📌 相关文章
- C#嵌套循环
- C#嵌套循环(1)
- C中的嵌套循环与示例(1)
- C中的嵌套循环与示例
- 嵌套循环 javascript (1)
- 嵌套循环 javascript (1)
- 嵌套循环 - Python 代码示例
- 嵌套循环 javascript 代码示例
- 嵌套循环 javascript 代码示例
- 嵌套循环 - 任何代码示例
- 嵌套循环 c++ 程序示例 - C++ (1)
- 嵌套循环 js - Javascript (1)
- 嵌套循环 js - Javascript 代码示例
- 带有示例的C++中的嵌套循环
- 带有示例的C++中的嵌套循环(1)
- Swift中的嵌套循环(1)
- Swift中的嵌套循环
- 嵌套循环 c++ 程序示例 - C++ 代码示例
- MATLAB嵌套循环(1)
- MATLAB嵌套循环
- 带有示例的Java嵌套循环(1)
- 带有示例的Java嵌套循环
- vue 嵌套循环 - Javascript (1)
- 嵌套循环拼图
- 深度嵌套循环 (1)
- vue 嵌套循环 - Javascript 代码示例
- 深度嵌套循环 - 任何代码示例
- 列表理解中的嵌套循环 - Python (1)
- 列表理解中的嵌套循环 - Python 代码示例
📜 C中的嵌套循环
📅 最后修改于: 2020-10-22 01:12:37 🧑 作者: Mango
C中的嵌套循环
C支持C中的循环嵌套。循环的嵌套是C中的功能,它允许在另一个循环中循环语句。让我们观察一下C中的嵌套循环的示例。
可以在另一个循环内定义任意数量的循环,即,对于定义任意数量的循环没有限制。嵌套级别可以定义为n次。您可以在另一个循环中定义任何类型的循环。例如,您可以在“ for”循环中定义“ while”循环。
嵌套循环的语法
Outer_loop
{
Inner_loop
{
// inner loop statements.
}
// outer loop statements.
}
Outer_loop和Inner_loop是有效的循环,可以是“ for”循环,“ while”循环或“ do-while”循环。
嵌套循环
嵌套的for循环表示在“ for”循环内定义的任何类型的循环。
for (initialization; condition; update)
{
for(initialization; condition; update)
{
// inner loop statements.
}
// outer loop statements.
}
嵌套的for循环示例
#include
int main()
{
int n;// variable declaration
printf("Enter the value of n :");
// Displaying the n tables.
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) // outer loop
{
for(int j=1;j<=10;j++) // inner loop
{
printf("%d\t",(i*j)); // printing the value.
}
printf("\n");
}
以上代码说明
- 首先,将“ i”变量初始化为1,然后将程序控制传递给i <= n。
- 程序控件检查条件’i <= n’是否为真。
- 如果条件为真,则程序控制转到内部循环。
- 内部循环将执行直到条件为真。
- 在执行内循环之后,控件将移回到外循环的更新,即i ++。
- 在增加循环计数器的值之后,再次检查条件,即i <= n。
- 如果条件为真,则将再次执行内部循环。
- 该过程将一直持续到外部循环的条件为真为止。
输出:
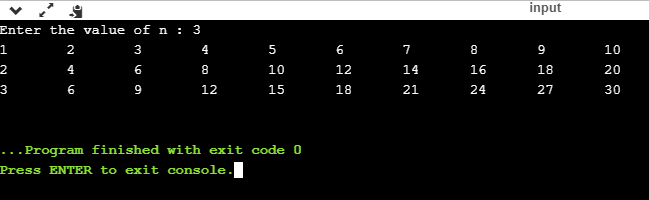
嵌套while循环
嵌套的while循环表示在while循环内定义的任何类型的循环。
while(condition)
{
while(condition)
{
// inner loop statements.
}
// outer loop statements.
}
嵌套while循环的示例
#include
int main()
{
int rows; // variable declaration
int columns; // variable declaration
int k=1; // variable initialization
printf("Enter the number of rows :"); // input the number of rows.
scanf("%d",&rows);
printf("\nEnter the number of columns :"); // input the number of columns.
scanf("%d",&columns);
int a[rows][columns]; //2d array declaration
int i=1;
while(i<=rows) // outer loop
{
int j=1;
while(j<=columns) // inner loop
{
printf("%d\t",k); // printing the value of k.
k++; // increment counter
j++;
}
i++;
printf("\n");
}
}
以上代码的说明。
- 我们创建了2d数组,即int a [rows] [columns]。
- 程序通过1初始化’i’变量。
- 现在,控制移至while循环,此循环检查条件是否为true,然后程序控制移至内部循环。
- 在执行内循环之后,控件将移至外循环的更新,即i ++。
- 在增加值“ i”之后,检查条件(i <=行)。
- 如果条件为真,则控件再次移至内部循环。
- 该过程一直持续到外部循环的条件为真为止。
输出:

嵌套的do..while循环
嵌套的do..while循环意味着在“ do..while”循环内定义的任何类型的循环。
do
{
do
{
// inner loop statements.
}while(condition);
// outer loop statements.
}while(condition);
嵌套的do..while循环示例。
#include
int main()
{
/*printing the pattern
********
********
********
******** */
int i=1;
do // outer loop
{
int j=1;
do // inner loop
{
printf("*");
j++;
}while(j<=8);
printf("\n");
i++;
}while(i<=4);
}
输出:
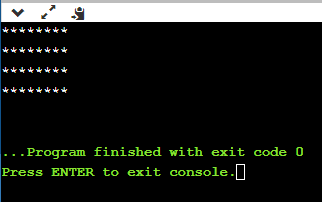
以上代码的说明。
- 首先,我们将外循环计数器变量(即“ i”)初始化为1。
- 我们知道do..while循环只执行一次而不检查条件,因此内部循环执行时不检查外部循环的条件。
- 内部循环执行后,控件将移至i ++的更新。
- 当循环计数器值增加时,将检查条件。如果外部循环中的条件为true,则执行内部循环。
- 该过程将一直持续到外部循环中的条件为真为止。