给定一个由 N 个整数组成的数组,在元素之间使用“+”和“-”检查是否有办法形成一个数字序列,该序列评估为可被 M 整除的数字
例子:
Input: arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 6}
M = 4
Output: True
Explanation:
There is a valid sequence i.e., (1 – 2
+ 3 + 4 + 6), which evaluates to 12 that
is divisible by 4
Input: arr = {1, 3, 9}
M = 2
Output: False
Explanation:
There is no sequence which evaluates to
a number divisible by M.
一个简单的解决方案是递归地考虑所有可能的情况,即在元素之间使用 ;+’ 或 ‘-‘运算符并维护存储结果的变量 sum。如果该结果可被 M 整除,则返回 true 否则返回 false。
递归实现如下:
C++
bool isPossible(int index, int sum)
{
// Base case
if (index == n) {
// check if sum is divisible by M
if ((sum % M) == 0)
return true;
return false;
}
// recursively call by considering '+'
// or '-' between index and index+1
// 1.Try placing '+'
bool placeAdd = isPossible(index + 1,
sum + arr[index]);
// 2. Try placing '-'
bool placeMinus = isPossible(index + 1,
sum - arr[index]);
if (placeAdd || placeMinus)
return true;
return false;
}Java
static boolean isPossible(int index, int sum)
{
// Base case
if (index == n)
{
// Check if sum is divisible by M
if ((sum % M) == 0)
return true;
return false;
}
// Recursively call by considering '+'
// or '-' between index and index+1
// 1.Try placing '+'
boolean placeAdd = isPossible(index + 1,
sum + arr[index]);
// 2. Try placing '-'
boolean placeMinus = isPossible(index + 1,
sum - arr[index]);
if (placeAdd || placeMinus)
return true;
return false;
}
// This code is contributed by rutvik_56.Python3
def isPossible(index, sum):
# Base case
if (index == n):
# check if sum is divisible by M
if ((sum % M) == 0):
return True;
return False;
# recursively call by considering '+'
# or '-' between index and index+1
# 1.Try placing '+'
placeAdd = isPossible(index + 1, sum + arr[index]);
# 2. Try placing '-'
placeMinus = isPossible(index + 1, sum - arr[index]);
if (placeAdd or placeMinus):
return True;
return False;
# This code is contributed by pratham76.C#
static bool isPossible(int index, int sum)
{
// Base case
if (index == n)
{
// Check if sum is divisible by M
if ((sum % M) == 0)
return true;
return false;
}
// Recursively call by considering '+'
// or '-' between index and index+1
// 1.Try placing '+'
bool placeAdd = isPossible(index + 1,
sum + arr[index]);
// 2. Try placing '-'
bool placeMinus = isPossible(index + 1,
sum - arr[index]);
if (placeAdd || placeMinus)
return true;
return false;
}
// This code is contributed by divyesh072019Javascript
C++
// C++ program to check if any
// valid sequence is divisible by M
#include
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 1000;
bool isPossible(int n, int index, int sum,
int M, int arr[], int dp[][MAX])
{
// Base case
if (index == n) {
// check if sum is divisible by M
if ((sum % M) == 0)
return true;
return false;
}
// check if the current state
// is already computed
if (dp[index][sum] != -1)
return dp[index][sum];
// 1.Try placing '+'
bool placeAdd = isPossible(n, index + 1,
sum + arr[index], M, arr, dp);
// 2. Try placing '-'
bool placeMinus = isPossible(n, index + 1,
sum - arr[index], M, arr, dp);
// calculate value of res for recursive case
bool res = (placeAdd || placeMinus);
// store the value for res for current
// states and return for parent call
dp[index][sum] = res;
return res;
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 6 };
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
int M = 4;
int dp[n + 1][MAX];
memset(dp, -1, sizeof(dp));
bool res;
res = isPossible(n, 0, 0, M, arr, dp);
cout << (res ? "True" : "False") << endl;
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to check if any
// valid sequence is divisible by M
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static final int MAX = 1000;
static boolean isPossible(int n, int index, int sum,
int M, int arr[], int dp[][])
{
// Base case
if (index == n)
{
// check if sum is divisible by M
if ((sum % M) == 0)
return true;
return false;
}
else if(sum < 0 || sum >= MAX)
return false;
// check if the current state
// is already computed
if (dp[index][sum] != -1)
{
if(dp[index][sum] == 0)
return false;
return true;
}
// 1.Try placing '+'
boolean placeAdd = isPossible(n, index + 1,
sum + arr[index], M, arr, dp);
// 2. Try placing '-'
boolean placeMinus = isPossible(n, index + 1,
sum - arr[index], M, arr, dp);
// calculate value of res for recursive case
boolean res = (placeAdd || placeMinus);
// store the value for res for current
// states and return for parent call
dp[index][sum] = (res) ? 1 : 0;
return res;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 6 };
int n = arr.length;
int M = 4;
int dp[][] = new int[n + 1][MAX];
for(int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++)
Arrays.fill(dp[i], -1);
boolean res;
res = isPossible(n, 0, 0, M, arr, dp);
System.out.println((res ? "True" : "False"));
}
}
// This code is contributed by ghanshyampandeyPython3
# Python3 program to check if any
# valid sequence is divisible by M
def isPossible(n, index, Sum, M, arr, dp):
global MAX
# Base case
if index == n:
# check if sum is divisible by M
if (Sum % M) == 0:
return True
return False
# check if the current state
# is already computed
if dp[index][Sum] != -1:
return dp[index][Sum]
# 1.Try placing '+'
placeAdd = isPossible(n, index + 1,
Sum + arr[index], M, arr, dp)
# 2. Try placing '-'
placeMinus = isPossible(n, index + 1,
Sum - arr[index], M, arr, dp)
# calculate value of res for recursive case
res = placeAdd or placeMinus
# store the value for res for current
# states and return for parent call
dp[index][Sum] = res
return res
MAX = 1000
arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 6]
n = len(arr)
M = 4
dp = [[-1]*MAX for i in range(n+1)]
res = isPossible(n, 0, 0, M, arr, dp)
if res:
print(True)
else:
print(False)
# this code is contributed by PranchalKC#
// C# program to check if any
// valid sequence is divisible by M
using System;
class GFG
{
static int MAX = 1000;
static Boolean isPossible(int n, int index, int sum,
int M, int []arr, int [,]dp)
{
// Base case
if (index == n)
{
// check if sum is divisible by M
if ((sum % M) == 0)
return true;
return false;
}
else if(sum < 0 || sum >= MAX)
return false;
// check if the current state
// is already computed
if (dp[index,sum] != -1)
{
if(dp[index,sum] == 0)
return false;
return true;
}
// 1.Try placing '+'
Boolean placeAdd = isPossible(n, index + 1,
sum + arr[index],
M, arr, dp);
// 2. Try placing '-'
Boolean placeMinus = isPossible(n, index + 1,
sum - arr[index],
M, arr, dp);
// calculate value of res for recursive case
Boolean res = (placeAdd || placeMinus);
// store the value for res for current
// states and return for parent call
dp[index,sum] = (res) ? 1 : 0;
return res;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
int []arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 6 };
int n = arr.Length;
int M = 4;
int [,]dp = new int[n + 1, MAX];
for(int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < MAX; j++)
dp[i, j] = -1;
Boolean res;
res = isPossible(n, 0, 0, M, arr, dp);
Console.WriteLine((res ? "True" : "False"));
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992Javascript
C++
#include
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 100;
int isPossible(int n, int index, int modulo,
int M, int arr[], int dp[][MAX])
{
// Calculate modulo for this call
modulo = ((modulo % M) + M) % M;
// Base case
if (index == n) {
// check if sum is divisible by M
if (modulo == 0)
return 1;
return 0;
}
// check if the current state is
// already computed
if (dp[index][modulo] != -1)
return dp[index][modulo];
// 1.Try placing '+'
int placeAdd = isPossible(n, index + 1,
modulo + arr[index], M, arr, dp);
// 2. Try placing '-'
int placeMinus = isPossible(n, index + 1,
modulo - arr[index], M, arr, dp);
// calculate value of res for recursive
// case
bool res = (placeAdd || placeMinus);
// store the value for res for current
// states and return for parent call
dp[index][modulo] = res;
return res;
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 6 };
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
int M = 4;
// MAX is the Maximum value M can take
int dp[n + 1][MAX];
memset(dp, -1, sizeof(dp));
bool res;
res = isPossible(n, 1, arr[0], M, arr, dp);
cout << (res ? "True" : "False") << endl;
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of above approach
class GFG
{
static int MAX = 100;
static int isPossible(int n, int index, int modulo,
int M, int arr[], int dp[][])
{
// Calculate modulo for this call
modulo = ((modulo % M) + M) % M;
// Base case
if (index == n)
{
// check if sum is divisible by M
if (modulo == 0)
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
// check if the current state is
// already computed
if (dp[index][modulo] != -1)
{
return dp[index][modulo];
}
// 1.Try placing '+'
int placeAdd = isPossible(n, index + 1,
modulo + arr[index], M, arr, dp);
// 2. Try placing '-'
int placeMinus = isPossible(n, index + 1,
modulo - arr[index], M, arr, dp);
// calculate value of res for
// recursive case
int res = placeAdd;
// store the value for res for current
// states and return for parent call
dp[index][modulo] = res;
return res;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 6};
int n = arr.length;
int M = 4;
// MAX is the Maximum value M can take
int dp[][] = new int[n + 1][MAX];
for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < MAX; j++)
{
dp[i][j] = -1;
}
}
boolean res;
if (isPossible(n, 1, arr[0], M, arr, dp) == 1)
{
res = true;
}
else
{
res = false;
}
System.out.println(res ? "True" : "False");
}
}
// This code is contributed by
// PrinciRaj1992Python3
# Python3 Program to Check if any
# valid sequence is divisible by M
MAX = 100
def isPossible(n, index, modulo,
M, arr, dp):
# Calculate modulo for this call
modulo = ((modulo % M) + M) % M
# Base case
if (index == n):
# check if sum is divisible by M
if (modulo == 0):
return 1
return 0
# check if the current state is
# already computed
if (dp[index][modulo] != -1):
return dp[index][modulo]
# 1.Try placing '+'
placeAdd = isPossible(n, index + 1, modulo +
arr[index], M, arr, dp)
# 2. Try placing '-'
placeMinus = isPossible(n, index + 1, modulo -
arr[index], M, arr, dp)
# calculate value of res
# for recursive case
res = bool(placeAdd or placeMinus)
# store the value for res for current
# states and return for parent call
dp[index][modulo] = res
return res
# Driver code
arr = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 6 ]
n = len(arr)
M = 4
# MAX is the Maximum value
# M can take
dp = [[-1] * (n + 1)] * MAX
res = isPossible(n, 1, arr[0],
M, arr, dp)
if(res == True):
print("True")
else:
print("False")
# This code is contributed by ash264C#
// C# implementation of above approach
using System;
class GFG
{
static int MAX = 100;
static int isPossible(int n, int index, int modulo,
int M, int []arr, int [,]dp)
{
// Calculate modulo for this call
modulo = ((modulo % M) + M) % M;
// Base case
if (index == n)
{
// check if sum is divisible by M
if (modulo == 0)
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
// check if the current state is
// already computed
if (dp[index, modulo] != -1)
{
return dp[index, modulo];
}
// 1.Try placing '+'
int placeAdd = isPossible(n, index + 1,
modulo + arr[index], M, arr, dp);
// 2. Try placing '-'
int placeMinus = isPossible(n, index + 1,
modulo - arr[index], M, arr, dp);
// calculate value of res for
// recursive case
int res = placeAdd;
// store the value for res for current
// states and return for parent call
dp[index, modulo] = res;
return res;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int []arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 6};
int n = arr.Length;
int M = 4;
// MAX is the Maximum value M can take
int [,]dp = new int[n + 1,MAX];
for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < MAX; j++)
{
dp[i, j] = -1;
}
}
bool res;
if (isPossible(n, 1, arr[0], M, arr, dp) == 1)
{
res = true;
}
else
{
res = false;
}
Console.WriteLine(res ? "True" : "False");
}
}
//This code is contributed by 29AjayKumarJavascript
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to check if any valid
// sequence is divisible by M
void func(int n, int m, int A[])
{
// DEclare mod array
vector ModArray(n);
int sum = 0;
// Calculate the mod array
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
ModArray[i] = A[i] % m;
sum += ModArray[i];
}
sum = sum % m;
// Check if sum is divisible by M
if (sum % m == 0) {
cout << "True";
return;
}
// Check if sum is not divisible by 2
if (sum % 2 != 0) {
cout << "False";
}
else {
// Remove the first element from
// the ModArray since it is not
// possible to place minus
// on the first element
ModArray.erase(ModArray.begin());
int i = 0;
// Decrease the size of array
int j = ModArray.size() - 1;
// Sort the array
sort(ModArray.begin(), ModArray.end());
sum = sum / 2;
int i1, i2;
// Loop until the pointer
// cross each other
while (i <= j) {
int s = ModArray[i] + ModArray[j];
// Check if sum becomes equal
if (s == sum) {
i1 = i;
i2 = j;
cout << "True";
break;
}
// Increase and decrease
// the pointer accordingly
else if (s > sum)
j--;
else
i++;
}
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int m = 2;
int a[] = { 1, 3, 9 };
int n = sizeof a / sizeof a[0];
// Function call
func(n, m, a);
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Function to check if any valid
// sequence is divisible by M
static void func(int n, int m, int []A)
{
// Declare mod array
Vector ModArray = new Vector<>();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
ModArray.add(0);
int sum = 0;
// Calculate the mod array
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
ModArray.set(i, A[i] % m);
sum += ((int)ModArray.get(i));
}
sum = sum % m;
// Check if sum is divisible by M
if (sum % m == 0)
{
System.out.println("True");
return;
}
// Check if sum is not divisible by 2
if (sum % 2 != 0)
{
System.out.println("False");
}
else
{
// Remove the first element from
// the ModArray since it is not
// possible to place minus
// on the first element
ModArray.remove(0);
int i = 0;
// Decrease the size of array
int j = ModArray.size() - 1;
// Sort the array
Collections.sort(ModArray);
sum = sum / 2;
int i1, i2;
// Loop until the pointer
// cross each other
while (i <= j)
{
int s = (int)ModArray.get(i) +
(int)ModArray.get(j);
// Check if sum becomes equal
if (s == sum)
{
i1 = i;
i2 = j;
System.out.println("True");
break;
}
// Increase and decrease
// the pointer accordingly
else if (s > sum)
j--;
else
i++;
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
int m = 2;
int []a = { 1, 3, 9 };
int n = a.length;
// Function call
func(n, m, a);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Stream_Cipher Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# Function to check if any valid
# sequence is divisible by M
def func(n, m, A):
# DEclare mod array
ModArray = [0]*n
Sum = 0
# Calculate the mod array
for i in range(n):
ModArray[i] = A[i] % m
Sum += ModArray[i]
Sum = Sum % m
# Check if sum is divisible by M
if (Sum % m == 0) :
print("True")
return
# Check if sum is not divisible by 2
if (Sum % 2 != 0) :
print("False")
else :
# Remove the first element from
# the ModArray since it is not
# possible to place minus
# on the first element
ModArray.pop(0)
i = 0
# Decrease the size of array
j = len(ModArray) - 1
# Sort the array
ModArray.sort()
Sum = Sum // 2
# Loop until the pointer
# cross each other
while (i <= j) :
s = ModArray[i] + ModArray[j]
# Check if sum becomes equal
if (s == Sum) :
i1 = i
i2 = j
print("True")
break
# Increase and decrease
# the pointer accordingly
elif (s > Sum):
j -= 1
else:
i += 1
# Driver code
m = 2
a = [ 1, 3, 9 ]
n = len(a)
# Function call
func(n, m, a)
# This code is contributed by divyeshrabadiya07C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System;
class GFG{
// Function to check if any valid
// sequence is divisible by M
static void func(int n, int m, int []A)
{
// Declare mod array
List ModArray = new List();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
ModArray.Add(0);
int sum = 0;
// Calculate the mod array
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
ModArray[i] = (A[i] % m);
sum += ((int)ModArray[i]);
}
sum = sum % m;
// Check if sum is divisible by M
if (sum % m == 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("True");
return;
}
// Check if sum is not divisible by 2
if (sum % 2 != 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("False");
}
else
{
// Remove the first element from
// the ModArray since it is not
// possible to place minus
// on the first element
ModArray.Remove(0);
int i = 0;
// Decrease the size of array
int j = ModArray.Count - 1;
// Sort the array
ModArray.Sort();
sum = sum / 2;
int i1, i2;
// Loop until the pointer
// cross each other
while (i <= j)
{
int s = (int)ModArray[i] +
(int)ModArray[j];
// Check if sum becomes equal
if (s == sum)
{
i1 = i;
i2 = j;
Console.WriteLine("True");
break;
}
// Increase and decrease
// the pointer accordingly
else if (s > sum)
j--;
else
i++;
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int m = 2;
int []a = { 1, 3, 9 };
int n = a.Length;
// Function call
func(n, m, a);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Stream_Cipher Javascript
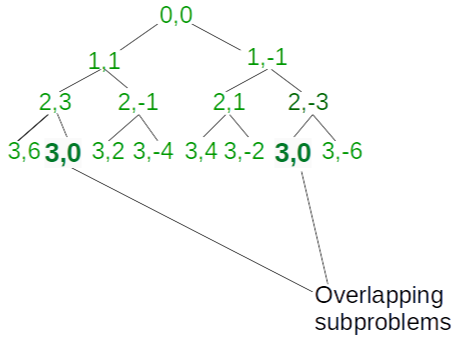
有重叠的子问题,如下图所示(注意:图像代表递归树,直到索引 = 3)
更好的方法:要优化上述方法,请使用动态规划。
方法 1:我们应用具有两种状态的动态规划:-
(i) 指数,
(ii) 总和
所以 DP[index][sum] 存储我们所在的当前索引,而 sum 存储直到该索引形成的序列的评估结果。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program to check if any
// valid sequence is divisible by M
#include
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 1000;
bool isPossible(int n, int index, int sum,
int M, int arr[], int dp[][MAX])
{
// Base case
if (index == n) {
// check if sum is divisible by M
if ((sum % M) == 0)
return true;
return false;
}
// check if the current state
// is already computed
if (dp[index][sum] != -1)
return dp[index][sum];
// 1.Try placing '+'
bool placeAdd = isPossible(n, index + 1,
sum + arr[index], M, arr, dp);
// 2. Try placing '-'
bool placeMinus = isPossible(n, index + 1,
sum - arr[index], M, arr, dp);
// calculate value of res for recursive case
bool res = (placeAdd || placeMinus);
// store the value for res for current
// states and return for parent call
dp[index][sum] = res;
return res;
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 6 };
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
int M = 4;
int dp[n + 1][MAX];
memset(dp, -1, sizeof(dp));
bool res;
res = isPossible(n, 0, 0, M, arr, dp);
cout << (res ? "True" : "False") << endl;
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to check if any
// valid sequence is divisible by M
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static final int MAX = 1000;
static boolean isPossible(int n, int index, int sum,
int M, int arr[], int dp[][])
{
// Base case
if (index == n)
{
// check if sum is divisible by M
if ((sum % M) == 0)
return true;
return false;
}
else if(sum < 0 || sum >= MAX)
return false;
// check if the current state
// is already computed
if (dp[index][sum] != -1)
{
if(dp[index][sum] == 0)
return false;
return true;
}
// 1.Try placing '+'
boolean placeAdd = isPossible(n, index + 1,
sum + arr[index], M, arr, dp);
// 2. Try placing '-'
boolean placeMinus = isPossible(n, index + 1,
sum - arr[index], M, arr, dp);
// calculate value of res for recursive case
boolean res = (placeAdd || placeMinus);
// store the value for res for current
// states and return for parent call
dp[index][sum] = (res) ? 1 : 0;
return res;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 6 };
int n = arr.length;
int M = 4;
int dp[][] = new int[n + 1][MAX];
for(int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++)
Arrays.fill(dp[i], -1);
boolean res;
res = isPossible(n, 0, 0, M, arr, dp);
System.out.println((res ? "True" : "False"));
}
}
// This code is contributed by ghanshyampandey
蟒蛇3
# Python3 program to check if any
# valid sequence is divisible by M
def isPossible(n, index, Sum, M, arr, dp):
global MAX
# Base case
if index == n:
# check if sum is divisible by M
if (Sum % M) == 0:
return True
return False
# check if the current state
# is already computed
if dp[index][Sum] != -1:
return dp[index][Sum]
# 1.Try placing '+'
placeAdd = isPossible(n, index + 1,
Sum + arr[index], M, arr, dp)
# 2. Try placing '-'
placeMinus = isPossible(n, index + 1,
Sum - arr[index], M, arr, dp)
# calculate value of res for recursive case
res = placeAdd or placeMinus
# store the value for res for current
# states and return for parent call
dp[index][Sum] = res
return res
MAX = 1000
arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 6]
n = len(arr)
M = 4
dp = [[-1]*MAX for i in range(n+1)]
res = isPossible(n, 0, 0, M, arr, dp)
if res:
print(True)
else:
print(False)
# this code is contributed by PranchalK
C#
// C# program to check if any
// valid sequence is divisible by M
using System;
class GFG
{
static int MAX = 1000;
static Boolean isPossible(int n, int index, int sum,
int M, int []arr, int [,]dp)
{
// Base case
if (index == n)
{
// check if sum is divisible by M
if ((sum % M) == 0)
return true;
return false;
}
else if(sum < 0 || sum >= MAX)
return false;
// check if the current state
// is already computed
if (dp[index,sum] != -1)
{
if(dp[index,sum] == 0)
return false;
return true;
}
// 1.Try placing '+'
Boolean placeAdd = isPossible(n, index + 1,
sum + arr[index],
M, arr, dp);
// 2. Try placing '-'
Boolean placeMinus = isPossible(n, index + 1,
sum - arr[index],
M, arr, dp);
// calculate value of res for recursive case
Boolean res = (placeAdd || placeMinus);
// store the value for res for current
// states and return for parent call
dp[index,sum] = (res) ? 1 : 0;
return res;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
int []arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 6 };
int n = arr.Length;
int M = 4;
int [,]dp = new int[n + 1, MAX];
for(int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < MAX; j++)
dp[i, j] = -1;
Boolean res;
res = isPossible(n, 0, 0, M, arr, dp);
Console.WriteLine((res ? "True" : "False"));
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992
Javascript
True时间复杂度: O(N*sum) 其中 sum 是整数序列的最大可能总和,N 是数组中的元素数。
方法 2(高效):这比方法 1 更有效。 在这里,我们也应用动态规划,但有两种不同的状态:
(i) 指数,
(ii) 模数
所以 DP[index][modulo] 存储了直到该索引形成的序列的评估结果的模数,与 M。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
#include
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 100;
int isPossible(int n, int index, int modulo,
int M, int arr[], int dp[][MAX])
{
// Calculate modulo for this call
modulo = ((modulo % M) + M) % M;
// Base case
if (index == n) {
// check if sum is divisible by M
if (modulo == 0)
return 1;
return 0;
}
// check if the current state is
// already computed
if (dp[index][modulo] != -1)
return dp[index][modulo];
// 1.Try placing '+'
int placeAdd = isPossible(n, index + 1,
modulo + arr[index], M, arr, dp);
// 2. Try placing '-'
int placeMinus = isPossible(n, index + 1,
modulo - arr[index], M, arr, dp);
// calculate value of res for recursive
// case
bool res = (placeAdd || placeMinus);
// store the value for res for current
// states and return for parent call
dp[index][modulo] = res;
return res;
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 6 };
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
int M = 4;
// MAX is the Maximum value M can take
int dp[n + 1][MAX];
memset(dp, -1, sizeof(dp));
bool res;
res = isPossible(n, 1, arr[0], M, arr, dp);
cout << (res ? "True" : "False") << endl;
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation of above approach
class GFG
{
static int MAX = 100;
static int isPossible(int n, int index, int modulo,
int M, int arr[], int dp[][])
{
// Calculate modulo for this call
modulo = ((modulo % M) + M) % M;
// Base case
if (index == n)
{
// check if sum is divisible by M
if (modulo == 0)
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
// check if the current state is
// already computed
if (dp[index][modulo] != -1)
{
return dp[index][modulo];
}
// 1.Try placing '+'
int placeAdd = isPossible(n, index + 1,
modulo + arr[index], M, arr, dp);
// 2. Try placing '-'
int placeMinus = isPossible(n, index + 1,
modulo - arr[index], M, arr, dp);
// calculate value of res for
// recursive case
int res = placeAdd;
// store the value for res for current
// states and return for parent call
dp[index][modulo] = res;
return res;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 6};
int n = arr.length;
int M = 4;
// MAX is the Maximum value M can take
int dp[][] = new int[n + 1][MAX];
for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < MAX; j++)
{
dp[i][j] = -1;
}
}
boolean res;
if (isPossible(n, 1, arr[0], M, arr, dp) == 1)
{
res = true;
}
else
{
res = false;
}
System.out.println(res ? "True" : "False");
}
}
// This code is contributed by
// PrinciRaj1992
蟒蛇3
# Python3 Program to Check if any
# valid sequence is divisible by M
MAX = 100
def isPossible(n, index, modulo,
M, arr, dp):
# Calculate modulo for this call
modulo = ((modulo % M) + M) % M
# Base case
if (index == n):
# check if sum is divisible by M
if (modulo == 0):
return 1
return 0
# check if the current state is
# already computed
if (dp[index][modulo] != -1):
return dp[index][modulo]
# 1.Try placing '+'
placeAdd = isPossible(n, index + 1, modulo +
arr[index], M, arr, dp)
# 2. Try placing '-'
placeMinus = isPossible(n, index + 1, modulo -
arr[index], M, arr, dp)
# calculate value of res
# for recursive case
res = bool(placeAdd or placeMinus)
# store the value for res for current
# states and return for parent call
dp[index][modulo] = res
return res
# Driver code
arr = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 6 ]
n = len(arr)
M = 4
# MAX is the Maximum value
# M can take
dp = [[-1] * (n + 1)] * MAX
res = isPossible(n, 1, arr[0],
M, arr, dp)
if(res == True):
print("True")
else:
print("False")
# This code is contributed by ash264
C#
// C# implementation of above approach
using System;
class GFG
{
static int MAX = 100;
static int isPossible(int n, int index, int modulo,
int M, int []arr, int [,]dp)
{
// Calculate modulo for this call
modulo = ((modulo % M) + M) % M;
// Base case
if (index == n)
{
// check if sum is divisible by M
if (modulo == 0)
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
// check if the current state is
// already computed
if (dp[index, modulo] != -1)
{
return dp[index, modulo];
}
// 1.Try placing '+'
int placeAdd = isPossible(n, index + 1,
modulo + arr[index], M, arr, dp);
// 2. Try placing '-'
int placeMinus = isPossible(n, index + 1,
modulo - arr[index], M, arr, dp);
// calculate value of res for
// recursive case
int res = placeAdd;
// store the value for res for current
// states and return for parent call
dp[index, modulo] = res;
return res;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int []arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 6};
int n = arr.Length;
int M = 4;
// MAX is the Maximum value M can take
int [,]dp = new int[n + 1,MAX];
for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < MAX; j++)
{
dp[i, j] = -1;
}
}
bool res;
if (isPossible(n, 1, arr[0], M, arr, dp) == 1)
{
res = true;
}
else
{
res = false;
}
Console.WriteLine(res ? "True" : "False");
}
}
//This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
Javascript
True时间复杂度: O(N*M)。
有效的方法:按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 相对于给定数字计算所有数组元素的模数并将其存储在新数组中,比如说 ModArray[]。
- 计算 ModArray 的总和并将其存储在 sum 中并检查 sum%M==0 则输出为“true”并返回。
- 如果总和为奇数,则以下情况不会被评估为可被 M 整除的数字。打印“False”并返回。
- 检查总和是否为偶数,然后将其除以 2,这是因为我们之前已经将它们相加,现在的任务是删除它,因此需要将其删除两次,因此数字应该是偶数。
- 从 ModArray 中删除第一个元素,因为不可能在第一个元素上放置减号。
- 现在解决方案转换为我们要评估是否存在解决方案的问题,以便 ModArray 的元素之和等于总和。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to check if any valid
// sequence is divisible by M
void func(int n, int m, int A[])
{
// DEclare mod array
vector ModArray(n);
int sum = 0;
// Calculate the mod array
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
ModArray[i] = A[i] % m;
sum += ModArray[i];
}
sum = sum % m;
// Check if sum is divisible by M
if (sum % m == 0) {
cout << "True";
return;
}
// Check if sum is not divisible by 2
if (sum % 2 != 0) {
cout << "False";
}
else {
// Remove the first element from
// the ModArray since it is not
// possible to place minus
// on the first element
ModArray.erase(ModArray.begin());
int i = 0;
// Decrease the size of array
int j = ModArray.size() - 1;
// Sort the array
sort(ModArray.begin(), ModArray.end());
sum = sum / 2;
int i1, i2;
// Loop until the pointer
// cross each other
while (i <= j) {
int s = ModArray[i] + ModArray[j];
// Check if sum becomes equal
if (s == sum) {
i1 = i;
i2 = j;
cout << "True";
break;
}
// Increase and decrease
// the pointer accordingly
else if (s > sum)
j--;
else
i++;
}
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int m = 2;
int a[] = { 1, 3, 9 };
int n = sizeof a / sizeof a[0];
// Function call
func(n, m, a);
}
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Function to check if any valid
// sequence is divisible by M
static void func(int n, int m, int []A)
{
// Declare mod array
Vector ModArray = new Vector<>();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
ModArray.add(0);
int sum = 0;
// Calculate the mod array
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
ModArray.set(i, A[i] % m);
sum += ((int)ModArray.get(i));
}
sum = sum % m;
// Check if sum is divisible by M
if (sum % m == 0)
{
System.out.println("True");
return;
}
// Check if sum is not divisible by 2
if (sum % 2 != 0)
{
System.out.println("False");
}
else
{
// Remove the first element from
// the ModArray since it is not
// possible to place minus
// on the first element
ModArray.remove(0);
int i = 0;
// Decrease the size of array
int j = ModArray.size() - 1;
// Sort the array
Collections.sort(ModArray);
sum = sum / 2;
int i1, i2;
// Loop until the pointer
// cross each other
while (i <= j)
{
int s = (int)ModArray.get(i) +
(int)ModArray.get(j);
// Check if sum becomes equal
if (s == sum)
{
i1 = i;
i2 = j;
System.out.println("True");
break;
}
// Increase and decrease
// the pointer accordingly
else if (s > sum)
j--;
else
i++;
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
int m = 2;
int []a = { 1, 3, 9 };
int n = a.length;
// Function call
func(n, m, a);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Stream_Cipher
蟒蛇3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# Function to check if any valid
# sequence is divisible by M
def func(n, m, A):
# DEclare mod array
ModArray = [0]*n
Sum = 0
# Calculate the mod array
for i in range(n):
ModArray[i] = A[i] % m
Sum += ModArray[i]
Sum = Sum % m
# Check if sum is divisible by M
if (Sum % m == 0) :
print("True")
return
# Check if sum is not divisible by 2
if (Sum % 2 != 0) :
print("False")
else :
# Remove the first element from
# the ModArray since it is not
# possible to place minus
# on the first element
ModArray.pop(0)
i = 0
# Decrease the size of array
j = len(ModArray) - 1
# Sort the array
ModArray.sort()
Sum = Sum // 2
# Loop until the pointer
# cross each other
while (i <= j) :
s = ModArray[i] + ModArray[j]
# Check if sum becomes equal
if (s == Sum) :
i1 = i
i2 = j
print("True")
break
# Increase and decrease
# the pointer accordingly
elif (s > Sum):
j -= 1
else:
i += 1
# Driver code
m = 2
a = [ 1, 3, 9 ]
n = len(a)
# Function call
func(n, m, a)
# This code is contributed by divyeshrabadiya07
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System;
class GFG{
// Function to check if any valid
// sequence is divisible by M
static void func(int n, int m, int []A)
{
// Declare mod array
List ModArray = new List();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
ModArray.Add(0);
int sum = 0;
// Calculate the mod array
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
ModArray[i] = (A[i] % m);
sum += ((int)ModArray[i]);
}
sum = sum % m;
// Check if sum is divisible by M
if (sum % m == 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("True");
return;
}
// Check if sum is not divisible by 2
if (sum % 2 != 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("False");
}
else
{
// Remove the first element from
// the ModArray since it is not
// possible to place minus
// on the first element
ModArray.Remove(0);
int i = 0;
// Decrease the size of array
int j = ModArray.Count - 1;
// Sort the array
ModArray.Sort();
sum = sum / 2;
int i1, i2;
// Loop until the pointer
// cross each other
while (i <= j)
{
int s = (int)ModArray[i] +
(int)ModArray[j];
// Check if sum becomes equal
if (s == sum)
{
i1 = i;
i2 = j;
Console.WriteLine("True");
break;
}
// Increase and decrease
// the pointer accordingly
else if (s > sum)
j--;
else
i++;
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int m = 2;
int []a = { 1, 3, 9 };
int n = a.Length;
// Function call
func(n, m, a);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Stream_Cipher
Javascript
False时间复杂度: O(n * log n)
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。