给定一个由N个以1为根的节点、一个整数K和一个由分配给每个节点的值组成的数组arr[]组成的二叉树,任务是计算给定二叉树中恰好有K 个不同节点的根到叶路径的数量树。
例子:
Input: N = 3, Edges[][] = {{1, 2}, {1, 3}}, arr[] = {3, 3, 2}, K = 2, Below is the given Tree:
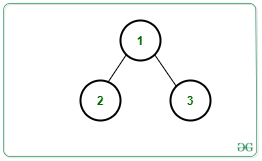
Output: 1
Explanation:
There exists only 1 distinct path i.e., Path 1 -> 3 contains 2 distinct nodes.
Hence, the answer is 1.
Input: N = 7, Edges[][] = {{1, 2}, {1, 3}, {2, 4}, {2, 5}, {3, 6}, {3, 7}}, arr[] = {2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 5, 2}, K = 1, Below is the given Tree:
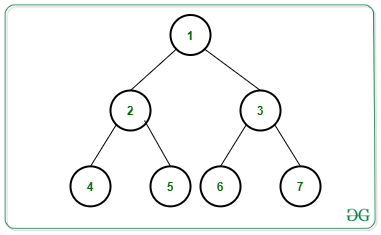
Output: 2
Explanation:
There exists only 2 distinct paths containing 1 distinct node:
1) Paths 1 -> 2 -> 4,
2) Paths 1 -> 3 -> 7
Hence, the answer is 2.
朴素的方法:最简单的方法是生成从根节点到叶节点的所有可能路径,对于每条路径,检查它是否包含K 个不同的节点。最后,打印这些路径的计数。
时间复杂度: O(N * H 2 ),其中 H 表示树的高度。
辅助空间: O(N);
高效方法:想法是使用 Preorder Traversal 和 Map 来计算从根到当前节点的路径中的不同节点。请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 将变量distinct_nodes初始化为0以存储从根到当前节点的不同节点的计数,并将ans初始化为0以存储具有K 个不同节点的不同根到叶路径的总数。
- 在给定的二叉树中执行 Preorder Traversal 并将从根到当前节点的不同节点的计数存储在映射M 中。
- 每当节点第一次出现在路径上时,将不同节点的计数增加1 。
- 如果路径上不同节点的数量大于K,则返回当前节点的父节点。
- 否则,继续访问当前节点的子节点,将当前节点值的频率增加1 。
- 在上面的步骤中,如果根到叶路径上不同节点的数量恰好等于K ,则将ans增加1 。
- 在上述步骤之后,打印ans的值作为结果计数。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Structure of a Tree Node
struct Node {
int key;
Node *left, *right;
};
// Function to create new tree node
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Function to count all root to leaf
// paths having K distinct nodes
void findkDistinctNodePaths(
Node* root, unordered_map freq,
int distinct_nodes, int k, int& ans)
{
// If current node is null
if (root == NULL)
return;
// Update count of distinct nodes
if (freq[root->key] == 0)
distinct_nodes++;
// If count > k then return to
// the parent node
if (distinct_nodes > k)
return;
// Update frequency of current node
freq[root->key]++;
// Go to the left subtree
findkDistinctNodePaths(root->left,
freq,
distinct_nodes,
k, ans);
// Go to the right subtree
findkDistinctNodePaths(root->right,
freq,
distinct_nodes,
k, ans);
// If current node is leaf node
if (root->left == NULL
&& root->right == NULL) {
// If count of distinct node
// is same as K, increment ans
if (distinct_nodes == k)
ans++;
}
}
// Function to find count of root to
// leaf paths having K distinct node
void printkDistinctNodePaths(Node* root,
int k)
{
// Initialize unordered map
unordered_map freq;
// Stores count of distinct node
int distinct_nodes = 0;
// Stores total count of nodes
int ans = 0;
// Perform Preorder Traversal
findkDistinctNodePaths(root, freq,
distinct_nodes,
k, ans);
// Print the final count
cout << ans;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
/* 2
/ \
/ \
1 3
/ \ / \
/ \ / \
4 2 -5 3
*/
// Given Binary Tree
Node* root = newNode(2);
root->left = newNode(1);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(2);
root->right->left = newNode(-5);
root->right->right = newNode(3);
// Given K
int K = 2;
// Function Call
printkDistinctNodePaths(root, K);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the
// above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Structure of a
// Tree Node
static class Node
{
int key;
Node left, right;
};
static int ans;
// Function to create
// new tree node
static Node newNode(int key)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = key;
temp.left = temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// Function to count all root
// to leaf paths having K
// distinct nodes
static void findkDistinctNodePaths(Node root,
HashMap freq,
int distinct_nodes,
int k)
{
// If current node is null
if (root == null)
return;
// Update count of distinct nodes
if (!freq.containsKey(root.key))
distinct_nodes++;
// If count > k then return
// to the parent node
if (distinct_nodes > k)
return;
// Update frequency of
// current node
if(freq.containsKey(root.key))
{
freq.put(root.key,
freq.get(root.key) + 1);
}
else
{
freq.put(root.key, 1);
}
// Go to the left subtree
findkDistinctNodePaths(root.left, freq,
distinct_nodes, k);
// Go to the right subtree
findkDistinctNodePaths(root.right, freq,
distinct_nodes, k);
// If current node is
// leaf node
if (root.left == null &&
root.right == null)
{
// If count of distinct node
// is same as K, increment ans
if (distinct_nodes == k)
ans++;
}
}
// Function to find count of root to
// leaf paths having K distinct node
static void printkDistinctNodePaths(Node root,
int k)
{
// Initialize unordered map
HashMap freq = new HashMap<>();
// Stores count of
// distinct node
int distinct_nodes = 0;
// Stores total
// count of nodes
ans = 0;
// Perform Preorder Traversal
findkDistinctNodePaths(root, freq,
distinct_nodes, k);
// Print the final count
System.out.print(ans);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/* 2
/ \
/ \
1 3
/ \ / \
/ \ / \
4 2 -5 3
*/
// Given Binary Tree
Node root = newNode(2);
root.left = newNode(1);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(2);
root.right.left = newNode(-5);
root.right.right = newNode(3);
// Given K
int K = 2;
// Function Call
printkDistinctNodePaths(root, K);
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1 Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# Structure of a Tree Node
class newNode:
def __init__(self, key):
self.key = key
self.left = None
self.right = None
ans = 0
# Function to count all root to leaf
# paths having K distinct nodes
def findkDistinctNodePaths(root, freq,
distinct_nodes, k):
global ans
# If current node is None
if (root == None):
return
# Update count of distinct nodes
if (root.key not in freq):
distinct_nodes += 1
# If count > k then return to
# the parent node
if (distinct_nodes > k):
return
# Update frequency of current node
if (root.key in freq):
freq[root.key] += 1
else:
freq[root.key] = freq.get(root.key, 0) + 1
# Go to the left subtree
findkDistinctNodePaths(root.left, freq,
distinct_nodes, k)
# Go to the right subtree
findkDistinctNodePaths(root.right, freq,
distinct_nodes, k)
# If current node is leaf node
if (root.left == None and
root.right == None):
# If count of distinct node
# is same as K, increment ans
if (distinct_nodes == k):
ans += 1
# Function to find count of root to
# leaf paths having K distinct node
def printkDistinctNodePaths(root, k):
global ans
# Initialize unordered map
freq = {}
# Stores count of distinct node
distinct_nodes = 0
# Perform Preorder Traversal
findkDistinctNodePaths(root, freq,
distinct_nodes, k)
# Print the final count
print(ans)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
''' 2
/ \
/ \
1 3
/ \ / \
/ \ / \
4 2 -5 3
'''
# Given Binary Tree
root = newNode(2)
root.left = newNode(1)
root.right = newNode(3)
root.left.left = newNode(4)
root.left.right = newNode(2)
root.right.left = newNode(-5)
root.right.right = newNode(3)
# Given K
K = 2
# Function Call
printkDistinctNodePaths(root, K)
# This code is contributed by SURENDRA_GANGWARC#
// C# program for the
// above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// Structure of a
// Tree Node
public class Node
{
public int key;
public Node left, right;
};
static int ans;
// Function to create
// new tree node
static Node newNode(int key)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = key;
temp.left = temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// Function to count all root
// to leaf paths having K
// distinct nodes
static void findkDistinctNodePaths(Node root,
Dictionary freq,
int distinct_nodes,
int k)
{
// If current node is null
if (root == null)
return;
// Update count of distinct nodes
if (!freq.ContainsKey(root.key))
distinct_nodes++;
// If count > k then return
// to the parent node
if (distinct_nodes > k)
return;
// Update frequency of
// current node
if (freq.ContainsKey(root.key))
{
freq[root.key] = freq[root.key] + 1;
}
else
{
freq.Add(root.key, 1);
}
// Go to the left subtree
findkDistinctNodePaths(root.left, freq,
distinct_nodes, k);
// Go to the right subtree
findkDistinctNodePaths(root.right, freq,
distinct_nodes, k);
// If current node is
// leaf node
if (root.left == null &&
root.right == null)
{
// If count of distinct node
// is same as K, increment ans
if (distinct_nodes == k)
ans++;
}
}
// Function to find count of root to
// leaf paths having K distinct node
static void printkDistinctNodePaths(Node root,
int k)
{
// Initialize unordered map
Dictionary freq = new Dictionary();
// Stores count of
// distinct node
int distinct_nodes = 0;
// Stores total
// count of nodes
ans = 0;
// Perform Preorder Traversal
findkDistinctNodePaths(root, freq,
distinct_nodes, k);
// Print the readonly count
Console.Write(ans);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
/* 2
/ \
/ \
1 3
/ \ / \
/ \ / \
4 2 -5 3
*/
// Given Binary Tree
Node root = newNode(2);
root.left = newNode(1);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(2);
root.right.left = newNode(-5);
root.right.right = newNode(3);
// Given K
int K = 2;
// Function Call
printkDistinctNodePaths(root, K);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi Singh 2
时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live