什么是超椭圆
超椭圆,也称为加布里埃尔·拉梅之后的拉梅曲线,是一种类似于椭圆的闭合曲线,保留了长半轴和半短轴的几何特征,并围绕它们对称,但整体形状不同。
在笛卡尔坐标系中,曲线上所有点(x,y)的集合满足方程
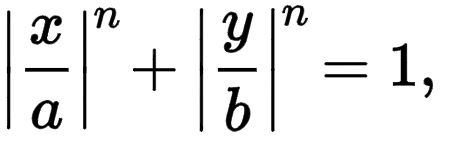
其中 n、a 和 b 是正数,竖线 | |数字周围表示数字的绝对值。
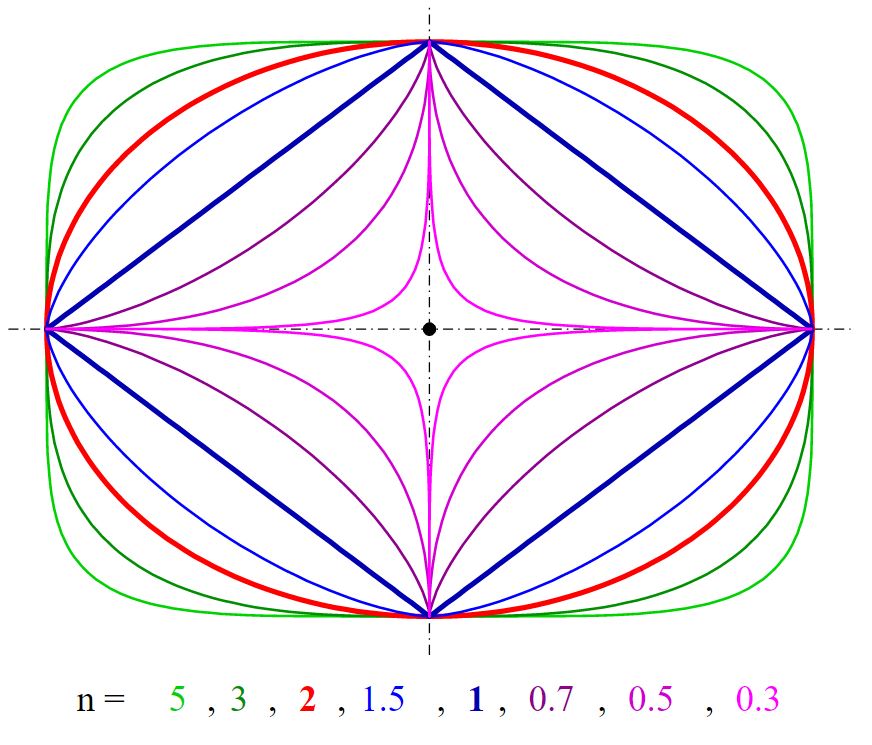
a = 1 和 b = 0.75
超椭圆的具体情况有很多,如下图所示: 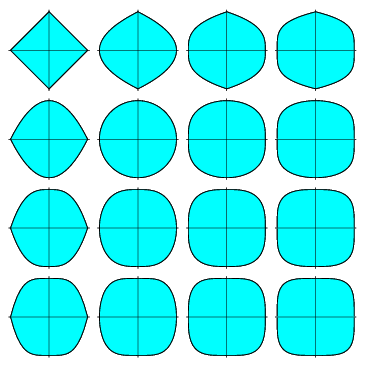
这些可以通过改变方程中的 n 值来实现。所以现在我们尝试在Python实现它,为此我们需要一些库。
所需模块:
- matplotlib :绘制方程的曲线。它是Python的第 3 方库,如果您想安装它,请单击此处。
- math :它是一个内置的Python库,几乎拥有所有数学工具。
# Python program to implement
# Superellipse
# importing the required libraries
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from math import sin, cos, pi
def sgn(x):
return ((x>0)-(x<0))*1
# parameter for marking the shape
a, b, n = 200, 200, 2.5
na = 2 / n
# defining the accuracy
step = 100
piece =(pi * 2)/step
xp =[];yp =[]
t = 0
for t1 in range(step + 1):
# because sin ^ n(x) is mathematically the same as (sin(x))^n...
x =(abs((cos(t)))**na)*a * sgn(cos(t))
y =(abs((sin(t)))**na)*b * sgn(sin(t))
xp.append(x);yp.append(y)
t+= piece
plt.plot(xp, yp) # plotting all point from array xp, yp
plt.title("Superellipse with parameter "+str(n))
plt.show()
输出:
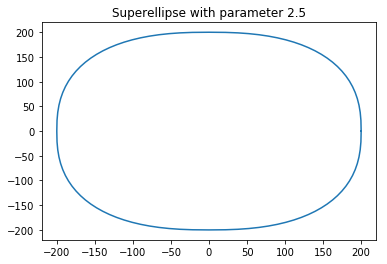
当 n = 2.5
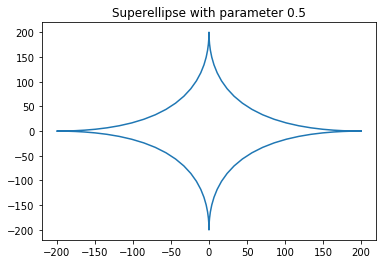
现在让我们看看当我们将 n 的值更改为 0.5 时会发生什么
# Python program to implement
# Superellipse
# importing the required libraries
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from math import sin, cos, pi
def sgn(x):
return ((x>0)-(x<0))*1
# parameter for marking the shape
a, b, n = 200, 200, 0.5
na = 2 / n
# defining the accuracy
step = 100
piece =(pi * 2)/step
xp =[];yp =[]
t = 0
for t1 in range(step + 1):
# because sin ^ n(x) is mathematically the same as (sin(x))^n...
x =(abs((cos(t)))**na)*a * sgn(cos(t))
y =(abs((sin(t)))**na)*b * sgn(sin(t))
xp.append(x);yp.append(y)
t+= piece
plt.plot(xp, yp) # plotting all point from array xp, yp
plt.title("Superellipse with parameter "+str(n))
plt.show()
输出:
Java程序的源代码。
// Java program to implement
// Superellipse
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.geom.Path2D;
import static java.lang.Math.pow;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.event.*;
public class SuperEllipse extends JPanel implements ChangeListener {
private double exp = 2.5;
public SuperEllipse()
{
setPreferredSize(new Dimension(650, 650));
setBackground(Color.white);
setFont(new Font("Serif", Font.PLAIN, 18));
}
void drawGrid(Graphics2D g)
{
g.setStroke(new BasicStroke(2));
g.setColor(new Color(0xEEEEEE));
int w = getWidth();
int h = getHeight();
int spacing = 25;
for (int i = 0; i < w / spacing; i++) {
g.drawLine(0, i * spacing, w, i * spacing);
g.drawLine(i * spacing, 0, i * spacing, w);
}
g.drawLine(0, h - 1, w, h - 1);
g.setColor(new Color(0xAAAAAA));
g.drawLine(0, w / 2, w, w / 2);
g.drawLine(w / 2, 0, w / 2, w);
}
void drawLegend(Graphics2D g)
{
g.setColor(Color.black);
g.setFont(getFont());
g.drawString("n = " + String.valueOf(exp), getWidth() - 150, 45);
g.drawString("a = b = 200", getWidth() - 150, 75);
}
void drawEllipse(Graphics2D g)
{
final int a = 200; // a = b
double[] points = new double[a + 1];
Path2D p = new Path2D.Double();
p.moveTo(a, 0);
// calculate first quadrant
for (int x = a; x >= 0; x--) {
points[x] = pow(pow(a, exp) - pow(x, exp), 1 / exp); // solve for y
p.lineTo(x, -points[x]);
}
// mirror to others
for (int x = 0; x <= a; x++)
p.lineTo(x, points[x]);
for (int x = a; x >= 0; x--)
p.lineTo(-x, points[x]);
for (int x = 0; x <= a; x++)
p.lineTo(-x, -points[x]);
g.translate(getWidth() / 2, getHeight() / 2);
g.setStroke(new BasicStroke(2));
g.setColor(new Color(0x25B0C4DE, true));
g.fill(p);
g.setColor(new Color(0xB0C4DE)); // LightSteelBlue
g.draw(p);
}
@Override
public void paintComponent(Graphics gg)
{
super.paintComponent(gg);
Graphics2D g = (Graphics2D)gg;
g.setRenderingHint(RenderingHints.KEY_ANTIALIASING,
RenderingHints.VALUE_ANTIALIAS_ON);
g.setRenderingHint(RenderingHints.KEY_TEXT_ANTIALIASING,
RenderingHints.VALUE_TEXT_ANTIALIAS_ON);
drawGrid(g);
drawLegend(g);
drawEllipse(g);
}
@Override
public void stateChanged(ChangeEvent e)
{
JSlider source = (JSlider)e.getSource();
exp = source.getValue() / 2.0;
repaint();
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame f = new JFrame();
f.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
f.setTitle("Super Ellipse");
f.setResizable(false);
SuperEllipse panel = new SuperEllipse();
f.add(panel, BorderLayout.CENTER);
JSlider exponent = new JSlider(JSlider.HORIZONTAL, 1, 9, 5);
exponent.addChangeListener(panel);
exponent.setMajorTickSpacing(1);
exponent.setPaintLabels(true);
exponent.setBackground(Color.white);
exponent.setBorder(BorderFactory.createEmptyBorder(20, 20, 20, 20));
Hashtable labelTable = new Hashtable<>();
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++)
labelTable.put(i, new JLabel(String.valueOf(i * 0.5)));
exponent.setLabelTable(labelTable);
f.add(exponent, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
f.pack();
f.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
f.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
输出:
参考链接:
1.维基百科——超椭圆
2. WolframMathWorld – 超椭圆