鉴于移动数字键盘。您只能按下当前按钮的上、左、右或下按钮,也可以选择再次按下同一按钮。圆角按钮(即 * 和 # )是无效的移动。
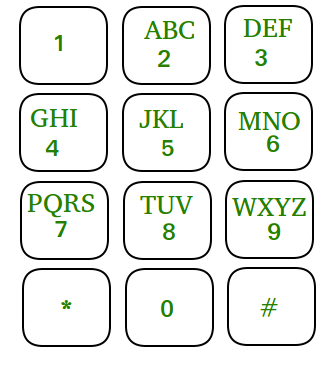
给定一个数字N ,您必须找到长度为 N 的不同数字,您可以从 0-9 之间的任何数字开始,在您只能从您按下的最后一个数字向上、向左、向右或向下移动的限制下,或者您可以选择再次按下相同的按钮。
例子:
Input: N = 1
Output: 10
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 and 9 are the possible numbers.
Input: N = 2
Output: 36
All the possible numbers are 00, 08, 11, 12, 14, 21, 22, 23, 25, …
Input: N = 6
Output: 7990
方法:我们在这里看到了很多解决这个问题的方法。
让X n i是n位以i结尾的数字的计数。
所以,通过这个符号,
X10 = 1 which is {0}
X11 = 1 which is {1}
X12 = 1 which is {2}
X13 = 1 which is {3}
and
X20 = 2 which are {00, 80}
X21 = 3 which are {11, 21, 41}
X22 = 4 which are {22, 12, 32, 52}
中心思想是,如果您知道X n i ,您可以获得关于X n + 1 j 的哪些信息
让我们借助一个例子来看看:
Suppose we know, X21 = 3 which are {11, 21, 41}
Because the last digit of all these numbers is 1, let’s look at the possible moves that we can have from 1:
- Pressing 1 again.
- Pressing 2 (moving right).
- Pressing 4 (moving down)
Now we can pick any element from our set {11, 21, 41} and make any valid move:
- {111, 211, 411} can be achieved with the first move.
- {112, 212, 412} with the second move.
- And {114, 214, 414} with the third.
我们可以看到,进行任何可能的移动,每次移动都会得到相同大小的集合。即在以 1 结尾的两位数字集合中有 3 个元素,我们得到了相同大小(3)的集合,从 1 开始的每一个可能的移动。
因此,可以看出 X 2 1贡献了 3 位数字,如下所示:
X31 += X21
X32 += X21
X34 += X21
所以,一般来说,如果我们知道 X n i ,我们就知道它对 X n+1 j 的贡献,其中 j 是从 i 开始的所有可能的移动。 ![]()
其中 0<=j<=9 并且从 j 我们可以有一个对 i 有效的
这个想法是首先从每个给定的键枚举所有可能的方向,并维护一个包含 10 个元素的数组,其中每个索引处的元素存储以该索引结尾的数字计数。
例如数组的初始值是:
Value 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Index 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
n = 1 的初始结果是数组中所有元素的总和,即 1+1+1+1+1+1+1+1+1+1 = 10,可以拨打 10 个数字。
如何更新 n > 1 的数组?
让我们首先枚举所有给定数字的所有方向:
| From | To (Possible moves) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0, 8 |
| 1 | 1, 2, 4 |
| 2 | 2, 1, 3, 5 |
| 3 | 3, 6, 2 |
| 4 | 4, 1, 7, 5 |
| 5 | 5, 4, 6, 2, 8 |
| 6 | 6, 3, 5, 9 |
| 7 | 7, 4, 8 |
| 8 | 8, 5, 0, 7, 9 |
| 9 | 9, 6, 8 |
上面列出的表格的第一行表明,如果数字的最后一位数字为零,我们可以移动到 0 或 8。
让我们详细看看 N = 2 的方法
For N = 1, Arr[10] is {1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1} indicating there are Arr[i] numbers ending with index i ![]()
Lets Create a new array, say Arr2[10] = {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
Now, for 0, possible moves are 0 and 8.
we already know ![]()
That would contribute 1 to {0, 8} i.e. ![]()
![]()
Arr2[10] = {1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0}
For 1, Possible moves are 1, 2, 4
we already know ![]()
That would contribute 1 to {1, 2, 4} i.e.![]()
![]()
![]()
Arr2[10] = {1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0}
For 2, Possible moves are 2, 1, 3, 4
we already know ![]()
That would contribute 1 to {2, 1, 3, 4}![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Arr2[10] = {1, 2, 2, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0}
and so on ….
Arr2[10] = {2, 3, 4, 3, 4, 5, 4, 3, 5, 3}
Sum = 2+3+4+3+4+5+4+3+5+3 = 36 (For N=2)
Arr2 now holds the values for ![]() and can be considered as starting point for n=3 and the process continues.
and can be considered as starting point for n=3 and the process continues.
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#define MAX 10
// Function to return the count of numbers possible
int getCount(int n)
{
// Array of list storing possible direction
// for each number from 0 to 9
// mylist[i] stores possible moves from index i
list mylist[MAX];
// Initializing list
mylist[0].assign({ 0, 8 });
mylist[1].assign({ 1, 2, 4 });
mylist[2].assign({ 2, 1, 3, 5 });
mylist[3].assign({ 3, 6, 2 });
mylist[4].assign({ 4, 1, 7, 5 });
mylist[5].assign({ 5, 4, 6, 2, 8 });
mylist[6].assign({ 6, 3, 5, 9 });
mylist[7].assign({ 7, 4, 8 });
mylist[8].assign({ 8, 5, 0, 7, 9 });
mylist[9].assign({ 9, 6, 8 });
// Storing values for n = 1
int Arr[MAX] = { 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 };
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
// To store the values for n = i
int Arr2[MAX] = { 0 };
// Loop to iterate through each index
for (int j = 0; j < MAX; j++) {
// For each move possible from j
// Increment the value of possible
// move positions by Arr[j]
for (int x : mylist[j]) {
Arr2[x] += Arr[j];
}
}
// Update Arr[] for next iteration
for (int j = 0; j < MAX; j++)
Arr[j] = Arr2[j];
}
// Find the count of numbers possible
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
sum += Arr[i];
return sum;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 2;
cout << getCount(n);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation of the approach
class GFG
{
static int MAX = 10;
// Function to return the count of numbers possible
static int getCount(int n)
{
// Array of list storing possible direction
// for each number from 0 to 9
// list[i] stores possible moves from index i
int [][] list = new int[MAX][];
// Initializing list
list[0] = new int [] { 0, 8 };
list[1] = new int [] { 1, 2, 4 };
list[2] = new int [] { 2, 1, 3, 5 };
list[3] = new int [] { 3, 6, 2 };
list[4] = new int [] { 4, 1, 7, 5 };
list[5] = new int [] { 5, 4, 6, 2, 8 };
list[6] = new int [] { 6, 3, 5, 9 };
list[7] = new int [] { 7, 4, 8 };
list[8] = new int [] { 8, 5, 0, 7, 9 };
list[9] = new int [] { 9, 6, 8 };
// Storing values for n = 1
int Arr[] = new int [] { 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 };
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
// To store the values for n = i
int Arr2[] = new int [MAX];
// Loop to iterate through each index
for (int j = 0; j < MAX; j++)
{
// For each move possible from j
// Increment the value of possible
// move positions by Arr[j]
for (int x = 0; x < list[j].length; x++)
{
Arr2[list[j][x]] += Arr[j];
}
}
// Update Arr[] for next iteration
for (int j = 0; j < MAX; j++)
Arr[j] = Arr2[j];
}
// Find the count of numbers possible
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
sum += Arr[i];
return sum;
}
// Driver code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int n = 2;
System.out.println(getCount(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by ihritikC#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
class GFG
{
static int MAX = 10;
// Function to return the count of numbers possible
static int getCount(int n)
{
// Array of list storing possible direction
// for each number from 0 to 9
// list[i] stores possible moves from index i
int [][] list = new int[MAX][];
// Initializing list
list[0] = new int [] { 0, 8 };
list[1] = new int [] { 1, 2, 4 };
list[2] = new int [] { 2, 1, 3, 5 };
list[3] = new int [] { 3, 6, 2 };
list[4] = new int [] { 4, 1, 7, 5 };
list[5] = new int [] { 5, 4, 6, 2, 8 };
list[6] = new int [] { 6, 3, 5, 9 };
list[7] = new int [] { 7, 4, 8 };
list[8] = new int [] { 8, 5, 0, 7, 9 };
list[9] = new int [] { 9, 6, 8 };
// Storing values for n = 1
int [] Arr = new int [] { 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 };
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
// To store the values for n = i
int [] Arr2 = new int [MAX];
// Loop to iterate through each index
for (int j = 0; j < MAX; j++)
{
// For each move possible from j
// Increment the value of possible
// move positions by Arr[j]
for (int x = 0; x < list[j].Length; x++)
{
Arr2[list[j][x]] += Arr[j];
}
}
// Update Arr[] for next iteration
for (int j = 0; j < MAX; j++)
Arr[j] = Arr2[j];
}
// Find the count of numbers possible
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
sum += Arr[i];
return sum;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main ()
{
int n = 2;
Console.WriteLine(getCount(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by ihritik36时间复杂度: O(N)
空间复杂度: O(1)
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。