考虑一排 n 个硬币,价值为 v1 。 . . vn,其中 n 是偶数。我们通过交替轮流与对手进行游戏。在每一轮中,玩家从该行中选择第一个或最后一个硬币,将其从该行中永久移除,并获得该硬币的价值。确定如果我们先行动,我们肯定能赢得的最大可能金额。
注意:对手和使用者一样聪明。
让我们通过几个例子来理解这个问题:
- 5, 3, 7, 10 : 用户收集最大值为 15(10 + 5)
- 8, 15, 3, 7 : 用户收集最大值为 22(7 + 15)
在每次移动中选择最好的是否会给出最佳解决方案?不。
在第二个例子中,这是如何完成游戏的:
- …….用户选择8。
…….对手选择15。
…….用户选择7。
…….对手选择3。
用户收集的总价值为 15(8 + 7) - …….用户选择7。
…….对手选择8。
…….用户选择15。
…….对手选择3。
用户收集的总价值为 22(7 + 15)
因此,如果用户遵循第二个游戏状态,尽管第一个动作不是最好的,但可以收集最大值。
做法:由于双方实力相当,双方都会尽量降低对方获胜的可能性。现在让我们看看对手是如何做到这一点的。
有两种选择:
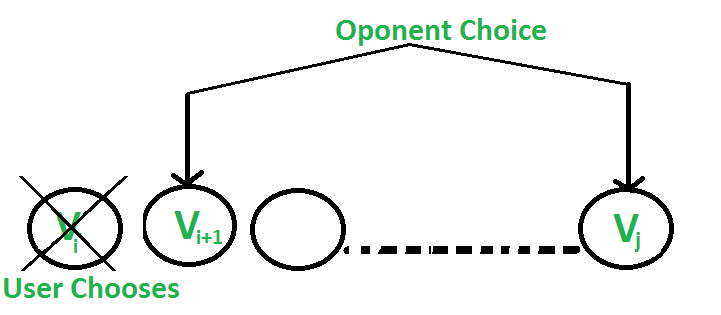
- 用户选择价值为“Vi”的“第 i 个”硬币:对手选择第 (i+1) 个硬币或第 j 个硬币。对手打算选择给用户留下最小价值的硬币。
即用户可以收集值Vi + min(F(i+2, j), F(i+1, j-1) ) 。
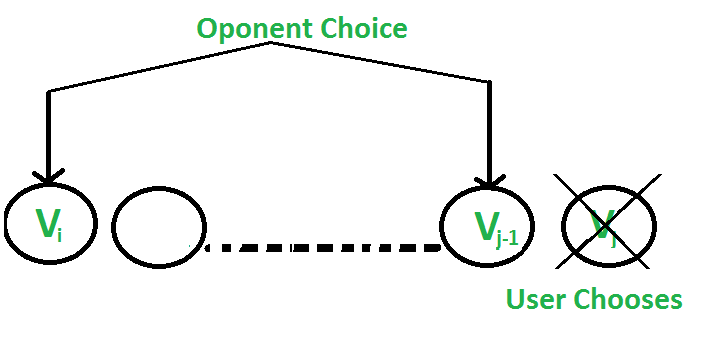
- 用户选择价值为“Vj”的“第j个”硬币:对手选择“第i个”硬币或“第(j-1)个”硬币。对手打算选择给用户留下最小价值的硬币,即用户可以收集价值Vj + min(F(i+1, j-1), F(i, j-2) ) 。
以下是基于上述两种选择的递归解决方案。我们最多有两个选择。
F(i, j) represents the maximum value the user
can collect from i'th coin to j'th coin.
F(i, j) = Max(Vi + min(F(i+2, j), F(i+1, j-1) ),
Vj + min(F(i+1, j-1), F(i, j-2) ))
As user wants to maximise the number of coins.
Base Cases
F(i, j) = Vi If j == i
F(i, j) = max(Vi, Vj) If j == i + 1C++
// C++ program to find out
// maximum value from a given
// sequence of coins
#include
using namespace std;
// Returns optimal value possible
// that a player can collect from
// an array of coins of size n.
// Note than n must be even
int optimalStrategyOfGame(
int* arr, int n)
{
// Create a table to store
// solutions of subproblems
int table[n][n];
// Fill table using above
// recursive formula. Note
// that the table is filled
// in diagonal fashion (similar
// to http:// goo.gl/PQqoS),
// from diagonal elements to
// table[0][n-1] which is the result.
for (int gap = 0; gap < n; ++gap) {
for (int i = 0, j = gap; j < n; ++i, ++j) {
// Here x is value of F(i+2, j),
// y is F(i+1, j-1) and
// z is F(i, j-2) in above recursive
// formula
int x = ((i + 2) <= j)
? table[i + 2][j]
: 0;
int y = ((i + 1) <= (j - 1))
? table[i + 1][j - 1]
: 0;
int z = (i <= (j - 2))
? table[i][j - 2]
: 0;
table[i][j] = max(
arr[i] + min(x, y),
arr[j] + min(y, z));
}
}
return table[0][n - 1];
}
// Driver program to test above function
int main()
{
int arr1[] = { 8, 15, 3, 7 };
int n = sizeof(arr1) / sizeof(arr1[0]);
printf("%d\n",
optimalStrategyOfGame(arr1, n));
int arr2[] = { 2, 2, 2, 2 };
n = sizeof(arr2) / sizeof(arr2[0]);
printf("%d\n",
optimalStrategyOfGame(arr2, n));
int arr3[] = { 20, 30, 2, 2, 2, 10 };
n = sizeof(arr3) / sizeof(arr3[0]);
printf("%d\n",
optimalStrategyOfGame(arr3, n));
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to find out maximum
// value from a given sequence of coins
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
// Returns optimal value possible
// that a player can collect from
// an array of coins of size n.
// Note than n must be even
static int optimalStrategyOfGame(
int arr[], int n)
{
// Create a table to store
// solutions of subproblems
int table[][] = new int[n][n];
int gap, i, j, x, y, z;
// Fill table using above recursive formula.
// Note that the tableis filled in diagonal
// fashion (similar to http:// goo.gl/PQqoS),
// from diagonal elements to table[0][n-1]
// which is the result.
for (gap = 0; gap < n; ++gap) {
for (i = 0, j = gap; j < n; ++i, ++j) {
// Here x is value of F(i+2, j),
// y is F(i+1, j-1) and z is
// F(i, j-2) in above recursive formula
x = ((i + 2) <= j)
? table[i + 2][j]
: 0;
y = ((i + 1) <= (j - 1))
? table[i + 1][j - 1]
: 0;
z = (i <= (j - 2))
? table[i][j - 2]
: 0;
table[i][j] = Math.max(
arr[i] + Math.min(x, y),
arr[j] + Math.min(y, z));
}
}
return table[0][n - 1];
}
// Driver program
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr1[] = { 8, 15, 3, 7 };
int n = arr1.length;
System.out.println(
""
+ optimalStrategyOfGame(arr1, n));
int arr2[] = { 2, 2, 2, 2 };
n = arr2.length;
System.out.println(
""
+ optimalStrategyOfGame(arr2, n));
int arr3[] = { 20, 30, 2, 2, 2, 10 };
n = arr3.length;
System.out.println(
""
+ optimalStrategyOfGame(arr3, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by vt_mPython3
# Python3 program to find out maximum
# value from a given sequence of coins
# Returns optimal value possible that
# a player can collect from an array
# of coins of size n. Note than n
# must be even
def optimalStrategyOfGame(arr, n):
# Create a table to store
# solutions of subproblems
table = [[0 for i in range(n)]
for i in range(n)]
# Fill table using above recursive
# formula. Note that the table is
# filled in diagonal fashion
# (similar to http://goo.gl / PQqoS),
# from diagonal elements to
# table[0][n-1] which is the result.
for gap in range(n):
for j in range(gap, n):
i = j - gap
# Here x is value of F(i + 2, j),
# y is F(i + 1, j-1) and z is
# F(i, j-2) in above recursive
# formula
x = 0
if((i + 2) <= j):
x = table[i + 2][j]
y = 0
if((i + 1) <= (j - 1)):
y = table[i + 1][j - 1]
z = 0
if(i <= (j - 2)):
z = table[i][j - 2]
table[i][j] = max(arr[i] + min(x, y),
arr[j] + min(y, z))
return table[0][n - 1]
# Driver Code
arr1 = [ 8, 15, 3, 7 ]
n = len(arr1)
print(optimalStrategyOfGame(arr1, n))
arr2 = [ 2, 2, 2, 2 ]
n = len(arr2)
print(optimalStrategyOfGame(arr2, n))
arr3 = [ 20, 30, 2, 2, 2, 10]
n = len(arr3)
print(optimalStrategyOfGame(arr3, n))
# This code is contributed
# by sahilshelangiaC#
// C# program to find out maximum
// value from a given sequence of coins
using System;
public class GFG {
// Returns optimal value possible that a player
// can collect from an array of coins of size n.
// Note than n must be even
static int optimalStrategyOfGame(int[] arr, int n)
{
// Create a table to store solutions of subproblems
int[, ] table = new int[n, n];
int gap, i, j, x, y, z;
// Fill table using above recursive formula.
// Note that the tableis filled in diagonal
// fashion (similar to http:// goo.gl/PQqoS),
// from diagonal elements to table[0][n-1]
// which is the result.
for (gap = 0; gap < n; ++gap) {
for (i = 0, j = gap; j < n; ++i, ++j) {
// Here x is value of F(i+2, j),
// y is F(i+1, j-1) and z is
// F(i, j-2) in above recursive formula
x = ((i + 2) <= j) ? table[i + 2, j] : 0;
y = ((i + 1) <= (j - 1)) ? table[i + 1, j - 1] : 0;
z = (i <= (j - 2)) ? table[i, j - 2] : 0;
table[i, j] = Math.Max(arr[i] + Math.Min(x, y),
arr[j] + Math.Min(y, z));
}
}
return table[0, n - 1];
}
// Driver program
static public void Main()
{
int[] arr1 = { 8, 15, 3, 7 };
int n = arr1.Length;
Console.WriteLine("" + optimalStrategyOfGame(arr1, n));
int[] arr2 = { 2, 2, 2, 2 };
n = arr2.Length;
Console.WriteLine("" + optimalStrategyOfGame(arr2, n));
int[] arr3 = { 20, 30, 2, 2, 2, 10 };
n = arr3.Length;
Console.WriteLine("" + optimalStrategyOfGame(arr3, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by ajitPHP
Javascript
输出:
22
4
42复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(n 2 )。
使用嵌套的 for 循环会使时间复杂度达到 n 2 。 - 辅助空间: O(n 2 )。
由于二维表用于存储状态。
注意:可以通过对每个选择使用较少数量的比较来优化上述解决方案。请参考以下。
游戏的最优策略| 2套
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。