Linux 中任何命令前的空格
默认情况下,history 命令不显示您在开头插入空格的命令。因此,要克服这个问题,您需要对.bashrc文件进行更改。
例如,假设您运行rm -rf /test*命令,并且在命令的开头插入了一个空格。如果您随后运行历史命令,您将得到除最后一次运行的命令(您在开始时使用空格运行)之外的命令列表。
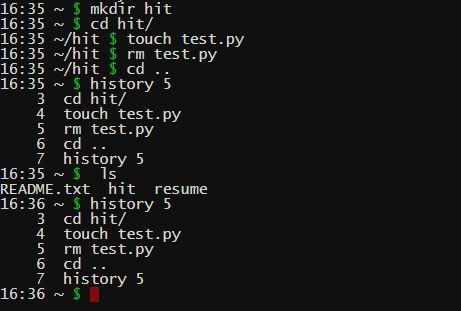
- Run “history 5” and see the 5 latest commands that you ran.
- Run ” ls” Add a white space at the beginning of the command
- Run “history 5″ again and you will see that ” ls” is missing.
请看下面的截图:
您可以使用 HISTCONTROL(在.bashrc中定义)来控制需要存储在历史文件中的内容。可能的选项是:
- HISTCONTROL=ignorespace (Commands starting with white spaces will not be stored).
- HISTCONTROL=ignoredups (Duplicate Commands will not be stored).
- HISTCONTROL=ignoreboth (It will ignore both of the above cases).
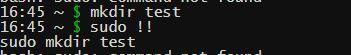
有趣的事实:如果你运行像"sudo !!"这样的命令,它会将 sudo 添加到您运行的上一个命令中。例如,尝试在终端中运行以下命令并查看。
- 运行“mkdir ~/Desktop/Test”
- 运行“须藤!!”
执行的第二个命令将是“ sudo mkdir ~/Desktop/Test ”。当您尝试在项目/系统中安装一些依赖项时,它很有用。如果您需要超级用户权限,这非常有用。