📌 相关文章
- Phalcon-数据库连接
- Phalcon连接到数据库(1)
- Phalcon连接到数据库
- Phalcon-数据库连接(1)
- Phalcon层
- Phalcon层(1)
- Phalcon-切换数据库(1)
- Phalcon-切换数据库
- Phalcon安装
- Phalcon安装(1)
- 什么是Phalcon
- 什么是Phalcon(1)
- Django数据库迁移
- Django数据库迁移(1)
- Phalcon表单
- Phalcon表单(1)
- Phalcon模型(1)
- Phalcon模型
- Phalcon-模型(1)
- Phalcon-模型
- Phalcon教程
- Phalcon教程(1)
- Phalcon教程
- 数据库迁移如何工作 (1)
- Phalcon请求(1)
- Phalcon请求
- Phalcon-视图
- Phalcon视图
- Phalcon视图(1)
📜 Phalcon-数据库迁移
📅 最后修改于: 2020-10-21 05:29:34 🧑 作者: Mango
由于以下原因,数据库迁移很重要-
-
数据库迁移有助于在指定的存储类型之间传输数据。
-
数据库迁移是指基于Web的应用程序从一个平台迁移到另一个平台的上下文。
-
通常进行此过程以跟踪过时的数据。
Phalcon以以下方式执行数据库迁移过程-
步骤1-在xampp / wamp目录中创建一个名为“ dbProject”的项目。
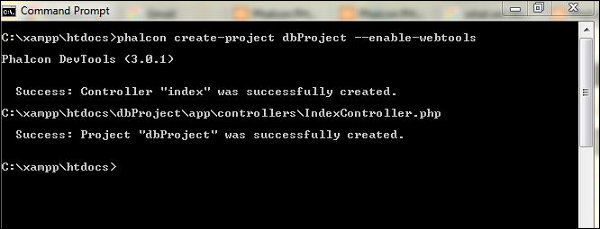
步骤2-为项目配置适当的数据库连接。
[
'adapter' => 'Mysql',
'host' => 'localhost',
'username' => 'root',
'password' => '',
'dbname' => 'demodb',
'charset' => 'utf8', ],
'application' => [ 'appDir' => APP_PATH . '/',
'controllersDir' => APP_PATH .
'/controllers/', 'modelsDir' => APP_PATH .
'/models/', 'migrationsDir' => APP_PATH .
'/migrations/', 'viewsDir' => APP_PATH .
'/views/','pluginsDir' => APP_PATH .
'/plugins/', 'libraryDir' => APP_PATH .
'/library/', 'cacheDir' => BASE_PATH .
'/cache/', 'baseUri' => '/dbProject/',
] ]);
步骤3-执行命令以迁移数据库“ demodb”中包含的表。现在,它包括一个表“ users”。
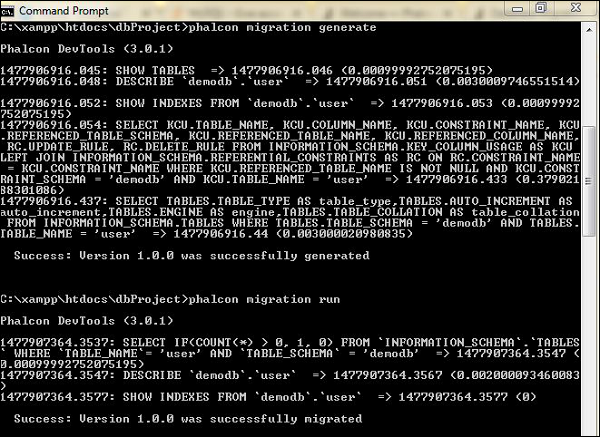
步骤4-迁移的数据库文件存储在“ app”文件夹中的迁移目录内。
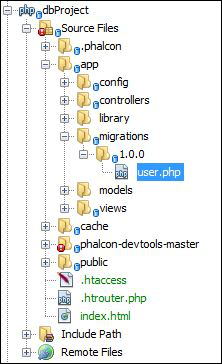
因此,表已成功迁移。
了解迁移文件的结构
迁移的文件具有一个唯一的类,该类扩展了Phalcon \ Mvc \ Model \ Migration类。 Phalcon中的Migration类包括方法up()和down() 。 up()方法用于执行迁移,而down方法用于回滚操作。
Users.php
morphTable('user', [
'columns' => [
new Column( 'Id', [
'type' => Column::TYPE_INTEGER,
'notNull' => true,
'autoIncrement' => true,
'size' => 11, 'first' => true ] ),
new Column( 'username', [
'type' => Column::TYPE_VARCHAR,
'notNull' => true,
'size' => 40,
'after' => 'Id' ] ),
new Column( 'email', [
'type' => Column::TYPE_VARCHAR,
'notNull' => true,
'size' => 40,
'after' => 'username' ] ),
new Column( 'password', [
'type' => Column::TYPE_VARCHAR,
'notNull' => true,
'size' => 10,
'after' => 'email' ] )
],
'indexes' => [new Index('PRIMARY', ['Id'], 'PRIMARY') ],
'options' => [ 'TABLE_TYPE' => 'BASE TABLE',
'AUTO_INCREMENT' => '3', 'ENGINE' => 'InnoDB',
'TABLE_COLLATION' => 'latin1_swedish_ci' ],
] );
}
/**
* Run the migrations
* * @return void
*/
public function up() {
}
/**
* Reverse the migrations
*
* @return void
*/
public function down() {
}
}
如上例所示,类UserMigration_100包含具有四个部分的关联数组,这些部分是-
-
列-包括一组表列。
-
索引-包括一组表索引。
-
参考-包括所有参考完整性约束(外键)。
-
选项-带有一组表创建选项的数组。
如上面的示例所示,数据库的1.0.0版本已成功迁移。 Phalcon可能包括并运行多个迁移过程,具体取决于数据库内容的保存方式。