给定一个数 n,打印所有小于或等于 n 的素数。还假定 n 是一个小数。
例子:
Input : n =10
Output : 2 3 5 7
Input : n = 20
Output: 2 3 5 7 11 13 17 19
当 n 小于 1000 万左右时,Eratosthenes 筛法是找到所有小于 n 的素数的最有效方法之一(参考 Wiki)。
以下是通过 Eratosthene 方法找到小于或等于给定整数n的所有素数的算法:
当算法终止时,列表中所有未标记的数字都是质数。
当算法终止时,列表中所有未标记的数字都是质数。
举例说明:
以n=50为例,所以我们需要打印所有小于或等于50的素数。
我们创建了一个从 2 到 50 的所有数字的列表。
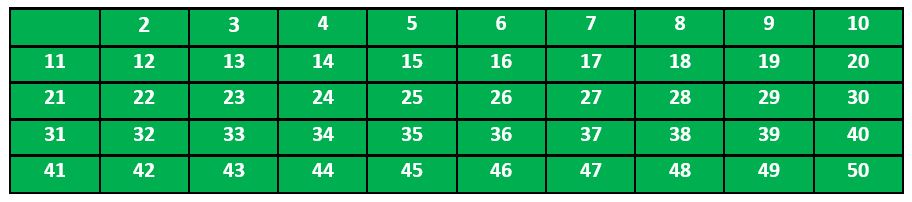
根据算法,我们将标记所有可被 2 整除且大于或等于其平方的数字。
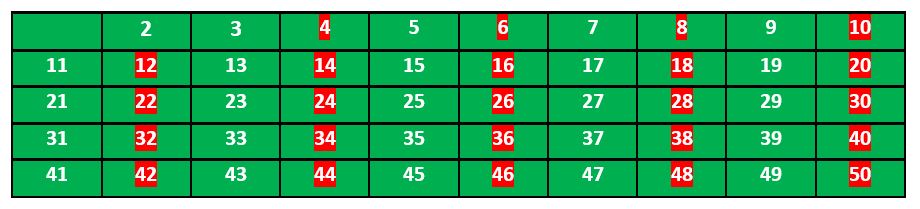
现在我们移动到下一个未标记的数字 3 并标记所有 3 的倍数且大于或等于它的平方的数字。
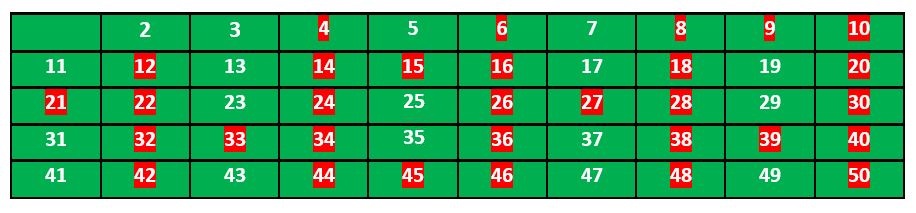
我们移动到下一个未标记的数字 5 并标记所有 5 的倍数并且大于或等于它的平方。
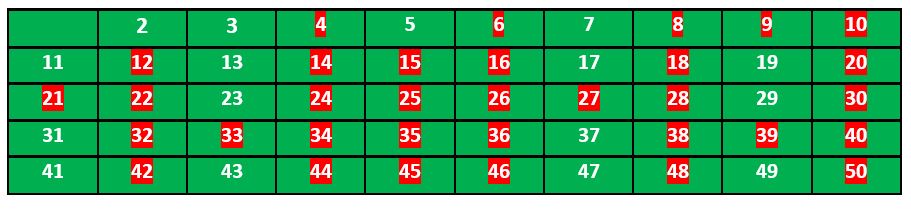
我们继续这个过程,我们的最终表将如下所示:
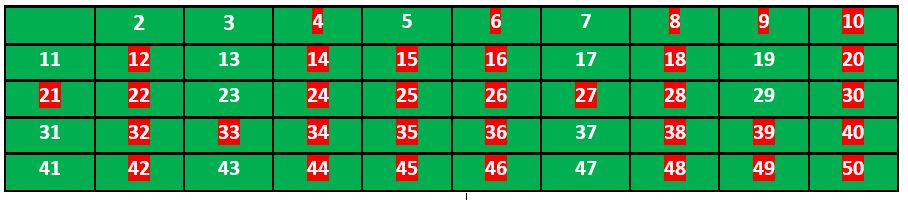
所以素数是未标记的数:2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47。
感谢Krishan Kumar提供上述解释。
执行:
下面是上述算法的实现。在下面的实现中,大小为 n 的布尔数组 arr[] 用于标记素数的倍数。
C++
// C++ program to print all primes
// smaller than or equal to
// n using Sieve of Eratosthenes
#include
using namespace std;
void SieveOfEratosthenes(int n)
{
// Create a boolean array
// "prime[0..n]" and initialize
// all entries it as true.
// A value in prime[i] will
// finally be false if i is
// Not a prime, else true.
bool prime[n + 1];
memset(prime, true, sizeof(prime));
for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; p++)
{
// If prime[p] is not changed,
// then it is a prime
if (prime[p] == true)
{
// Update all multiples
// of p greater than or
// equal to the square of it
// numbers which are multiple
// of p and are less than p^2
// are already been marked.
for (int i = p * p; i <= n; i += p)
prime[i] = false;
}
}
// Print all prime numbers
for (int p = 2; p <= n; p++)
if (prime[p])
cout << p << " ";
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int n = 30;
cout << "Following are the prime numbers smaller "
<< " than or equal to " << n << endl;
SieveOfEratosthenes(n);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to print all
// primes smaller than or equal to
// n using Sieve of Eratosthenes
class SieveOfEratosthenes {
void sieveOfEratosthenes(int n)
{
// Create a boolean array
// "prime[0..n]" and
// initialize all entries
// it as true. A value in
// prime[i] will finally be
// false if i is Not a
// prime, else true.
boolean prime[] = new boolean[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
prime[i] = true;
for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; p++)
{
// If prime[p] is not changed, then it is a
// prime
if (prime[p] == true)
{
// Update all multiples of p
for (int i = p * p; i <= n; i += p)
prime[i] = false;
}
}
// Print all prime numbers
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
if (prime[i] == true)
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String args[])
{
int n = 30;
System.out.print(
"Following are the prime numbers ");
System.out.println("smaller than or equal to " + n);
SieveOfEratosthenes g = new SieveOfEratosthenes();
g.sieveOfEratosthenes(n);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Amit Khandelwal.Python
# Python program to print all
# primes smaller than or equal to
# n using Sieve of Eratosthenes
def SieveOfEratosthenes(n):
# Create a boolean array
# "prime[0..n]" and initialize
# all entries it as true.
# A value in prime[i] will
# finally be false if i is
# Not a prime, else true.
prime = [True for i in range(n+1)]
p = 2
while (p * p <= n):
# If prime[p] is not
# changed, then it is a prime
if (prime[p] == True):
# Update all multiples of p
for i in range(p * p, n+1, p):
prime[i] = False
p += 1
# Print all prime numbers
for p in range(2, n+1):
if prime[p]:
print p,
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
n = 30
print "Following are the prime numbers smaller",
print "than or equal to", n
SieveOfEratosthenes(n)C#
// C# program to print all primes
// smaller than or equal to n
// using Sieve of Eratosthenes
using System;
namespace prime {
public class GFG {
public static void SieveOfEratosthenes(int n)
{
// Create a boolean array
// "prime[0..n]" and
// initialize all entries
// it as true. A value in
// prime[i] will finally be
// false if i is Not a
// prime, else true.
bool[] prime = new bool[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
prime[i] = true;
for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; p++)
{
// If prime[p] is not changed,
// then it is a prime
if (prime[p] == true)
{
// Update all multiples of p
for (int i = p * p; i <= n; i += p)
prime[i] = false;
}
}
// Print all prime numbers
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
if (prime[i] == true)
Console.Write(i + " ");
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
int n = 30;
Console.WriteLine(
"Following are the prime numbers");
Console.WriteLine("smaller than or equal to " + n);
SieveOfEratosthenes(n);
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sam007.PHP
Javascript
输出
Following are the prime numbers smaller than or equal to 30
2 3 5 7 11 13 17 19 23 29 时间复杂度: O(n*log(log(n)))
您可能还想看:
- Eratosthenes 筛的时间复杂度是 n*log(log(n)) 吗?
- 分段筛。
- 时间复杂度为 0(n) 的 Eratosthenes 筛分法
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。