给定三个整数A 、 B和L ,任务是打印从范围[A, B]到L级的三元康托尔集。
三元康托集:三元康托集是通过去除线段的中间部分并将其分成 3 部分并用剩余的较短线段重复此过程而构建的集合。下面是康托尔集的图示。

三元康托集的图示
例子:
Input: A = 0, B = 1, L = 2
Output:
Level 0: [0.000000] — [1.000000]
Level 1: [0.000000] — [0.333333] [0.666667] — [1.000000]
Level 2: [0.000000] — [0.111111] [0.222222] — [0.333333] [0.666667] — [0.777778] [0.888889] — [1.000000]
Explanation: For the given range [0, 1], in level 1, it is divided into three parts ([0, 0.33], [0.33, 0.67], [0.67, 1]). From the three parts, the middle part is ignored. This process is continued for every part in the subsequent executions.
Input: A = 0, B = 9, L = 3
Output:
Level_0: [0.000000] — [9.000000]
Level_1: [0.000000] — [3.000000] [6.000000] — [9.000000]
Level_2: [0.000000] — [1.000000] [2.000000] — [3.000000] [6.000000] — [7.000000] [8.000000] — [9.000000]
Level_3: [0.000000] — [0.333333] [0.666667] — [1.000000] [2.000000] — [2.333333] [2.666667] — [3.000000] [6.000000] — [6.333333] [6.666667] — [7.000000] [8.000000] — [8.333333] [8.666667] — [9.000000]
方法:
- 为 Set 的每个节点创建一个链表数据结构,具有起始值、结束值和指向下一个节点的指针。
- 使用作为输入给出的开始和结束值初始化列表。
- 对于下一个级别:
- 创建一个新节点,其中开始值和结束值之间的差异为
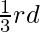 的初始值,即起始值是
的初始值,即起始值是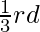 小于初始结束值。
小于初始结束值。 - 进一步修改原节点,使最终值为
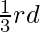 更多的初始起始值。
更多的初始起始值。 - 将指向新节点的指针相应地放在原始节点之后
- 创建一个新节点,其中开始值和结束值之间的差异为
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation to find the cantor set
// for n levels and
// for a given start_num and end_num
#include
using namespace std;
// The Linked List Structure for the Cantor Set
typedef struct cantor {
double start, end;
struct cantor* next;
} Cantor;
// Function to initialize the Cantor Set List
Cantor* startList(Cantor* head,
double start_num,
double end_num)
{
if (head == NULL) {
head = new Cantor;
head->start = start_num;
head->end = end_num;
head->next = NULL;
}
return head;
}
// Function to propogate the list
// by adding new nodes for the next levels
Cantor* propagate(Cantor* head)
{
Cantor* temp = head;
if (temp != NULL) {
Cantor* newNode
= new Cantor;
double diff
= (((temp->end) - (temp->start)) / 3);
// Modifying the start and end values
// for the next level
newNode->end = temp->end;
temp->end = ((temp->start) + diff);
newNode->start = (newNode->end) - diff;
// Changing the pointers
// to the next node
newNode->next = temp->next;
temp->next = newNode;
// Recursively call the function
// to generate the Cantor Set
// for the entire level
propagate(temp->next->next);
}
return head;
}
// Function to print a level of the Set
void print(Cantor* temp)
{
while (temp != NULL) {
printf("[%lf] -- [%lf]\t",
temp->start, temp->end);
temp = temp->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
// Function to build and display
// the Cantor Set for each level
void buildCantorSet(int A, int B, int L)
{
Cantor* head = NULL;
head = startList(head, A, B);
for (int i = 0; i < L; i++) {
cout <<"Level_"<< i<<" : ";
print(head);
propagate(head);
}
cout <<"Level_"<< L<<" : ";
print(head);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int A = 0;
int B = 9;
int L = 2;
buildCantorSet(A, B, L);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by shivanisingh C
// C implementation to find the cantor set
// for n levels and
// for a given start_num and end_num
#include
#include
#include
// The Linked List Structure for the Cantor Set
typedef struct cantor {
double start, end;
struct cantor* next;
} Cantor;
// Function to initialize the Cantor Set List
Cantor* startList(Cantor* head,
double start_num,
double end_num)
{
if (head == NULL) {
head = (Cantor*)malloc(sizeof(Cantor));
head->start = start_num;
head->end = end_num;
head->next = NULL;
}
return head;
}
// Function to propogate the list
// by adding new nodes for the next levels
Cantor* propagate(Cantor* head)
{
Cantor* temp = head;
if (temp != NULL) {
Cantor* newNode
= (Cantor*)malloc(sizeof(Cantor));
double diff
= (((temp->end) - (temp->start)) / 3);
// Modifying the start and end values
// for the next level
newNode->end = temp->end;
temp->end = ((temp->start) + diff);
newNode->start = (newNode->end) - diff;
// Changing the pointers
// to the next node
newNode->next = temp->next;
temp->next = newNode;
// Recursively call the function
// to generate the Cantor Set
// for the entire level
propagate(temp->next->next);
}
return head;
}
// Function to print a level of the Set
void print(Cantor* temp)
{
while (temp != NULL) {
printf("[%lf] -- [%lf]\t",
temp->start, temp->end);
temp = temp->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
// Function to build and display
// the Cantor Set for each level
void buildCantorSet(int A, int B, int L)
{
Cantor* head = NULL;
head = startList(head, A, B);
for (int i = 0; i < L; i++) {
printf("Level_%d : ", i);
print(head);
propagate(head);
}
printf("Level_%d : ", L);
print(head);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int A = 0;
int B = 9;
int L = 2;
buildCantorSet(A, B, L);
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation to find the cantor set
// for n levels and
// for a given start_num and end_num
class GFG
{
// The Linked List Structure for the Cantor Set
static class Cantor
{
double start, end;
Cantor next;
};
static Cantor Cantor;
// Function to initialize the Cantor Set List
static Cantor startList(Cantor head, double start_num,
double end_num)
{
if (head == null)
{
head = new Cantor();
head.start = start_num;
head.end = end_num;
head.next = null;
}
return head;
}
// Function to propogate the list
// by adding new nodes for the next levels
static Cantor propagate(Cantor head)
{
Cantor temp = head;
if (temp != null)
{
Cantor newNode = new Cantor();
double diff = (((temp.end) - (temp.start)) / 3);
// Modifying the start and end values
// for the next level
newNode.end = temp.end;
temp.end = ((temp.start) + diff);
newNode.start = (newNode.end) - diff;
// Changing the pointers
// to the next node
newNode.next = temp.next;
temp.next = newNode;
// Recursively call the function
// to generate the Cantor Set
// for the entire level
propagate(temp.next.next);
}
return head;
}
// Function to print a level of the Set
static void print(Cantor temp)
{
while (temp != null)
{
System.out.printf("[%f] -- [%f]", temp.start, temp.end);
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.printf("\n");
}
// Function to build and display
// the Cantor Set for each level
static void buildCantorSet(int A, int B, int L)
{
Cantor head = null;
head = startList(head, A, B);
for (int i = 0; i < L; i++)
{
System.out.printf("Level_%d : ", i);
print(head);
propagate(head);
}
System.out.printf("Level_%d : ", L);
print(head);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int A = 0;
int B = 9;
int L = 2;
buildCantorSet(A, B, L);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-JiC#
// C# implementation to find the cantor set
// for n levels and
// for a given start_num and end_num
using System;
class GFG
{
// The Linked List Structure for the Cantor Set
class Cantor
{
public double start, end;
public Cantor next;
};
static Cantor cantor;
// Function to initialize the Cantor Set List
static Cantor startList(Cantor head, double start_num,
double end_num)
{
if (head == null)
{
head = new Cantor();
head.start = start_num;
head.end = end_num;
head.next = null;
}
return head;
}
// Function to propogate the list
// by adding new nodes for the next levels
static Cantor propagate(Cantor head)
{
Cantor temp = head;
if (temp != null)
{
Cantor newNode = new Cantor();
double diff = (((temp.end) - (temp.start)) / 3);
// Modifying the start and end values
// for the next level
newNode.end = temp.end;
temp.end = ((temp.start) + diff);
newNode.start = (newNode.end) - diff;
// Changing the pointers
// to the next node
newNode.next = temp.next;
temp.next = newNode;
// Recursively call the function
// to generate the Cantor Set
// for the entire level
propagate(temp.next.next);
}
return head;
}
// Function to print a level of the Set
static void print(Cantor temp)
{
while (temp != null)
{
Console.Write("[{0:F6}] -- [{1:F6}]",
temp.start, temp.end);
temp = temp.next;
}
Console.Write("\n");
}
// Function to build and display
// the Cantor Set for each level
static void buildCantorSet(int A, int B, int L)
{
Cantor head = null;
head = startList(head, A, B);
for (int i = 0; i < L; i++)
{
Console.Write("Level_{0} : ", i);
print(head);
propagate(head);
}
Console.Write("Level_{0} : ", L);
print(head);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int A = 0;
int B = 9;
int L = 2;
buildCantorSet(A, B, L);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-JiLevel_0 : [0.000000] — [9.000000]
Level_1 : [0.000000] — [3.000000] [6.000000] — [9.000000]
Level_2 : [0.000000] — [1.000000] [2.000000] — [3.000000] [6.000000] — [7.000000] [8.000000] — [9.000000]
参考资料:康托集维基百科
相关文章:乔治康托有理数集的第N 项
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live