先决条件: Android 上的 Kotlin 协程
Kotlin 团队将协程定义为“轻量级线程”。它们是实际线程可以执行的任务。协程在 1.3 版中添加到 Kotlin 中,并且基于其他语言的既定概念。 Kotlin 协程引入了一种新的并发风格,可用于 Android 以简化异步代码。
The official documentation says that coroutines are lightweight threads. By lightweight, it means that creating coroutines doesn’t allocate new threads. Instead, they use predefined thread pools and smart scheduling for the purpose of which task to execute next and which tasks later.
Kotlin 中主要有两个函数来启动协程。
- 发射{ }
- 异步{}
启动函数
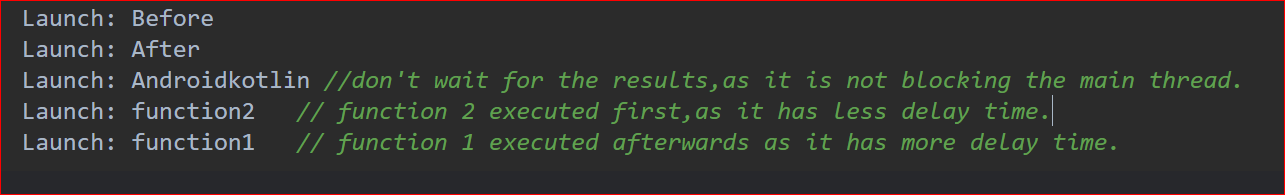
启动不会阻塞主线程,但另一方面,由于启动不是挂起调用,因此其余代码的执行不会等待启动结果。以下是使用 Launch 的 Kotlin 程序:
Kotlin
// Kotlin Program For better understanding of launch
fun GFG()
{
var resultOne = "Android"
var resultTwo = "Kotlin"
Log.i("Launch", "Before")
launch(Dispatchers.IO) { resultOne = function1() }
launch(Dispatchers.IO) { resultTwo = function2() }
Log.i("Launch", "After")
val resultText = resultOne + resultTwo
Log.i("Launch", resultText)
}
suspend fun function1(): String
{
delay(1000L)
val message = "function1"
Log.i("Launch", message)
return message
}
suspend fun function2(): String
{
delay(100L)
val message = "function2"
Log.i("Launch", message)
return message
}Kotlin
// pseudo kotlin code for demonstration of launch
GlobalScope.launch(Dispatchers.Main)
{
// do on IO thread
fetchUserAndSaveInDatabase()
}
suspend fun fetchUserAndSaveInDatabase()
{
// fetch user from network
// save user in database
// and do not return anything
}Kotlin
// kotlin program for demonstration of async
fun GFG
{
Log.i("Async", "Before")
val resultOne = Async(Dispatchers.IO) { function1() }
val resultTwo = Async(Dispatchers.IO) { function2() }
Log.i("Async", "After")
val resultText = resultOne.await() + resultTwo.await()
Log.i("Async", resultText)
}
suspend fun function1(): String
{
delay(1000L)
val message = "function1"
Log.i("Async", message)
return message
}
suspend fun function2(): String
{
delay(100L)
val message = "function2"
Log.i("Async", message)
return message
}当您在 Android IDE 中运行代码时,日志结果将是:
科特林
// pseudo kotlin code for demonstration of launch
GlobalScope.launch(Dispatchers.Main)
{
// do on IO thread
fetchUserAndSaveInDatabase()
}
suspend fun fetchUserAndSaveInDatabase()
{
// fetch user from network
// save user in database
// and do not return anything
}
由于fetchUserAndSaveInDatabase()不返回任何内容,我们可以使用启动来完成该任务,然后在主线程上执行某些操作。
何时使用启动?
Launch 可以用在用户不想使用返回结果的地方,稍后用于执行其他一些工作。例如,它可以用于涉及更新或更改颜色等任务的地方,因为在这种情况下返回的信息将毫无用处。
异步函数
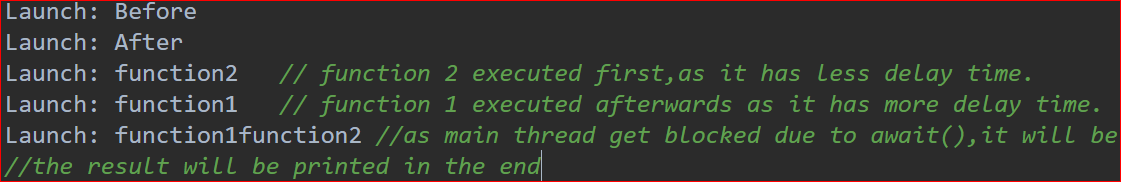
Async 也用于启动协程,但它会在程序中的await()函数的入口点阻塞主线程。以下是使用 Async 的 Kotlin 程序:
科特林
// kotlin program for demonstration of async
fun GFG
{
Log.i("Async", "Before")
val resultOne = Async(Dispatchers.IO) { function1() }
val resultTwo = Async(Dispatchers.IO) { function2() }
Log.i("Async", "After")
val resultText = resultOne.await() + resultTwo.await()
Log.i("Async", resultText)
}
suspend fun function1(): String
{
delay(1000L)
val message = "function1"
Log.i("Async", message)
return message
}
suspend fun function2(): String
{
delay(100L)
val message = "function2"
Log.i("Async", message)
return message
}
需要注意的一个重点是 Async 使两个网络并行调用 result1 和 result2,而在启动时不会进行并行函数调用。当您在 Android IDE 中运行代码时,日志结果将是:
什么时候使用异步?
当并行进行两个或多个网络调用时,但您需要在计算输出之前等待答案,即对并行运行的多个任务的结果使用异步。如果您使用 async 并且不等待结果,它将与启动完全相同。
差异表
下面是 Launch 和 Async 之间的差异表:
|
Launch |
Async |
|---|---|
| The launch is basically fire and forget. | Async is basically performing a task and return a result. |
| launch{} does not return anything. | async{ }, which has an await() function returns the result of the coroutine. |
| launch{} cannot be used when you need the parallel execution of network calls. | Use async only when you need the parallel execution network calls. |
| launch{} will not block your main thread. | Async will block the main thread at the entry point of the await() function. |
| Execution of other parts of the code will not wait for the launch result since launch is not a suspend call | Execution of the other parts of the code will have to wait for the result of the await() function. |
| It is not possible for the launch to work like async in any case or condition. | If you use async and do not wait for the result, it will work exactly the same as launch. |
| Launch can be used at places if you don’t need the result from the method called. | Use async when you need the results from the multiple tasks that run in parallel. |
| Example: It can be used at places involving tasks like update or changing color like fetch User And Save In Database. | Example: Imagine the condition, when we have to fetch two users’ data from the database by using two parallel network calls and then use them for computing some results based on their data. |