员工管理系统 (EMS)是一种软件,用于处理公司的主要内务管理功能。 EMS 帮助公司跟踪所有员工及其记录。它用于使用计算机化系统管理公司。
员工管理系统的目标:
- 建立员工表。
- 插入新条目。
- 删除条目。
- 搜索记录。
员工资料:
- 名称
- 员工ID
- 指定
- 经验
- 年龄
方法:
- 为了存储员工的数据,创建一个用户定义的数据类型来存储有关员工的信息。下面是数据类型的声明:
struct employee {
string name;
long int code;
string designation;
int exp;
int age;
};- 构建员工表:构建员工表的想法是使用上述结构数据类型的数组,该数组将用于存储有关员工的信息。为了在索引 i 处存储信息,数据存储为:
struct employee emp[10];
emp[i].name = "GeeksforGeeks"
emp[i].code = "12345"
emp[i].designation = "Organisation"
emp[i].exp = 10
emp[i].age = 10- 在记录中删除:由于我们使用数组来存储数据,因此删除任何索引处的数据都会将该索引处的所有数据移1,并通过将数组的大小减1来删除数组的最后一个数据。
- 在记录中搜索:对于基于任何参数在记录中搜索,其思想是遍历数据,如果在任何索引处的值参数与存储的记录匹配,则打印该员工的所有信息。
下面是C语言中员工管理系统的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
#define max 20
using namespace std;
// Structure of Employee
struct employee {
string name;
long int code;
string designation;
int exp;
int age;
};
int num;
void showMenu();
// Array of Employees to store the
// data in the form of the Structure
// of the Array
employee emp[max], tempemp[max],
sortemp[max], sortemp1[max];
// Function to build the given datatype
void build()
{
cout << "Build The Table\n";
cout << "Maximum Entries can be "
<< max << "\n";
cout << "Enter the number of "
<< "Entries required";
cin >> num;
if (num > 20) {
cout << "Maximum number of "
<< "Entries are 20\n";
num = 20;
}
cout << "Enter the following data:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
cout << "Name ";
cin >> emp[i].name;
cout << "Employee ID ";
cin >> emp[i].code;
cout << "Designation ";
cin >> emp[i].designation;
cout << "Experience ";
cin >> emp[i].exp;
cout << "Age ";
cin >> emp[i].age;
}
showMenu();
}
// Function to insert the data into
// given data type
void insert()
{
if (num < max) {
int i = num;
num++;
cout << "Enter the information "
<< "of the Employee\n";
cout << "Name ";
cin >> emp[i].name;
cout << "Employee ID ";
cin >> emp[i].code;
cout << "Designation ";
cin >> emp[i].designation;
cout << "Experience ";
cin >> emp[i].exp;
cout << "Age ";
cin >> emp[i].age;
}
else {
cout << "Employee Table Full\n";
}
showMenu();
}
// Function to delete record at index i
void deleteIndex(int i)
{
for (int j = i; j < num - 1; j++) {
emp[j].name = emp[j + 1].name;
emp[j].code = emp[j + 1].code;
emp[j].designation
= emp[j + 1].designation;
emp[j].exp = emp[j + 1].exp;
emp[j].age = emp[j + 1].age;
}
return;
}
// Function to delete record
void deleteRecord()
{
cout << "Enter the Employee ID "
<< "to Delete Record";
int code;
cin >> code;
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
if (emp[i].code == code) {
deleteIndex(i);
num--;
break;
}
}
showMenu();
}
void searchRecord()
{
cout << "Enter the Employee"
<< " ID to Search Record";
int code;
cin >> code;
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
// If the data is found
if (emp[i].code == code) {
cout << "Name "
<< emp[i].name << "\n";
cout << "Employee ID "
<< emp[i].code << "\n";
cout << "Designation "
<< emp[i].designation << "\n";
cout << "Experience "
<< emp[i].exp << "\n";
cout << "Age "
<< emp[i].age << "\n";
break;
}
}
showMenu();
}
// Function to show menu
void showMenu()
{
cout << "-------------------------"
<< "GeeksforGeeks Employee"
<< " Management System"
<< "-------------------------\n\n";
cout << "Availiable Options:\n\n";
cout << "Build Table (1)\n";
cout << "Insert New Entry (2)\n";
cout << "Delete Entry (3)\n";
cout << "Search a Record (4)\n";
cout << "Exit (5)\n";
int option;
// Input Options
cin >> option;
// Call function on the bases of the
// above option
if (option == 1) {
build();
}
else if (option == 2) {
insert();
}
else if (option == 3) {
deleteRecord();
}
else if (option == 4) {
searchRecord();
}
else if (option == 5) {
return;
}
else {
cout << "Expected Options"
<< " are 1/2/3/4/5";
showMenu();
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
showMenu();
return 0;
} 输出:
下面是上述程序的输出:
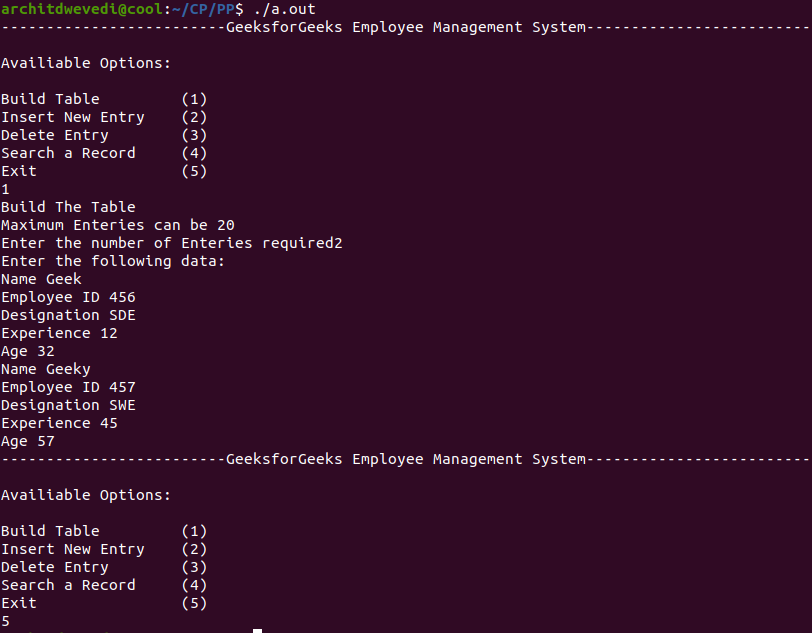
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live