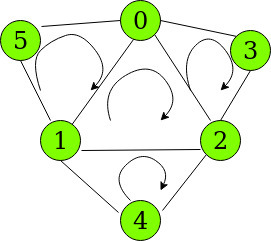
Cycles such as 5 -> 0 -> 2 -> 1 -> 5 are not considered as it comprises of inner cycles {5 -> 0 -> 1} and {0 -> 1 -> 2}
方法:
由于 V 个顶点需要 V 个边形成 1 个循环,因此可以使用以下公式表示所需循环的数量:
(Edges - Vertices) + 1插图:
N = 6, E = 9, edges = [{0, 1}, {1, 2}, {0, 2}, {3, 0}, {3, 2}, {4, 1}, {4, 2}, {5, 1}, {5, 0}]
Number of Cycles = 9 – 6 + 1 = 4
The 4 cycles in the graph are:
{5, 0, 1}, {0, 1, 2}, {3, 0, 2} and {1, 2, 4}
该公式还涵盖了单个顶点可能具有自循环的情况。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation for the
// above approach.
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to return the
// count of required cycles
int numberOfCycles(int N, int E,
int edges[][2])
{
vector graph[N];
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
graph[edges[i][0]]
.push_back(edges[i][1]);
graph[edges[i][1]]
.push_back(edges[i][0]);
}
// Return the number of cycles
return (E - N) + 1;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int N = 6;
int E = 9;
int edges[][2] = { { 0, 1 },
{ 1, 2 },
{ 2, 0 },
{ 5, 1 },
{ 5, 0 },
{ 3, 0 },
{ 3, 2 },
{ 4, 2 },
{ 4, 1 } };
int k = numberOfCycles(N, E,
edges);
cout << k << endl;
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation for the
// above approach.
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Function to return the
// count of required cycles
static int numberOfCycles(int N, int E,
int edges[][])
{
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Vector []graph = new Vector[N];
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
graph[i] = new Vector();
for(int i = 0; i < E; i++)
{
graph[edges[i][0]].add(edges[i][1]);
graph[edges[i][1]].add(edges[i][0]);
}
// Return the number of cycles
return (E - N) + 1;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 6;
int E = 9;
int edges[][] = { { 0, 1 },
{ 1, 2 },
{ 2, 0 },
{ 5, 1 },
{ 5, 0 },
{ 3, 0 },
{ 3, 2 },
{ 4, 2 },
{ 4, 1 } };
int k = numberOfCycles(N, E, edges);
System.out.print(k + "\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit Katiyar Python3
# Python3 implementation for the
# above approach.
# Function to return the
# count of required cycles
def numberOfCycles(N, E, edges):
graph=[[] for i in range(N)]
for i in range(E):
graph[edges[i][0]].append(edges[i][1]);
graph[edges[i][1]].append(edges[i][0]);
# Return the number of cycles
return (E - N) + 1;
# Driver Code
if __name__=='__main__':
N = 6;
E = 9;
edges = [ [ 0, 1 ],
[ 1, 2 ],
[ 2, 0 ],
[ 5, 1 ],
[ 5, 0 ],
[ 3, 0 ],
[ 3, 2 ],
[ 4, 2 ],
[ 4, 1 ] ];
k = numberOfCycles(N, E,edges);
print(k)
# This code is contributed by rutvik_56C#
// C# implementation for the
// above approach.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// Function to return the
// count of required cycles
static int numberOfCycles(int N, int E,
int [,]edges)
{
List []graph = new List[N];
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
graph[i] = new List();
for(int i = 0; i < E; i++)
{
graph[edges[i, 0]].Add(edges[i, 1]);
graph[edges[i, 1]].Add(edges[i, 0]);
}
// Return the number of cycles
return (E - N) + 1;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int N = 6;
int E = 9;
int [,]edges = { { 0, 1 }, { 1, 2 },
{ 2, 0 }, { 5, 1 },
{ 5, 0 }, { 3, 0 },
{ 3, 2 }, { 4, 2 },
{ 4, 1 } };
int k = numberOfCycles(N, E, edges);
Console.Write(k + "\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rohit_ranjan Javascript
4时间复杂度: O(E)
辅助空间: O(N)
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live