先决条件 – 聚集和非聚集索引上的 SQL 查询
1. 聚集索引:
仅当以下两个条件都满足时才会创建聚集索引 –
- 您移动到辅助存储器中的数据或文件应该按顺序或排序顺序排列。
- 应该有非键值,这意味着它可以有重复的值。
每当您在表中应用聚集索引时,它只会在该表中执行排序。您可以像主键一样在表中只创建一个聚集索引。聚集索引与字典一样,按字母顺序排列数据。
在聚集索引中,索引包含指向块但不包含直接数据的指针。

聚集索引示例 –
如果您将主键应用于任何列,那么它将自动成为聚集索引。
create table Student
( Roll_No int primary key,
Name varchar(50),
Gender varchar(30),
Mob_No bigint );
insert into Student
values (4, 'ankita', 'female', 9876543210 );
insert into Student
values (3, 'anita', 'female', 9675432890 );
insert into Student
values (5, 'mahima', 'female', 8976453201 ); 在这个例子中,Roll no 是一个主键,它会自动充当一个聚集索引。
此代码的输出将按卷号的递增顺序产生。
| Roll_No | Name | Gender | Mob_No |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | anita | female | 9675432890 |
| 4 | ankita | female | 9876543210 |
| 5 | mahima | female | 8976453201 |
一张表只能有一个聚簇索引,但多列可以有一个聚簇索引,这种类型的索引称为复合索引。
2. 非聚集索引:
非聚集索引类似于一本书的索引。一本书的索引由章节名称和页码组成,如果您想阅读任何主题或章节,则可以使用该书的索引直接转到该页面。无需翻阅一本书的每一页。
数据存放在一处,索引存放在另一处。既然,数据和非聚集索引是分开存储的,那么一个表中可以有多个非聚集索引。
在非聚集索引中,索引包含指向数据的指针。
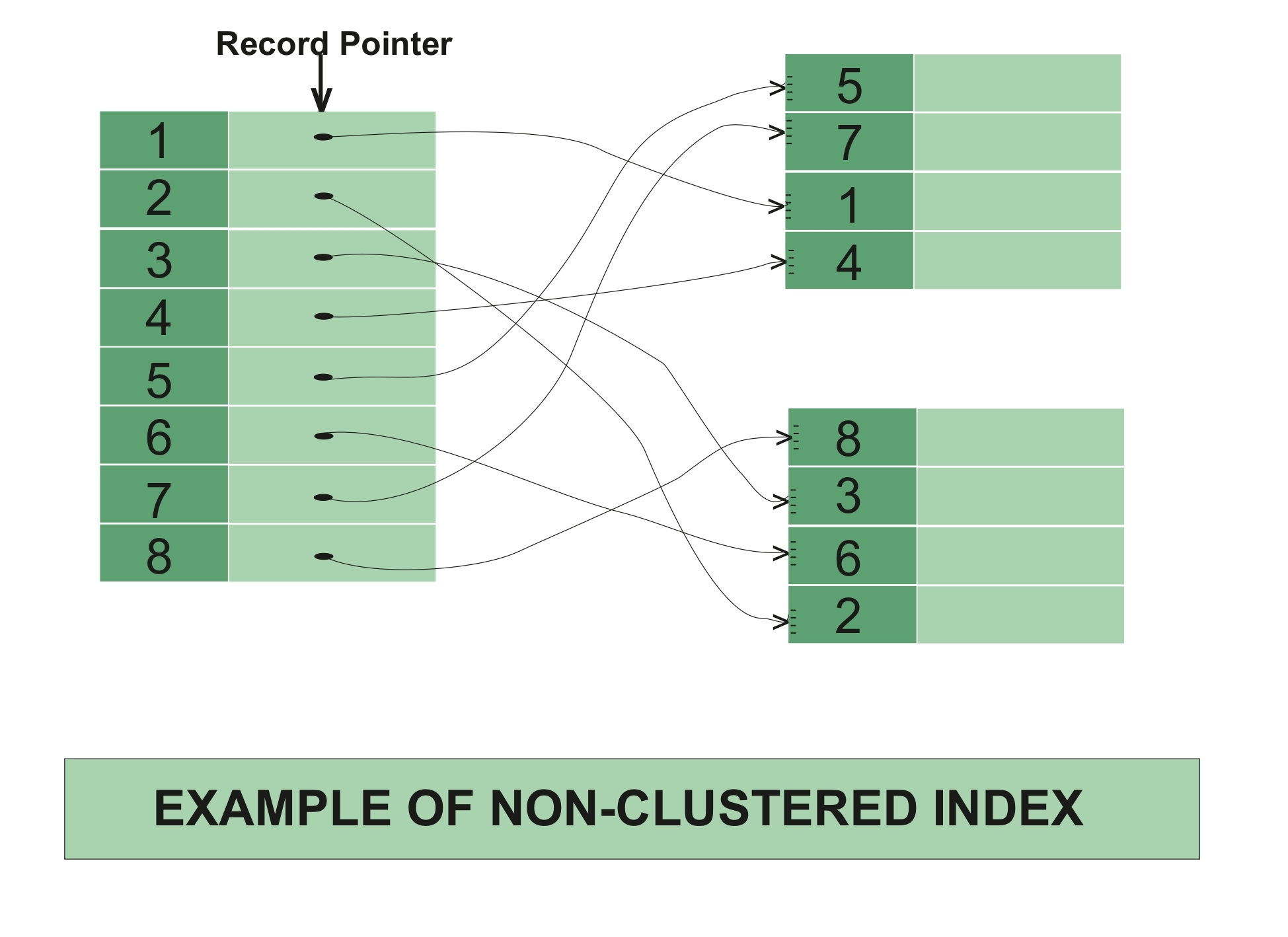
非聚集索引示例 –
create table Student
( Roll_No int primary key,
Name varchar(50),
Gender varchar(30),
Mob_No bigint );
insert into Student
values (4, 'afzal', 'male', 9876543210 );
insert into Student
values (3, 'sudhir', 'male', 9675432890 );
insert into Student
values (5, 'zoya', 'female', 8976453201 );
create nonclustered index NIX_FTE_Name
on Student (Name ASC); 这里,roll no 是主键,因此自动有一个聚集索引。
如果我们想在 NAME 列中应用非聚集索引(按升序),那么将为该列创建新表。
应用非聚集索引前的输出:
| Roll_No | Name | Gender | Mob_No |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | sudhir | male | 9675432890 |
| 4 | afzal | male | 9876543210 |
| 5 | zoya | female | 8976453201 |
应用非聚集索引后的输出:
| Name | Row address |
|---|---|
| Afzal | 3452 |
| Sudhir | 5643 |
| zoya | 9876 |
使用行地址是因为,如果有人要搜索数据中的 sudhir,那么通过使用行地址,他/她将直接转到该行地址并可以直接获取数据。
聚集索引和非聚集索引的区别:
| CLUSTERED INDEX | NON-CLUSTERED INDEX |
|---|---|
| Clustered index is faster. | Non-clustered index is slower. |
| Clustered index requires less memory for operations. | Non-Clustered index requires more memory for operations. |
| In clustered index, index is the main data. | In Non-Clustered index, index is the copy of data. |
| A table can have only one clustered index. | A table can have multiple non-clustered index. |
| Clustered index has inherent ability of storing data on the disk. | Non-Clustered index does not have inherent ability of storing data on the disk. |
| Clustered index store pointers to block not data. | Non-Clustered index store both value and a pointer to actual row that holds data. |
| In Clustered index leaf nodes are actual data itself. | In Non-Clustered index leaf nodes are not the actual data itself rather they only contains included columns. |
| In Clustered index, Clustered key defines order of data within table. | In Non-Clustered index, index key defines order of data within index. |
| A Clustered index is a type of index in which table records are physically reordered to match the index. | A Non-Clustered index is a special type of index in which logical order of index does not match physical stored order of the rows on disk. |