就像任何其他编程语言一样, Java有一组保留的关键字并具有特殊含义。在本文中,我们将看到关键字 volatile 和瞬态之间的区别。
在讨论差异之前,让我们首先了解它们各自的实际含义。
易挥发的:
Volatile 关键字用于标记 JVM 和线程以从主内存读取其值,而不使用线程堆栈中存在的缓存值。它用于Java中的并发编程。
Java
class GFG extends Thread {
// using volatile
volatile boolean working = true;
// if non-volatile it will
// sleep in main and
// runtime error will coocur
public void run()
{
long count = 0;
while (working) {
count++;
}
System.out.println("Thread terminated."
+ count);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
throws InterruptedException
{
GFG test = new GFG();
test.start();
Thread.sleep(100);
System.out.println("After Sleeping in Main");
test.working = false;
test.join();
System.out.println("Working set to "
+ test.working);
}
}Java
import java.io.*;
class Test implements Serializable {
// Making Accesskey transient for security
transient String accessKey;
// Making age transient as age can be
// calculated from Date of Birth
// and current date.
transient int age;
// serialize other fields
String name, address;
public Test(String accessKey, int age,
String name, String address)
{
this.accessKey = accessKey;
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
this.address = address;
}
}
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
throws Exception
{
ObjectInputStream in
= new ObjectInputStream(
(new FileInputStream(
"login_details.txt")));
Test obj = (Test)in.readObject();
/* Transient variable will be shown
null due to security reasons.*/
System.out.println("Accesskey: "
+ obj.accessKey);
System.out.println("Age: "
+ obj.age);
System.out.println("Name: "
+ obj.name);
System.out.println("Address: "
+ obj.address);
}
}输出:
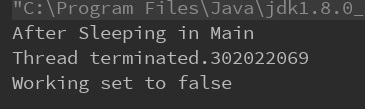
易失性代码输出
短暂的:
Transient 关键字与实例变量一起使用以将其从序列化过程中消除。在序列化过程中,不保存瞬态字段或变量的值。
Java
import java.io.*;
class Test implements Serializable {
// Making Accesskey transient for security
transient String accessKey;
// Making age transient as age can be
// calculated from Date of Birth
// and current date.
transient int age;
// serialize other fields
String name, address;
public Test(String accessKey, int age,
String name, String address)
{
this.accessKey = accessKey;
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
this.address = address;
}
}
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
throws Exception
{
ObjectInputStream in
= new ObjectInputStream(
(new FileInputStream(
"login_details.txt")));
Test obj = (Test)in.readObject();
/* Transient variable will be shown
null due to security reasons.*/
System.out.println("Accesskey: "
+ obj.accessKey);
System.out.println("Age: "
+ obj.age);
System.out.println("Name: "
+ obj.name);
System.out.println("Address: "
+ obj.address);
}
}
输出:
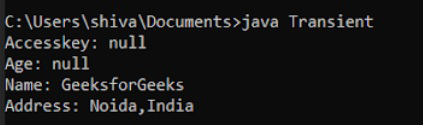
瞬态代码输出
下表描述了差异:
| Transient | Volatile |
|---|---|
| The Transient marked variable prevents it from being serialized. | The Volatile marked variable follows happen-before relationship on visibility in multithreaded java program which reduces the risk of memory consistency errors. |
| It gives control and flexibility over to exclude some object methods from serialization process. | It prevents JVM from doing re-ordering which could compromise synchronization. |
| During deserialization they are initialized with a default value. | They are not initialized with a default value. |
| It cannot be used with the static keyword as static variable do not belong to individual instance. During serialization, only object’s current state is concerned. | It can be used with the static keyword. |
| It cannot be used with the final keyword. Although JVM doesn’t complain about it but during deserialization one will face problem of reinitializing a variable. | It can be used with the final keyword. |