Java do-while 循环与示例
当我们需要重复执行一个语句块时, Java中的循环就派上用场了。 Java do-while 循环是一个退出控制循环。因此,与 for 或 while 循环不同,do-while 在执行循环体的语句后检查条件。
句法:
do
{
// Loop Body
Update_expression
}
// Condition check
while (test_expression);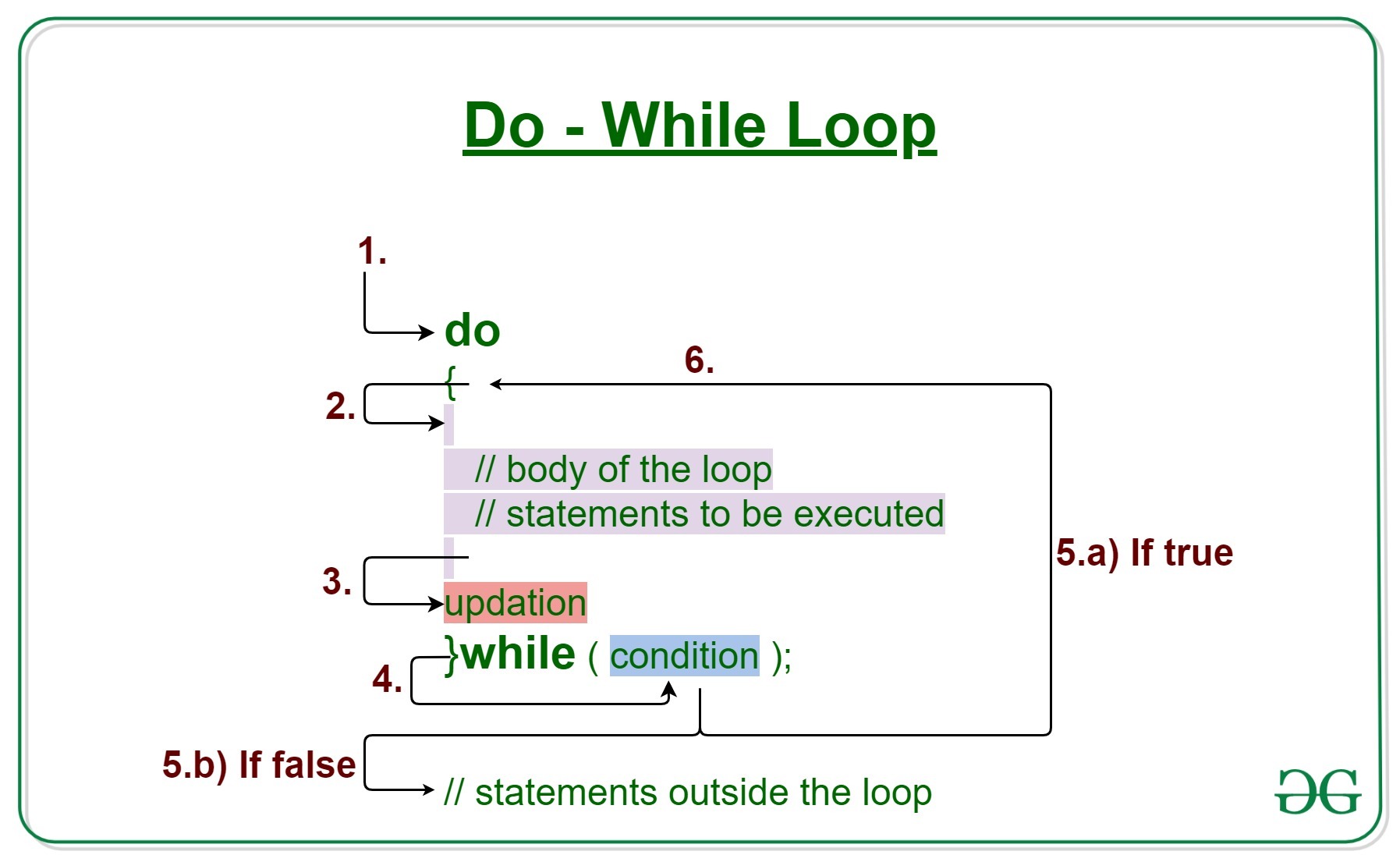
插图:
Java
// Java Program to Illusterate One Time Iteration
// Inside do-while Loop
// When Condition IS Not Satisfied
// Class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// initial counter variable
int i = 0;
do {
// Body of loop that will execute minimum
// 1 time for sure no matter what
System.out.println("Print statement");
i++;
}
// Checking condition
// Note: It is being checked after
// minimum 1 iteration
while (i < 0);
}
}Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Do-while Loop
// Class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Declaring and initialization expression
int i = 1;
// Do-while loop
do {
// Body od do-while loop
// Print statement
System.out.println("Hello World");
// Update expression
i++;
}
// Test expression
while (i < 6);
}
}Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Do-while Loop
// Class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Declaring and initializing integer values
int x = 21, sum = 0;
// Do-while loop
do {
// Execution statements(Body of loop)
// Here, the line will be printed even
// if the condition is false
sum += x;
x--;
}
// Now checking condition
while (x > 10);
// Summing up
System.out.println("Summation: " + sum);
}
}输出
Print statement输出说明:
在上面的代码中,我们发现条件是稍后检查的,因为 do 内部的主体将被执行一次而不会失败,因为条件是稍后检查的。因此,每当我们想在终端上显示菜单以及稍后的继续命令时,我们总是使用 do-while 循环。
do-while 循环的组成部分
A. 测试表达式:在这个表达式中,我们要测试条件。如果条件评估为真,那么我们将执行循环体并转到更新表达式。否则,我们将退出 while 循环。例如:
i <= 10B. 更新表达式:执行循环体后,该表达式将循环变量增加/减少某个值。例如:
i++;do-While循环的执行
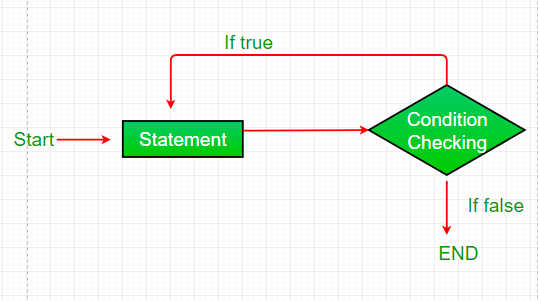
- 控制落入do-while循环。
- 循环体内的语句被执行。
- 更新发生。
- 流程跳转到 Condition
- 条件经过测试。
- 如果 Condition 为真,请转到步骤 6。
- 如果 Condition 产生 false,则流程将超出循环
- 流程返回到第 2 步。
流程图 do-while 循环:
执行:
示例 1:该程序将尝试打印 5 次“Hello World”。
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Do-while Loop
// Class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Declaring and initialization expression
int i = 1;
// Do-while loop
do {
// Body od do-while loop
// Print statement
System.out.println("Hello World");
// Update expression
i++;
}
// Test expression
while (i < 6);
}
}
输出:
Hello World
Hello World
Hello World
Hello World
Hello WorldAuxiliary Space: O(1)
输出说明:
该程序将按如下方式执行:
- 程序开始。
- i 用值 1 初始化。
- 执行进入循环
- “Hello World”第一次打印。
- 更新完成。现在 i = 2。
- 检查条件。 2 < 6 为真。
- 执行进入循环。
- “Hello World”第二次被打印出来。
- 更新完成。现在 i = 3。
- 检查条件。 3 < 6 为真。
- 执行进入循环
- “Hello World”第三次打印
- 更新完成。现在 i = 4。
- 检查条件。 4 < 6 为真。
- 执行进入循环
- “Hello World”第四次打印
- 更新完成。现在 i = 5。
- 检查条件。 5 < 6 为真。
- 执行进入循环
- “Hello World”第五次打印
- 更新完成。现在 i = 6。
- 检查条件。 6 < 6 产生错误。
- 流程在循环之外。
示例 2
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Do-while Loop
// Class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Declaring and initializing integer values
int x = 21, sum = 0;
// Do-while loop
do {
// Execution statements(Body of loop)
// Here, the line will be printed even
// if the condition is false
sum += x;
x--;
}
// Now checking condition
while (x > 10);
// Summing up
System.out.println("Summation: " + sum);
}
}
输出:
Summation: 176相关文章:
- Java中的循环
- 带有示例的Java For 循环
- Java while 循环与示例
- C、C++、 Java中while和do-while循环的区别
- C、C++、 Java中for和do-while循环的区别