整数序列![]() 被称为 UpDown,如果不等式
被称为 UpDown,如果不等式![]() 成立。
成立。
给你一个序列![]() .您最多可以在序列中插入一个整数。它可以是任何整数。添加一个整数(或选择不添加)后,找到新序列的最长子段的长度,即 UpDown。
.您最多可以在序列中插入一个整数。它可以是任何整数。添加一个整数(或选择不添加)后,找到新序列的最长子段的长度,即 UpDown。
子段是序列的连续部分。也就是说,一个子段![]() 将是形式
将是形式![]() 对于一些
对于一些![]() 和
和![]() .
.
在 2019 年区域计算奥林匹克竞赛中提出了这个问题。
例子:
Input: arr[] = {1, 10, 3, 20, 25, 24}
Output: 7
Suppose we insert 5 between 20 and 25, the whole sequence (1, 10, 3, 20, 5, 25, 24)
becomes an UpDown Sequence and hence the answer is 7.
Input: arr[] = {100, 1, 10, 3, 4, 6, 11}
Output: 6
Suppose we insert 4 between 4 and 6, the sequence (1, 10, 3, 4, 4, 6) becomes an UpDown
Sequence and hence the answer is 6. We can verify that this is the best possible
solution.
方法:让我们首先定义两种类型的序列:-
- UpDown Sequence (UD) :形式的序列
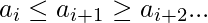 也就是说,序列首先从增加开始。
也就是说,序列首先从增加开始。 - DownUp Sequence (DU) :形式的序列
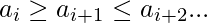 也就是说,序列从先递减开始。
也就是说,序列从先递减开始。
让我们先找出UD和DU序列的长度,而不考虑问题的其他部分。为此,让我们定义![]() 是最长的 UpDown 序列开始于
是最长的 UpDown 序列开始于![]() 和
和是最长的 DownUp 序列开始于
![]() .
.
循环关系为![]() 是 :-
是 :-
(1) 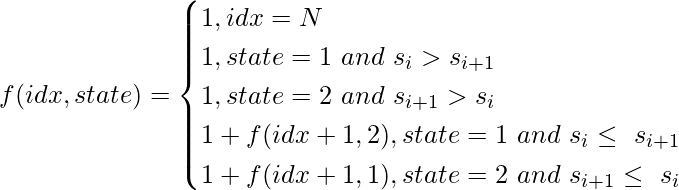
这里,N 是序列的长度,状态是 1 或 2,分别代表 UD 和 DU 序列。在形成递推关系时,我们使用了一个事实,即在一个 UD 序列中
*** QuickLaTeX cannot compile formula:
*** Error message:
Error: Nothing to show, formula is empty
, 那个部分
*** QuickLaTeX cannot compile formula:
*** Error message:
Error: Nothing to show, formula is empty
是 DU 序列,反之亦然。我们可以使用动态规划来计算![]() 然后将我们的结果存储在数组dp[N][2] 中。
然后将我们的结果存储在数组dp[N][2] 中。
现在,请注意,始终可以在 UpDown 序列的末尾插入一个整数,以将序列的长度增加 1,同时保留 UpDown 不等式。为什么 ?假设一个 UD 序列在![]() 因为
因为![]() 当我们期望它是
当我们期望它是![]() .我们可以插入一个整数
.我们可以插入一个整数![]() 之间
之间![]() 和
和![]() .现在,
.现在, ![]() 很满意。
很满意。
对于 UD 序列在![]() 因为
因为![]() 当我们期望它是
当我们期望它是![]() .但是我们实际上不必插入任何东西。我们只需要找到可能的最长 UD 序列的长度。
.但是我们实际上不必插入任何东西。我们只需要找到可能的最长 UD 序列的长度。
观察到 UD 序列是以下各项的组合:-
- UD 序列 I + x + UD 序列 II如果 UD 序列 I 的长度是奇数
- UD 序列 I + x + DU 序列 I如果 UD 序列 I 的长度为偶数
其中,x 是插入的元素。
所以对于每个 i,我们计算从 i 开始的最长 UD 序列的长度。将该长度设为 y。
如果 y 是奇数,我们在那里插入一个元素(理论上)并计算从 i+y 开始的最长 UD 序列的长度。因此,插入元素后从 i 开始的最长 UD 序列是dp[i][1] + 1 + dp[i+y][1] 。
如果 y 是偶数,我们在那里插入一个元素(理论上)并计算从 i+y 开始的最长 DU 序列的长度。因此,插入元素后从 i 开始的最长 UD 序列是dp[i][1] + 1 + dp[i+y][2] 。
最终答案是所有 i 中的最大值。
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to recursively fill the dp array
int f(int i, int state, int A[], int dp[][3], int N)
{
if (i >= N)
return 0;
// If f(i, state) is already calculated
// then return the value
else if (dp[i][state] != -1) {
return dp[i][state];
}
// Calculate f(i, state) according to the
// recurrence relation and store in dp[][]
else {
if (i == N - 1)
dp[i][state] = 1;
else if (state == 1 && A[i] > A[i + 1])
dp[i][state] = 1;
else if (state == 2 && A[i] < A[i + 1])
dp[i][state] = 1;
else if (state == 1 && A[i] <= A[i + 1])
dp[i][state] = 1 + f(i + 1, 2, A, dp, N);
else if (state == 2 && A[i] >= A[i + 1])
dp[i][state] = 1 + f(i + 1, 1, A, dp, N);
return dp[i][state];
}
}
// Function that calls the resucrsive function to
// fill the dp array and then returns the result
int maxLenSeq(int A[], int N)
{
int i, tmp, y, ans;
// dp[][] array for storing result
// of f(i, 1) and f(1, 2)
int dp[1000][3];
// Populating the array dp[] with -1
memset(dp, -1, sizeof dp);
// Make sure that longest UD and DU
// sequence starting at each
// index is calculated
for (i = 0; i < N; i++) {
tmp = f(i, 1, A, dp, N);
tmp = f(i, 2, A, dp, N);
}
// Assume the answer to be -1
// This value will only increase
ans = -1;
for (i = 0; i < N; i++) {
// y is the length of the longest
// UD sequence starting at i
y = dp[i][1];
if (i + y >= N)
ans = max(ans, dp[i][1] + 1);
// If length is even then add an integer
// and then a DU sequence starting at i + y
else if (y % 2 == 0) {
ans = max(ans, dp[i][1] + 1 + dp[i + y][2]);
}
// If length is odd then add an integer
// and then a UD sequence starting at i + y
else if (y % 2 == 1) {
ans = max(ans, dp[i][1] + 1 + dp[i + y][1]);
}
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int A[] = { 1, 10, 3, 20, 25, 24 };
int n = sizeof(A) / sizeof(int);
cout << maxLenSeq(A, n);
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of the approach
class GFG
{
// Function to recursively fill the dp array
static int f(int i, int state, int A[],
int dp[][], int N)
{
if (i >= N)
return 0;
// If f(i, state) is already calculated
// then return the value
else if (dp[i][state] != -1)
{
return dp[i][state];
}
// Calculate f(i, state) according to the
// recurrence relation and store in dp[][]
else
{
if (i == N - 1)
dp[i][state] = 1;
else if (state == 1 && A[i] > A[i + 1])
dp[i][state] = 1;
else if (state == 2 && A[i] < A[i + 1])
dp[i][state] = 1;
else if (state == 1 && A[i] <= A[i + 1])
dp[i][state] = 1 + f(i + 1, 2, A, dp, N);
else if (state == 2 && A[i] >= A[i + 1])
dp[i][state] = 1 + f(i + 1, 1, A, dp, N);
return dp[i][state];
}
}
// Function that calls the resucrsive function to
// fill the dp array and then returns the result
static int maxLenSeq(int A[], int N)
{
int i,j, tmp, y, ans;
// dp[][] array for storing result
// of f(i, 1) and f(1, 2)
int dp[][] = new int[1000][3];
// Populating the array dp[] with -1
for(i= 0; i < 1000; i++)
for(j = 0; j < 3; j++)
dp[i][j] = -1;
// Make sure that longest UD and DU
// sequence starting at each
// index is calculated
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
tmp = f(i, 1, A, dp, N);
tmp = f(i, 2, A, dp, N);
}
// Assume the answer to be -1
// This value will only increase
ans = -1;
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
// y is the length of the longest
// UD sequence starting at i
y = dp[i][1];
if (i + y >= N)
ans = Math.max(ans, dp[i][1] + 1);
// If length is even then add an integer
// and then a DU sequence starting at i + y
else if (y % 2 == 0)
{
ans = Math.max(ans, dp[i][1] + 1 + dp[i + y][2]);
}
// If length is odd then add an integer
// and then a UD sequence starting at i + y
else if (y % 2 == 1)
{
ans = Math.max(ans, dp[i][1] + 1 + dp[i + y][1]);
}
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int A[] = { 1, 10, 3, 20, 25, 24 };
int n = A.length;
System.out.println(maxLenSeq(A, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by AnkitRai01Python3
# Python3 implementation of the approach
# Function to recursively fill the dp array
def f(i, state, A, dp, N):
if i >= N:
return 0
# If f(i, state) is already calculated
# then return the value
elif dp[i][state] != -1:
return dp[i][state]
# Calculate f(i, state) according to the
# recurrence relation and store in dp[][]
else:
if i == N - 1:
dp[i][state] = 1
elif state == 1 and A[i] > A[i + 1]:
dp[i][state] = 1
elif state == 2 and A[i] < A[i + 1]:
dp[i][state] = 1
elif state == 1 and A[i] <= A[i + 1]:
dp[i][state] = 1 + f(i + 1, 2, A, dp, N)
elif state == 2 and A[i] >= A[i + 1]:
dp[i][state] = 1 + f(i + 1, 1, A, dp, N)
return dp[i][state]
# Function that calls the resucrsive function to
# fill the dp array and then returns the result
def maxLenSeq(A, N):
# dp[][] array for storing result
# of f(i, 1) and f(1, 2)
# Populating the array dp[] with -1
dp = [[-1, -1, -1] for i in range(1000)]
# Make sure that longest UD and DU
# sequence starting at each
# index is calculated
for i in range(N):
tmp = f(i, 1, A, dp, N)
tmp = f(i, 2, A, dp, N)
# Assume the answer to be -1
# This value will only increase
ans = -1
for i in range(N):
# y is the length of the longest
# UD sequence starting at i
y = dp[i][1]
if (i + y) >= N:
ans = max(ans, dp[i][1] + 1)
# If length is even then add an integer
# and then a DU sequence starting at i + y
elif y % 2 == 0:
ans = max(ans, dp[i][1] + 1 + dp[i + y][2])
# If length is odd then add an integer
# and then a UD sequence starting at i + y
elif y % 2 == 1:
ans = max(ans, dp[i][1] + 1 + dp[i + y][1])
return ans
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
A = [1, 10, 3, 20, 25, 24]
n = len(A)
print(maxLenSeq(A, n))
# This code is contributed by
# sanjeev2552C#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
class GFG
{
// Function to recursively fill the dp array
static int f(int i, int state, int []A,
int [,]dp, int N)
{
if (i >= N)
return 0;
// If f(i, state) is already calculated
// then return the value
else if (dp[i, state] != -1)
{
return dp[i, state];
}
// Calculate f(i, state) according to the
// recurrence relation and store in dp[,]
else
{
if (i == N - 1)
dp[i, state] = 1;
else if (state == 1 && A[i] > A[i + 1])
dp[i, state] = 1;
else if (state == 2 && A[i] < A[i + 1])
dp[i, state] = 1;
else if (state == 1 && A[i] <= A[i + 1])
dp[i, state] = 1 + f(i + 1, 2, A, dp, N);
else if (state == 2 && A[i] >= A[i + 1])
dp[i, state] = 1 + f(i + 1, 1, A, dp, N);
return dp[i, state];
}
}
// Function that calls the resucrsive function to
// fill the dp array and then returns the result
static int maxLenSeq(int []A, int N)
{
int i, j, tmp, y, ans;
// dp[,] array for storing result
// of f(i, 1) and f(1, 2)
int [,]dp = new int[1000, 3];
// Populating the array dp[] with -1
for(i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
for(j = 0; j < 3; j++)
dp[i, j] = -1;
// Make sure that longest UD and DU
// sequence starting at each
// index is calculated
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
tmp = f(i, 1, A, dp, N);
tmp = f(i, 2, A, dp, N);
}
// Assume the answer to be -1
// This value will only increase
ans = -1;
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
// y is the length of the longest
// UD sequence starting at i
y = dp[i, 1];
if (i + y >= N)
ans = Math.Max(ans, dp[i, 1] + 1);
// If length is even then add an integer
// and then a DU sequence starting at i + y
else if (y % 2 == 0)
{
ans = Math.Max(ans, dp[i, 1] + 1 +
dp[i + y, 2]);
}
// If length is odd then add an integer
// and then a UD sequence starting at i + y
else if (y % 2 == 1)
{
ans = Math.Max(ans, dp[i, 1] + 1 +
dp[i + y, 1]);
}
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main (String[] args)
{
int []A = { 1, 10, 3, 20, 25, 24 };
int n = A.Length;
Console.WriteLine(maxLenSeq(A, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumarJavascript
7时间复杂度: O(n)
空间复杂度: O(n)