大批:
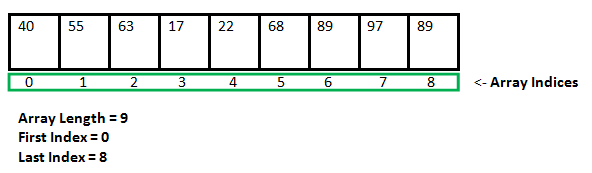
数组是存储在连续内存位置的项目的集合。这个想法是将多个相同类型的项目存储在一起。这使得通过简单地将偏移量添加到基值,即数组的第一个元素的内存位置(通常由数组的名称表示)来更容易地计算每个元素的位置。
阵列的图示如下:
队列:
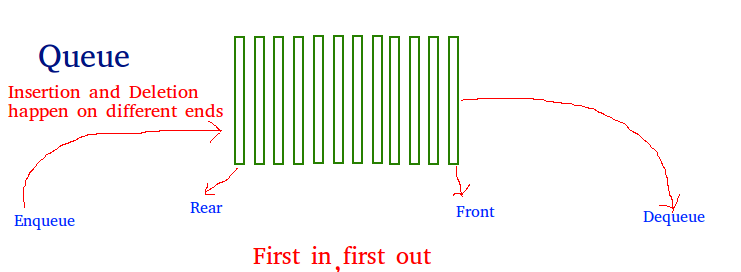
队列是一种线性结构,遵循执行操作的特定顺序。顺序是先进先出 (FIFO) 。队列的一个很好的例子是资源的任何消费者队列,其中先来的消费者首先得到服务。堆栈和队列之间的区别在于删除。在堆栈中,我们删除最近添加的项目;在队列中,我们删除最近最少添加的项目。
队列的图示如下:
堆:
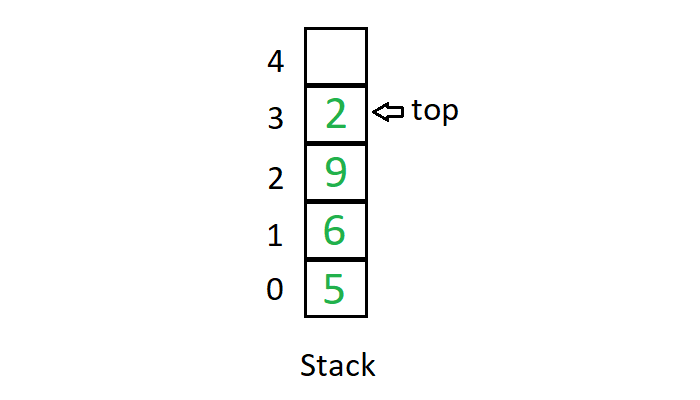
Stack 是一种线性数据结构,其中元素只能从列表的一侧插入和删除,称为top 。堆栈遵循LIFO (后进先出)原则,即最后插入的元素是第一个出来的元素。将元素插入堆栈称为推入操作,从堆栈中删除元素称为弹出操作。在堆栈中,我们始终使用名为 top的指针跟踪列表中的最后一个元素。
堆栈的图解表示如下:
下面是数组、堆栈和队列之间差异的表格表示:
| Queues | Array | Stack |
|---|---|---|
| Queues are based on the FIFO principle, i.e., the element inserted at the first, is the first element to come out of the list. | In the array the elements belong to indexes, i.e., if you want to get into the fourth element you have to write the variable name with its index or location within the square bracket eg arr[4] | Stacks are based on the LIFO principle, i.e., the element inserted at the last, is the first element to come out of the list. |
| Insertion and deletion in Queues takes place only from rear and front respectively. | Insertion and deletion in array can be done at any index in the array. | Insertion and deletion in stacks take place only from one end of the list called the top. |
| Queue has a dynamic and fixed size. | Array has a fixed size. | Stack has a dynamic and fixed size. |
| Queue can contain elements of different data type. | Array contains elements of same data type. | The stack can contain elements of the different data types. |
| Different types of Queues are circular queue, priority queue, doubly ended queue | Different types of Arrays are 1D, 2D, etc | Stack has only one type. |
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。