📌 相关文章
- C#Break语句
- C中的Break语句(1)
- C C++中的Break语句(1)
- C++ break语句
- c++ break 语句 - C++ (1)
- C++ break语句(1)
- C#– Break语句
- C / C++中的Break语句
- R Break语句(1)
- R Break语句
- C++ break语句
- C#Break语句(1)
- C++ break语句(1)
- C / C++中的Break语句
- C C++中的Break语句(1)
- c++ break 语句 - C++ 代码示例
- Java Break语句
- Java中的break语句
- Java Break语句(1)
- Java中的break语句(1)
- Scala Break语句(1)
- Scala 中的 Break 语句(1)
- Scala 中的 Break 语句
- Scala Break语句
- Dart – Break 语句(1)
- Dart – Break 语句
- Swift – Break 语句
- Swift – Break 语句(1)
- R 中的 Break 和 Next 语句(1)
📜 C中的Break语句
📅 最后修改于: 2020-10-22 01:13:14 🧑 作者: Mango
C中断声明
break是C语言中的一个关键字,用于使程序控制脱离循环。 break语句在循环或switch语句内使用。 break语句逐个中断循环,即,在嵌套循环的情况下,它首先中断内部循环,然后继续进行外部循环。 C中的break语句可用于以下两种情况:
- 带开关盒
- 带循环
句法:
//loop or switch case
break;
c中的中断流程图
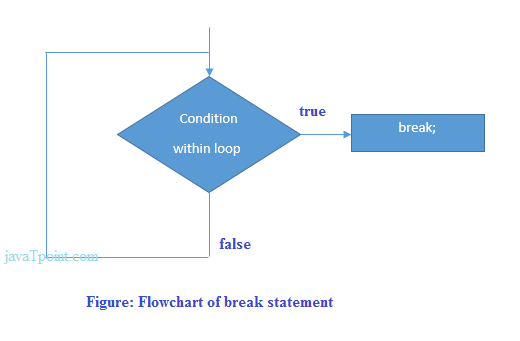
例
#include
#include
void main ()
{
int i;
for(i = 0; i<10; i++)
{
printf("%d ",i);
if(i == 5)
break;
}
printf("came outside of loop i = %d",i);
}
输出量
0 1 2 3 4 5 came outside of loop i = 5
带开关案例的C中断语句示例
单击此处查看使用switch语句进行C中断的示例。
带有嵌套循环的C break语句
在这种情况下,它只会破坏内部循环,而不会破坏外部循环。
#include
int main(){
int i=1,j=1;//initializing a local variable
for(i=1;i<=3;i++){
for(j=1;j<=3;j++){
printf("%d &d\n",i,j);
if(i==2 && j==2){
break;//will break loop of j only
}
}//end of for loop
return 0;
}
输出量
1 1
1 2
1 3
2 1
2 2
3 1
3 2
3 3
如您在控制台上看到的输出,由于打印i == 2和j == 2后有一个break语句,所以未打印2 3。但是会打印3 1,3 2和3 3,因为break语句仅用于中断内部循环。
带while循环的break语句
考虑下面的示例在while循环中使用break语句。
#include
void main ()
{
int i = 0;
while(1)
{
printf("%d ",i);
i++;
if(i == 10)
break;
}
printf("came out of while loop");
}
输出量
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 came out of while loop
带do-while循环的break语句
考虑以下示例,将break语句与do-while循环一起使用。
#include
void main ()
{
int n=2,i,choice;
do
{
i=1;
while(i<=10)
{
printf("%d X %d = %d\n",n,i,n*i);
i++;
}
printf("do you want to continue with the table of %d , enter any non-zero value to continue.",n+1);
scanf("%d",&choice);
if(choice == 0)
{
break;
}
n++;
}while(1);
}
输出量
2 X 1 = 2
2 X 2 = 4
2 X 3 = 6
2 X 4 = 8
2 X 5 = 10
2 X 6 = 12
2 X 7 = 14
2 X 8 = 16
2 X 9 = 18
2 X 10 = 20
do you want to continue with the table of 3 , enter any non-zero value to continue.1
3 X 1 = 3
3 X 2 = 6
3 X 3 = 9
3 X 4 = 12
3 X 5 = 15
3 X 6 = 18
3 X 7 = 21
3 X 8 = 24
3 X 9 = 27
3 X 10 = 30
do you want to continue with the table of 4 , enter any non-zero value to continue.0