可以使用嵌套循环在匹配的列上连接两个不同的表,但更有效和可扩展的方法是使用多映射。这个想法是从我们想要连接的每个列值映射到包含它的所有行,以从两个表中的一个表生成一个多映射。
生成的多重映射必须是基于哈希的。散列本质上是一种将大元素转换为表示相同元素的小元素的技术。因此,为较小的表生成 multimap,从而减少其生成时间和内存大小。
例子:
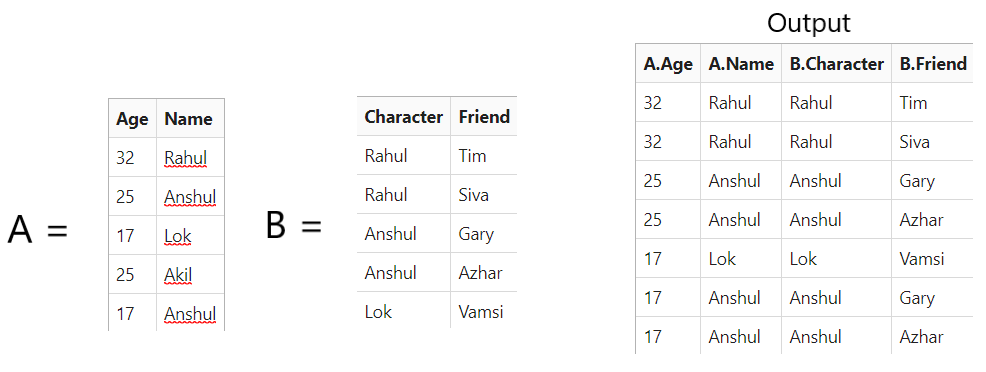
方法:
- 创建两个表。
- 现在,获取两个表上列的 ID。
- 然后创建并实现一个多映射来映射到表 B 的各个行。
- 打印完以上步骤后的结果。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for hashjoin on two tables
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// Generate two tables to join
using tab_t = vector >;
// Table 1
tab_t tab1{ // Age Name
{ "32", "Rahul" },
{ "25", "Anshul" },
{ "17", "Lok" },
{ "25", "Akil" },
{ "17", "Anshul" }
};
// Table 2
tab_t tab2{ // Student Friend
{ "Rahul", "Tim" },
{ "Rahul", "Siva" },
{ "Anshul", "Gary" },
{ "Anshul", "Azhar" },
{ "Lok", "Vamsi" }
};
// Overloading of Output Operator
ostream& operator<<(ostream& o,
const tab_t& t)
{
// Iterate through the tablt t
for (size_t i = 0; i < t.size(); ++i) {
o << i << ":";
for (const auto& e : t[i])
o << '\t' << e;
o << endl;
}
return o;
}
// Function that perform join operation
// on the two tables
tab_t Join(const tab_t& a, size_t columna,
const tab_t& b, size_t columnb)
{
unordered_multimap hashmap;
// Use of Hashmap
for (size_t i = 0;
i < a.size(); ++i) {
hashmap.insert({ a[i][columna], i });
}
// Perform Mapping
tab_t result;
for (size_t i = 0; i < b.size(); ++i) {
auto range = hashmap.equal_range(
b[i][columnb]);
// Create new joined table
for (auto it = range.first;
it != range.second; ++it) {
tab_t::value_type row;
// Insert values to row
row.insert(row.end(),
a[it->second].begin(),
a[it->second].end());
row.insert(row.end(),
b[i].begin(),
b[i].end());
// Push the row
result.push_back(move(row));
}
}
return result;
}
// Driver Code
int main(int argc, char const* argv[])
{
int ret = 0;
// Given Tables
cout << "Table A: " << endl
<< tab1 << endl;
cout << "Table B: " << endl
<< tab2 << endl;
// Function Call
auto tab3 = Join(tab1, 1, tab2, 0);
// Print the joined table
cout << "Joined tables: " << endl
<< tab3 << endl;
return ret;
} Python3
# Python program for hashjoin on two tables
from collections import defaultdict
# Function that perform join operation
# on the two tables
def hashJoin(table1, index1, table2, index2):
h = defaultdict(list)
# Hash
for s in table1:
h[s[index1]].append(s)
# Perform join operation
return [(s, r) for r in table2 for s in h[r[index2]]]
# Driver Code
# Given two tables
table1 = [("32", "Rahul"),
("25", "Anshul"),
("17", "Lok"),
("25", "Akil"),
("17", "Anshul")]
table2 = [("Rahul", "Tim"),
("Rahul", "Siva"),
("Anshul", "Gary"),
("Anshul", "Azhar"),
("Lok", "Vamsi")]
# Print the resultant table
for row in hashJoin(table1, 1, table2, 0):
print(row)输出:
Table A:
0: 32 Rahul
1: 25 Anshul
2: 17 Lok
3: 25 Akil
4: 17 Anshul
Table B:
0: Rahul Tim
1: Rahul Siva
2: Anshul Gary
3: Anshul Azhar
4: Lok Vamsi
Joined tables:
0: 32 Rahul Rahul Tim
1: 32 Rahul Rahul Siva
2: 17 Anshul Anshul Gary
3: 25 Anshul Anshul Gary
4: 17 Anshul Anshul Azhar
5: 25 Anshul Anshul Azhar
6: 17 Lok Lok Vamsi
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。