在本文中,我们将讨论 Cassandra 中的轻量级事务(LWT),这也有助于提高性能。
有时插入或更新操作必须是唯一的,这需要先读后写。先读后写对性能有影响——明智地使用! CQL 轻量级事务 (LWT) 通过在插入和更新上使用 IF 子句解决了此类问题。
例如:
创建密钥空间:
CREATE KEYSPACE IF NOT EXIST keyspace1
WITH replication = {'class': 'SimpleStrategy',
'replication_factor' : 2}; 创建表:
CREATE TABLE User (
U_email text,
U_password int,
U_id UUID,
PRIMARY KEY (email)
); 阅读使用以下 CQL 查询。
Select *
from keyspace1.User
where U_email = ‘ashish@gmail.com’; 输出:
| U_email | U_password | U_id |
|---|---|---|
[0 行]
要将数据插入表中,请使用以下 CQL 查询。
Insert into keyspace1.User (U_email, U_password, U_id)
values (‘ashish@gmail.com’, ‘password_A’, uuid())
if not exists; 我们来看一下。

现在,LWT 创建了该行。
Select *
from keyspace1.User
where U_email = ‘ashish@gmail.com’; 输出:
| U_email | U_password | U_id |
|---|---|---|
| ashish@gmail.com | password_A | 1a2b3c4d5e6789 |
[1 行] LWT 创建了该行
现有行上的 LWT:
Insert into keyspace1.User (U_email, U_password, U_id)
values (‘ashish@gmail.com’, ‘password_XYZ’, uuid())
if not exists; 我们来看一下,

这是上述 CQL 查询的输出。
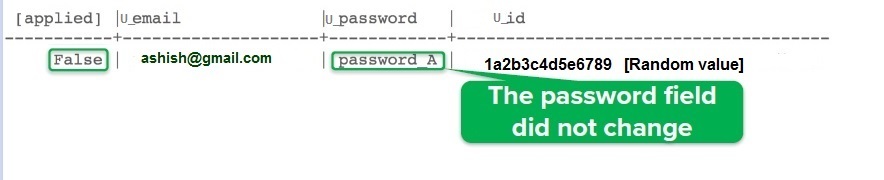
Select *
from keyspace1.User
where U_email = ‘ashish@gmail.com’; 输出:

更新行上的轻量级事务(LWT):
用于更新现有行的 CQL 查询,现在我们正在对此应用 LWT。用于更新现有行的 CQL 查询。
UPDATE keyspace1.User SET U_password = 'password_XYZ'
WHERE U_email = 'ashish@gmail.com'
IF U_password = 'password_A' ; 运算符可用于 UPDATE 命令:
=, <,, >=, != and IN 我们来看一下,
