操作系统中有两种类型的碎片,它们分别是:内部碎片和外部碎片。
内部碎片:
当内存被拆分为已安装大小的块时,就会发生内部碎片。每当一个方法请求内存时,安装的大小块就会分配给该方法。以防万一分配给方法的内存比请求的内存大一些,那么分配的和请求的内存之间的区别在于内部碎片。
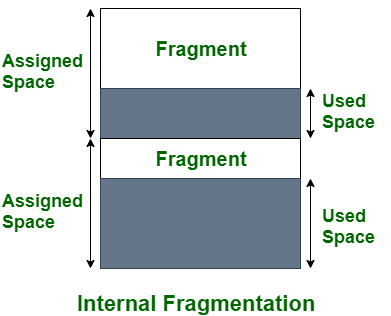
上图清楚地显示了内部碎片,因为分配的内存与所需空间或内存之间的差异称为内部碎片。
外部碎片:
当内存中有足够数量的区域来满足方法的内存请求时,就会发生外部碎片。但是进程的内存请求无法满足,因为提供的内存是在非连续的方式中。无论您应用最适合还是最适合的内存分配策略,它都会导致外部碎片。
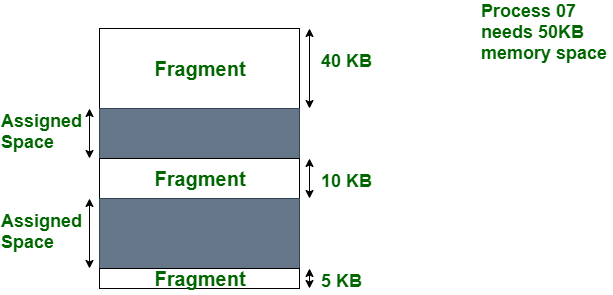
在上图中,我们可以看到,有足够的空间 (55 KB) 来运行 process-07(需要 50 KB),但内存(片段)不是连续的。在这里,我们使用压缩、分页或分段来使用空闲空间来运行进程。
内部碎片和外部碎片之间的区别:-
| S.NO | Internal fragmentation | External fragmentation |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | In internal fragmentation fixed-sized memory, blocks square measure appointed to process. | In external fragmentation, variable-sized memory blocks square measure appointed to method. |
| 2. | Internal fragmentation happens when the method or process is larger than the memory. | External fragmentation happens when the method or process is removed. |
| 3. | The solution of internal fragmentation is best-fit block. | Solution of external fragmentation is compaction, paging and segmentation. |
| 4. | Internal fragmentation occurs when memory is divided into fixed sized partitions. | External fragmentation occurs when memory is divided into variable size partitions based on the size of processes. |
| 5. | The difference between memory allocated and required space or memory is called Internal fragmentation. | The unused spaces formed between non-contiguous memory fragments are too small to serve a new process, is called External fragmentation . |