先决条件 – 寻址模式
1. 间接寻址方式:
在间接寻址模式下,指令中的地址字段指向存在操作数有效地址的内存位置或寄存器。
需要两次内存访问。一个用于获取存储在给定地址字段中的值。其次在找到的地址处获取操作数的有效地址。它可以进一步分为寄存器间接寻址和存储器间接寻址。
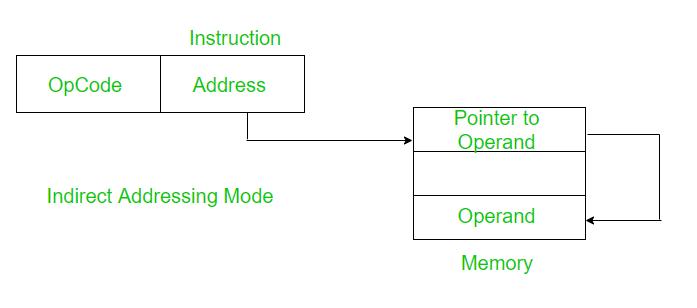
示例:将存储在寄存器 B 中的地址内容相加。
ADD [B] 指令的地址字段,这里寄存器 B 保存操作数的地址。
2. 立即寻址模式:
在立即寻址模式下,操作数是指令的一部分。
Here the Operand = Address Field 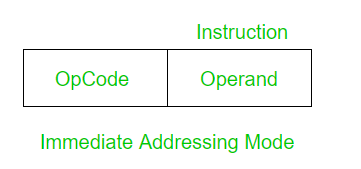
示例:将 8 添加到累加器。
ADD 8 获取数据不需要内存引用。因此不需要额外的计算来计算出有效地址。这是一种快速的方法。但缺点是范围有限
现在让我们比较直接寻址模式和立即寻址模式。
| Indirect Addressing Mode | Immediate Addressing Mode |
|---|---|
| The address field of the instruction holds the address of the operand. | There is no address field as the operand is a part of the instruction. |
| It requires two reference to memory. | It does not require any reference to memory. |
| It is slower compared to immediate mode. | It is a faster process. |
| It has more range than in immediate mode. | It has a limited range. |
| It is further classified into two categories. | No further classification. |
| Example: ADD [B] | Example: ADD 5 |