先决条件:磁盘调度算法和 SCAN 磁盘调度算法
给定一组磁盘磁道号和初始磁头位置,如果使用C-SCAN磁盘调度算法,我们的任务是找到为访问所有请求的磁道而执行的寻道操作总数。
什么是 C-SCAN(环形电梯)磁盘调度算法?
Circular SCAN (C-SCAN) 调度算法是 SCAN 磁盘调度算法的改进版本,它通过更统一地为请求提供服务来解决 SCAN 算法效率低下的问题。像 SCAN(电梯算法)一样,C-SCAN 将头部从服务所有请求的一端移动到另一端。但是,一旦磁头到达另一端,它会立即返回到磁盘的开头,而不为回程中的任何请求提供服务(见下图),并在到达开头后再次开始服务。这也被称为“圆形电梯算法”,因为它本质上将圆柱体视为从最后一个圆柱体到第一个圆柱体的圆形列表。
算法:
- 让 Request 数组表示一个数组,存储已按到达时间升序请求的曲目的索引。 ‘head’ 是磁盘磁头的位置。
- 磁头仅在从 0 到磁盘大小的正确方向上服务。
- 向左行驶时不要维修任何轨道。
- 当我们到达起点(左端)时,反转方向。
- 在朝着正确的方向前进时,它会一一为所有轨道提供服务。
- 在正确方向移动时,计算轨道与头部的绝对距离。
- 使用此距离增加总寻道计数。
- 当前服务的轨道位置现在成为新的磁头位置。
- 转到第 6 步,直到我们到达磁盘的右端。
- 如果我们到达磁盘的右端,则反转方向并转到步骤 3,直到请求阵列中的所有磁道都没有得到服务。
例子:
Input:
Request sequence = {176, 79, 34, 60, 92, 11, 41, 114}
Initial head position = 50
Output:
Initial position of head: 50
Total number of seek operations = 389
Seek Sequence is
60
79
92
114
176
199
0
11
34
41下图显示了使用 SCAN 服务请求的轨道的顺序。
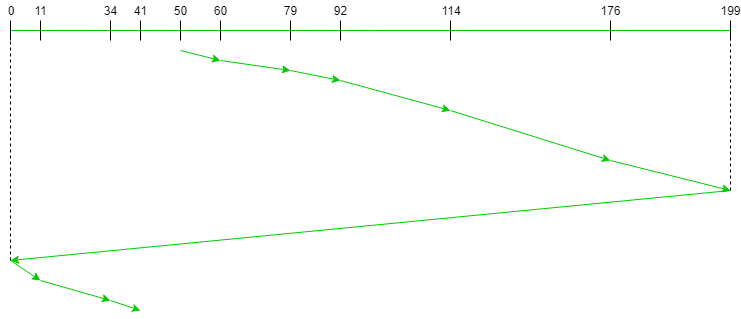
因此,总寻道计数计算如下:
= (60-50)+(79-60)+(92-79)
+(114-92)+(176-114)+(199-176)+(199-0)
+(11-0)+(34-11)+(41-34)
= 389执行:
下面给出C-SCAN算法的实现。
笔记:
distance 变量用于存储磁头与当前磁道位置之间的绝对距离。 disk_size 是磁盘的大小。 Vectors left 和 right 分别存储初始头部位置左侧和右侧的所有请求轨迹。
C++
// C++ program to demonstrate
// C-SCAN Disk Scheduling algorithm
#include
using namespace std;
// Code by Vikram Chaurasia
int size = 8;
int disk_size = 200;
void CSCAN(int arr[], int head)
{
int seek_count = 0;
int distance, cur_track;
vector left, right;
vector seek_sequence;
// appending end values
// which has to be visited
// before reversing the direction
left.push_back(0);
right.push_back(disk_size - 1);
// tracks on the left of the
// head will be serviced when
// once the head comes back
// to the beginning (left end).
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (arr[i] < head)
left.push_back(arr[i]);
if (arr[i] > head)
right.push_back(arr[i]);
}
// sorting left and right vectors
std::sort(left.begin(), left.end());
std::sort(right.begin(), right.end());
// first service the requests
// on the right side of the
// head.
for (int i = 0; i < right.size(); i++) {
cur_track = right[i];
// appending current track to seek sequence
seek_sequence.push_back(cur_track);
// calculate absolute distance
distance = abs(cur_track - head);
// increase the total count
seek_count += distance;
// accessed track is now new head
head = cur_track;
}
// once reached the right end
// jump to the beginning.
head = 0;
// adding seek count for head returning from 199 to 0
seek_count += (disk_size - 1);
// Now service the requests again
// which are left.
for (int i = 0; i < left.size(); i++) {
cur_track = left[i];
// appending current track to seek sequence
seek_sequence.push_back(cur_track);
// calculate absolute distance
distance = abs(cur_track - head);
// increase the total count
seek_count += distance;
// accessed track is now the new head
head = cur_track;
}
cout << "Total number of seek operations = "
<< seek_count << endl;
cout << "Seek Sequence is" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < seek_sequence.size(); i++) {
cout << seek_sequence[i] << endl;
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// request array
int arr[size] = { 176, 79, 34, 60, 92, 11, 41, 114 };
int head = 50;
cout << "Initial position of head: " << head << endl;
CSCAN(arr, head);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to demonstrate
// C-SCAN Disk Scheduling algorithm
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static int size = 8;
static int disk_size = 200;
public static void CSCAN(int arr[], int head)
{
int seek_count = 0;
int distance, cur_track;
Vector left = new Vector();
Vector right = new Vector();
Vector seek_sequence
= new Vector();
// Appending end values which has
// to be visited before reversing
// the direction
left.add(0);
right.add(disk_size - 1);
// Tracks on the left of the
// head will be serviced when
// once the head comes back
// to the beggining (left end).
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (arr[i] < head)
left.add(arr[i]);
if (arr[i] > head)
right.add(arr[i]);
}
// Sorting left and right vectors
Collections.sort(left);
Collections.sort(right);
// First service the requests
// on the right side of the
// head.
for (int i = 0; i < right.size(); i++) {
cur_track = right.get(i);
// Appending current track to seek sequence
seek_sequence.add(cur_track);
// Calculate absolute distance
distance = Math.abs(cur_track - head);
// Increase the total count
seek_count += distance;
// Accessed track is now new head
head = cur_track;
}
// Once reached the right end
// jump to the beggining.
head = 0;
// adding seek count for head returning from 199 to
// 0
seek_count += (disk_size - 1);
// Now service the requests again
// which are left.
for (int i = 0; i < left.size(); i++) {
cur_track = left.get(i);
// Appending current track to
// seek sequence
seek_sequence.add(cur_track);
// Calculate absolute distance
distance = Math.abs(cur_track - head);
// Increase the total count
seek_count += distance;
// Accessed track is now the new head
head = cur_track;
}
System.out.println("Total number of seek "
+ "operations = " + seek_count);
System.out.println("Seek Sequence is");
for (int i = 0; i < seek_sequence.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(seek_sequence.get(i));
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
// Request array
int arr[] = { 176, 79, 34, 60, 92, 11, 41, 114 };
int head = 50;
System.out.println("Initial position of head: "
+ head);
CSCAN(arr, head);
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyesh072019 Python3
# Python3 program to demonstrate
# C-SCAN Disk Scheduling algorithm
size = 8
disk_size = 200
def CSCAN(arr, head):
seek_count = 0
distance = 0
cur_track = 0
left = []
right = []
seek_sequence = []
# Appending end values
# which has to be visited
# before reversing the direction
left.append(0)
right.append(disk_size - 1)
# Tracks on the left of the
# head will be serviced when
# once the head comes back
# to the beggining (left end).
for i in range(size):
if (arr[i] < head):
left.append(arr[i])
if (arr[i] > head):
right.append(arr[i])
# Sorting left and right vectors
left.sort()
right.sort()
# First service the requests
# on the right side of the
# head.
for i in range(len(right)):
cur_track = right[i]
# Appending current track
# to seek sequence
seek_sequence.append(cur_track)
# Calculate absolute distance
distance = abs(cur_track - head)
# Increase the total count
seek_count += distance
# Accessed track is now new head
head = cur_track
# Once reached the right end
# jump to the beggining.
head = 0
# adding seek count for head returning from 199 to 0
seek_count += (disk_size - 1)
# Now service the requests again
# which are left.
for i in range(len(left)):
cur_track = left[i]
# Appending current track
# to seek sequence
seek_sequence.append(cur_track)
# Calculate absolute distance
distance = abs(cur_track - head)
# Increase the total count
seek_count += distance
# Accessed track is now the new head
head = cur_track
print("Total number of seek operations =",
seek_count)
print("Seek Sequence is")
print(*seek_sequence, sep="\n")
# Driver code
# request array
arr = [176, 79, 34, 60,
92, 11, 41, 114]
head = 50
print("Initial position of head:", head)
CSCAN(arr, head)
# This code is contributed by rag2127C#
// C# program to demonstrate
// C-SCAN Disk Scheduling algorithm
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
static int size = 8;
static int disk_size = 200;
static void CSCAN(int[] arr, int head)
{
int seek_count = 0;
int distance, cur_track;
List left = new List();
List right = new List();
List seek_sequence = new List();
// Appending end values which has
// to be visited before reversing
// the direction
left.Add(0);
right.Add(disk_size - 1);
// Tracks on the left of the
// head will be serviced when
// once the head comes back
// to the beggining (left end).
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (arr[i] < head)
left.Add(arr[i]);
if (arr[i] > head)
right.Add(arr[i]);
}
// Sorting left and right vectors
left.Sort();
right.Sort();
// First service the requests
// on the right side of the
// head.
for (int i = 0; i < right.Count; i++) {
cur_track = right[i];
// Appending current track to seek sequence
seek_sequence.Add(cur_track);
// Calculate absolute distance
distance = Math.Abs(cur_track - head);
// Increase the total count
seek_count += distance;
// Accessed track is now new head
head = cur_track;
}
// Once reached the right end
// jump to the beggining.
head = 0;
// adding seek count for head returning from 199 to
// 0
seek_count += (disk_size - 1);
// Now service the requests again
// which are left.
for (int i = 0; i < left.Count; i++) {
cur_track = left[i];
// Appending current track to
// seek sequence
seek_sequence.Add(cur_track);
// Calculate absolute distance
distance = Math.Abs(cur_track - head);
// Increase the total count
seek_count += distance;
// Accessed track is now the new head
head = cur_track;
}
Console.WriteLine("Total number of seek "
+ "operations = " + seek_count);
Console.WriteLine("Seek Sequence is");
for (int i = 0; i < seek_sequence.Count; i++) {
Console.WriteLine(seek_sequence[i]);
}
}
// Driver code
static void Main()
{
// Request array
int[] arr = { 176, 79, 34, 60, 92, 11, 41, 114 };
int head = 50;
Console.WriteLine("Initial position of head: "
+ head);
CSCAN(arr, head);
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyeshrabadiya07 Javascript
输出
Initial position of head: 50
Total number of seek operations = 389
Seek Sequence is
60
79
92
114
176
199
0
11
34
41