访问修饰符是代码中确定该变量范围的元素。正如我们所知,共有三种访问修饰符可用,即 public、protected 和 private。让我们看看 Protected 和 Private 访问修饰符之间的区别。
访问修饰符 1:受保护
声明为 protected 的方法或变量可在同一包或不同包中访问。通过使用 protected 关键字,我们可以声明方法/变量受保护。
句法:
protected void method_name(){
......code goes here..........
}例子:
Java
// Java Program to illustrate Protected Access Modifier
// Importing input output classes
import java.io.*;
// Main class
public class Main {
// Input custom string
protected String name = "Geeks for Geeks";
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating an object of Main class
Main obj1 = new Main();
// Displaying the object content as created
// above of Main class itself
System.out.println( obj1.name );
}
}Java
// Java Program to illustrate Private Access Modifier
// Importing input output classes
import java.io.*;
// Main class
public class Main {
// Input custom string
private String name = "Geeks for Geeks";
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an object of Main class
Main obj1 = new Main();
// Displaying the object content as created
// above of Main class itself
System.out.println(obj1.name);
}
}输出
Geeks for Geeks访问修饰符 2:私有
声明为私有的方法或变量只能在声明它们的类中访问。通过使用private关键字,我们可以将方法/变量设置为私有。
句法:
private void method_name(){
......code goes here..........
}例子:
Java
// Java Program to illustrate Private Access Modifier
// Importing input output classes
import java.io.*;
// Main class
public class Main {
// Input custom string
private String name = "Geeks for Geeks";
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an object of Main class
Main obj1 = new Main();
// Displaying the object content as created
// above of Main class itself
System.out.println(obj1.name);
}
}
输出
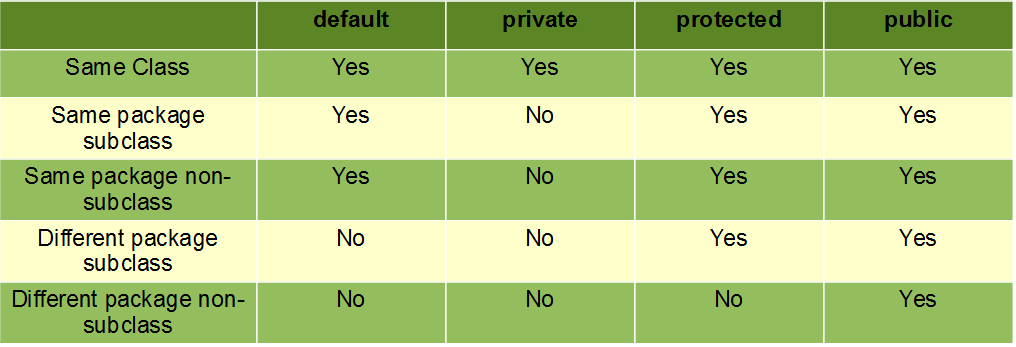
Geeks for Geeks现在在了解了它们的内部工作原理之后,让我们来总结这些访问修饰符之间有针对性的主要区别。
| Protected | Private |
|---|---|
| The keyword used is ‘protected.’ | The keyword used is ‘private.’ |
| Protected can be used within the same class | Private can be used within a same class |
| Protected can be used in the same package subclass | Private can not be used in the same package subclass |
| Protected can be used in different package subclass | Private can not be used in different package subclass |
| Protected can not be used in different package non-subclass | Private can not be used in different package non-subclass |