逻辑地址是在程序运行时由 CPU 生成的。逻辑地址是虚拟地址,因为它在物理上并不存在,因此也称为虚拟地址。该地址用作 CPU 访问物理内存位置的参考。术语“逻辑地址空间”用于表示程序视角生成的所有逻辑地址的集合。
称为内存管理单元的硬件设备用于将逻辑地址映射到其对应的物理地址。
物理地址标识所需数据在存储器中的物理位置。用户从不直接处理物理地址,而是可以通过其对应的逻辑地址进行访问。用户程序生成逻辑地址,认为程序运行在这个逻辑地址,但程序需要物理内存才能执行,因此,逻辑地址必须通过MMU映射到物理地址才能使用。术语物理地址空间用于与逻辑地址空间中的逻辑地址相对应的所有物理地址。
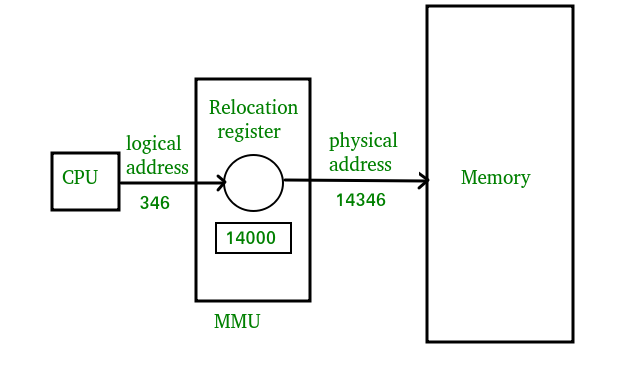
将虚拟地址映射到物理地址
操作系统中逻辑地址和物理地址的区别
- 逻辑地址和物理地址之间的基本区别在于,逻辑地址是从程序的角度由 CPU 生成的,而物理地址是存在于内存单元中的位置。
- 逻辑地址空间是 CPU 为程序生成的所有逻辑地址的集合,而映射到相应逻辑地址的所有物理地址的集合称为物理地址空间。
- 逻辑地址在物理上并不存在于内存中,而物理地址是内存中可以物理访问的位置。
- 相同的逻辑地址由编译时和加载时地址绑定方法生成,而它们在运行时地址绑定方法中彼此不同。详情请参考这里。
- 逻辑地址在程序运行时由 CPU 生成,而物理地址由内存管理单元 (MMU) 计算。
对比图:
| Parameter | LOGICAL ADDRESS | PHYSICAL ADDRESS |
|---|---|---|
| Basic | generated by CPU | location in a memory unit |
| Address Space | Logical Address Space is set of all logical addresses generated by CPU in reference to a program. | Physical Address is set of all physical addresses mapped to the corresponding logical addresses. |
| Visibility | User can view the logical address of a program. | User can never view physical address of program. |
| Generation | generated by the CPU | Computed by MMU |
| Access | The user can use the logical address to access the physical address. | The user can indirectly access physical address but not directly. |