先决条件 – 数字签名
直接数字签名仅包括两方,一是发送消息,另一方是接收消息。根据直接数字签名,双方相互信任并知道公钥。消息容易被破坏,发件人可以随时拒绝他发送的消息。
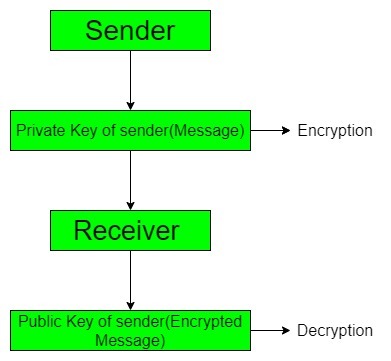
仲裁数字签名包括三方,一是发送方,二是接收方,三是仲裁者,仲裁者将成为他们之间发送和接收消息的媒介。由于默认情况下包含时间戳,因此消息不太容易损坏。

直接和仲裁数字签名的区别:
| S No. | Direct Digital Signature | Arbitrated Digital Signature |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | It only require the communicating parties. | It requires arbiter along with communicating parties to send or receive messages. |
| 2. | In this the digital signature encrypts the whole plain text with the sending party’s private key. | The encrypted message is send by X to arbiter Z with Y’s id, timestamp and some random number PQ. |
| 3. | The message is directly transmitted between both parties without any help of a intermediate. | Arbiter is needed to transmit the message. |
| 4. | Timestamp is not maintained by both side. | Timestamp is maintained by all three members by default. |
| 5. | In case the confidentiality is needed the message will be encrypt with receiver’s public key or a shared key. | The arbiter provides confidentiality of the message. |
| 6. | Vulnerable to any kind of replay attack. | The timestamp is used to protect the message from any kind of replay attack. |
| 7. | It clocks a processing speed of 16 MHz. | While Raspberry Pi clocks a processing speed of 1.4 GHz. |
| 8. | It is implemented using public key. | It is implemented using private key. |