📌 相关文章
- c# 在运行时编译代码 - C# (1)
- 字符串的编译时间与运行时间解析(1)
- 字符串的编译时间与运行时间解析
- C语言中的编译过程(1)
- C语言中的编译过程
- c# 在运行时编译代码 - C# 代码示例
- C语言 |组5(1)
- C语言 | 2套(1)
- C语言 | 6套(1)
- C语言 |组5
- C语言中的宏(1)
- C语言 | 7套
- C语言 | 6套
- C语言中的宏
- C语言 | 8套
- C语言 | 7套(1)
- C语言中的X宏(1)
- C语言 | 8套(1)
- C语言 | 2套
- C语言中的X宏
- 编译和运行之间的区别 (1)
- VS代码|用C ++编译并运行(1)
- VS代码|用C ++编译并运行(1)
- VS代码|用C++编译并运行(1)
- VS代码|用C ++编译并运行
- VS代码|用C++编译并运行
- VS代码|用C ++编译并运行
- 用g ++编译
- 用g ++编译(1)
📜 C语言中的编译时间与运行时
📅 最后修改于: 2020-10-22 00:50:49 🧑 作者: Mango
编译时间与运行时
编译时和运行时是软件开发中使用的两个编程术语。编译时是将源代码转换为可执行代码的时间,而运行时是指开始运行可执行代码的时间。编译时和运行时都引用不同类型的错误。
编译时错误
编译时错误是我们编写错误语法时发生的错误。如果我们编写任何编程语言的语法或语义错误,那么编译器将抛出编译时错误。在从程序中清除所有错误之前,编译器将不允许运行该程序。从程序中删除所有错误后,编译器将生成可执行文件。
编译时错误可能是:
- 语法错误
- 语义错误
语法错误
当程序员不遵循任何编程语言的语法时,编译器将引发语法错误。
例如,
整数a,b:
上面的声明像C一样生成编译时错误,每个语句都以分号结尾,但是我们在该语句的末尾添加了一个冒号(:)。
语义错误
当语句对编译器没有意义时,存在语义错误。
例如,
a + b = c;
上面的语句抛出编译时错误。在上面的语句中,我们将’c’的值分配给’a’和’b’的和,这在C编程语言中是不可能的,因为它只能在赋值运算符的左边包含一个变量,而在赋值运算符的右边仅包含一个变量。赋值运算符可以包含多个变量。
上面的语句可以改写为:
c = a + b;
运行时错误
运行时错误是在执行期间和编译之后发生的错误。运行时错误的示例为零除以此类推。由于编译器未指出这些错误,因此不容易检测到这些错误。
让我们看一下编译时和运行时之间的区别:
| Compile-time | Runtime |
|---|---|
| The compile-time errors are the errors which are produced at the compile-time, and they are detected by the compiler. | The runtime errors are the errors which are not generated by the compiler and produce an unpredictable result at the execution time. |
| In this case, the compiler prevents the code from execution if it detects an error in the program. | In this case, the compiler does not detect the error, so it cannot prevent the code from the execution. |
| It contains the syntax and semantic errors such as missing semicolon at the end of the statement. | It contains the errors such as division by zero, determining the square root of a negative number. |
编译时错误示例
#include
int main()
{
int a=20;
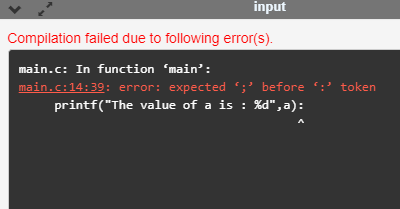
printf("The value of a is : %d",a):
return 0;
}
在上面的代码中,我们尝试print’a’的值,但是会引发错误。我们将冒号放在语句的末尾而不是分号,因此此代码生成了编译时错误。
输出量
运行时错误示例
#include
int main()
{
int a=20;
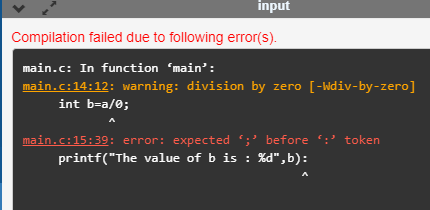
int b=a/0; // division by zero
printf("The value of b is : %d",b):
return 0;
}
在上面的代码中,我们尝试将’b’的值除以零,这将引发运行时错误。
输出量