给定一个二叉树,其中每个节点都具有以下结构。
struct node {
int key;
struct node *left,*right,*random;
} 随机指针指向二叉树的任意一个随机节点,甚至可以指向NULL,克隆给定的二叉树。
方法一(使用哈希)
这个想法是在哈希表中存储从给定树节点到克隆树节点的映射。以下是详细步骤。
1) 递归遍历给定的 Binary 并复制键值、左指针和右指针到克隆树。复制时,将给定树节点到克隆树节点的映射存储在哈希表中。在下面的伪代码中,’cloneNode’ 是克隆树的当前访问节点,’treeNode’ 是给定树的当前访问节点。
cloneNode->key = treeNode->key
cloneNode->left = treeNode->left
cloneNode->right = treeNode->right
map[treeNode] = cloneNode 2)递归遍历两棵树并使用哈希表中的条目设置随机指针。
cloneNode->random = map[treeNode->random] 以下是上述想法的 C++ 实现。以下实现使用来自 C++ STL 的 unordered_map。注意 map 没有实现哈希表,它实际上是基于自平衡二叉搜索树。
CPP
// A hashmap based C++ program to clone a binary
// tree with random pointers
#include
#include
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child,
a pointer to right child and a pointer to
random node*/
struct Node
{
int key;
struct Node* left, *right, *random;
};
/* Helper function that allocates a new Node with the
given data and NULL left, right and random pointers. */
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
temp->random = temp->right = temp->left = NULL;
return (temp);
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its Nodes in inorder*/
void printInorder(Node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
/* First recur on left sutree */
printInorder(node->left);
/* then print data of Node and its random */
cout << "[" << node->key << " ";
if (node->random == NULL)
cout << "NULL], ";
else
cout << node->random->key << "], ";
/* now recur on right subtree */
printInorder(node->right);
}
// This function creates clone by copying key and left and right pointers
// This function also stores mapping from given tree node to clone.
Node* copyLeftRightNode(Node* treeNode, unordered_map &mymap)
{
if (treeNode == NULL)
return NULL;
Node* cloneNode = newNode(treeNode->key);
mymap[treeNode] = cloneNode;
cloneNode->left = copyLeftRightNode(treeNode->left, mymap);
cloneNode->right = copyLeftRightNode(treeNode->right, mymap);
return cloneNode;
}
// This function copies random node by using the hashmap built by
// copyLeftRightNode()
void copyRandom(Node* treeNode, Node* cloneNode, unordered_map &mymap)
{
if (cloneNode == NULL)
return;
cloneNode->random = mymap[treeNode->random];
copyRandom(treeNode->left, cloneNode->left, mymap);
copyRandom(treeNode->right, cloneNode->right, mymap);
}
// This function makes the clone of given tree. It mainly uses
// copyLeftRightNode() and copyRandom()
Node* cloneTree(Node* tree)
{
if (tree == NULL)
return NULL;
unordered_map mymap;
Node* newTree = copyLeftRightNode(tree, mymap);
copyRandom(tree, newTree, mymap);
return newTree;
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
//Test No 1
Node *tree = newNode(1);
tree->left = newNode(2);
tree->right = newNode(3);
tree->left->left = newNode(4);
tree->left->right = newNode(5);
tree->random = tree->left->right;
tree->left->left->random = tree;
tree->left->right->random = tree->right;
// Test No 2
// tree = NULL;
// Test No 3
// tree = newNode(1);
// Test No 4
/* tree = newNode(1);
tree->left = newNode(2);
tree->right = newNode(3);
tree->random = tree->right;
tree->left->random = tree;
*/
cout << "Inorder traversal of original binary tree is: \n";
printInorder(tree);
Node *clone = cloneTree(tree);
cout << "\n\nInorder traversal of cloned binary tree is: \n";
printInorder(clone);
return 0;
} CPP
#include
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child, a pointer to right
child and a pointer to random node*/
struct Node
{
int key;
struct Node* left, *right, *random;
};
/* Helper function that allocates a new Node with the
given data and NULL left, right and random pointers. */
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
temp->random = temp->right = temp->left = NULL;
return (temp);
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its Nodes in inorder*/
void printInorder(Node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
/* First recur on left sutree */
printInorder(node->left);
/* then print data of Node and its random */
cout << "[" << node->key << " ";
if (node->random == NULL)
cout << "NULL], ";
else
cout << node->random->key << "], ";
/* now recur on right subtree */
printInorder(node->right);
}
// This function creates new nodes cloned tree and puts new cloned node
// in between current node and it's left child
// i.e. if current node is A and it's left child is B ( A --- >> B ),
// then new cloned node with key A wil be created (say cA) and
// it will be put as
// A --- >> cA --- >> B
// Here B can be a NULL or a non-NULL left child
// Right child pointer will be set correctly
// i.e. if for current node A, right child is C in original tree
// (A --- >> C) then corresponding cloned nodes cA and cC will like
// cA ---- >> cC
Node* copyLeftRightNode(Node* treeNode)
{
if (treeNode == NULL)
return NULL;
Node* left = treeNode->left;
treeNode->left = newNode(treeNode->key);
treeNode->left->left = left;
if(left != NULL)
left->left = copyLeftRightNode(left);
treeNode->left->right = copyLeftRightNode(treeNode->right);
return treeNode->left;
}
// This function sets random pointer in cloned tree as per original tree
// i.e. if node A's random pointer points to node B, then
// in cloned tree, cA wil point to cB (cA and cB are new node in cloned
// tree corresponding to node A and B in original tree)
void copyRandomNode(Node* treeNode, Node* cloneNode)
{
if (treeNode == NULL)
return;
if(treeNode->random != NULL)
cloneNode->random = treeNode->random->left;
else
cloneNode->random = NULL;
if(treeNode->left != NULL && cloneNode->left != NULL)
copyRandomNode(treeNode->left->left, cloneNode->left->left);
copyRandomNode(treeNode->right, cloneNode->right);
}
// This function will restore left pointers correctly in
// both original and cloned tree
void restoreTreeLeftNode(Node* treeNode, Node* cloneNode)
{
if (treeNode == NULL)
return;
if (cloneNode->left != NULL)
{
Node* cloneLeft = cloneNode->left->left;
treeNode->left = treeNode->left->left;
cloneNode->left = cloneLeft;
}
else
treeNode->left = NULL;
restoreTreeLeftNode(treeNode->left, cloneNode->left);
restoreTreeLeftNode(treeNode->right, cloneNode->right);
}
//This function makes the clone of given tree
Node* cloneTree(Node* treeNode)
{
if (treeNode == NULL)
return NULL;
Node* cloneNode = copyLeftRightNode(treeNode);
copyRandomNode(treeNode, cloneNode);
restoreTreeLeftNode(treeNode, cloneNode);
return cloneNode;
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
/* //Test No 1
Node *tree = newNode(1);
tree->left = newNode(2);
tree->right = newNode(3);
tree->left->left = newNode(4);
tree->left->right = newNode(5);
tree->random = tree->left->right;
tree->left->left->random = tree;
tree->left->right->random = tree->right;
// Test No 2
// Node *tree = NULL;
/*
// Test No 3
Node *tree = newNode(1);
// Test No 4
Node *tree = newNode(1);
tree->left = newNode(2);
tree->right = newNode(3);
tree->random = tree->right;
tree->left->random = tree;
Test No 5
Node *tree = newNode(1);
tree->left = newNode(2);
tree->right = newNode(3);
tree->left->left = newNode(4);
tree->left->right = newNode(5);
tree->right->left = newNode(6);
tree->right->right = newNode(7);
tree->random = tree->left;
*/
// Test No 6
Node *tree = newNode(10);
Node *n2 = newNode(6);
Node *n3 = newNode(12);
Node *n4 = newNode(5);
Node *n5 = newNode(8);
Node *n6 = newNode(11);
Node *n7 = newNode(13);
Node *n8 = newNode(7);
Node *n9 = newNode(9);
tree->left = n2;
tree->right = n3;
tree->random = n2;
n2->left = n4;
n2->right = n5;
n2->random = n8;
n3->left = n6;
n3->right = n7;
n3->random = n5;
n4->random = n9;
n5->left = n8;
n5->right = n9;
n5->random = tree;
n6->random = n9;
n9->random = n8;
/* Test No 7
Node *tree = newNode(1);
tree->left = newNode(2);
tree->right = newNode(3);
tree->left->random = tree;
tree->right->random = tree->left;
*/
cout << "Inorder traversal of original binary tree is: \n";
printInorder(tree);
Node *clone = cloneTree(tree);
cout << "\n\nInorder traversal of cloned binary tree is: \n";
printInorder(clone);
return 0;
} Inorder traversal of original binary tree is:
[4 1], [2 NULL], [5 3], [1 5], [3 NULL],
Inorder traversal of cloned binary tree is:
[4 1], [2 NULL], [5 3], [1 5], [3 NULL], 方法二(临时修改给定的二叉树)
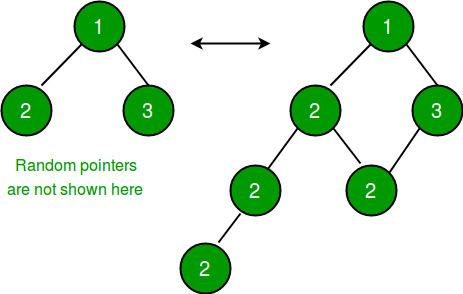
1.在克隆树中创建新节点,并在原始树中相应节点的左指针边缘之间插入原始树中的每个新节点(见下图)。
即如果当前节点是 A 并且它的左子节点是 B ( A — >> B ),那么将创建具有键 A 的新克隆节点(比如 cA),它将被放置为 A — >> cA — >> B ( B 可以是 NULL 或非 NULL 左孩子)。右子指针将被正确设置,即如果对于当前节点 A,原始树中的右孩子是 C (A — >> C) 那么对应的克隆节点 cA 和 cC 将喜欢 cA —- >> cC
2.按照原树在克隆树中设置随机指针
即如果节点 A 的随机指针指向节点 B,那么在克隆树中,cA 将指向 cB(cA 和 cB 是克隆树中的新节点,对应于原始树中的节点 A 和 B)
3.在原始树和克隆树中正确恢复左指针
以下是上述算法的 C++ 实现。
CPP
#include
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child, a pointer to right
child and a pointer to random node*/
struct Node
{
int key;
struct Node* left, *right, *random;
};
/* Helper function that allocates a new Node with the
given data and NULL left, right and random pointers. */
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
temp->random = temp->right = temp->left = NULL;
return (temp);
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its Nodes in inorder*/
void printInorder(Node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
/* First recur on left sutree */
printInorder(node->left);
/* then print data of Node and its random */
cout << "[" << node->key << " ";
if (node->random == NULL)
cout << "NULL], ";
else
cout << node->random->key << "], ";
/* now recur on right subtree */
printInorder(node->right);
}
// This function creates new nodes cloned tree and puts new cloned node
// in between current node and it's left child
// i.e. if current node is A and it's left child is B ( A --- >> B ),
// then new cloned node with key A wil be created (say cA) and
// it will be put as
// A --- >> cA --- >> B
// Here B can be a NULL or a non-NULL left child
// Right child pointer will be set correctly
// i.e. if for current node A, right child is C in original tree
// (A --- >> C) then corresponding cloned nodes cA and cC will like
// cA ---- >> cC
Node* copyLeftRightNode(Node* treeNode)
{
if (treeNode == NULL)
return NULL;
Node* left = treeNode->left;
treeNode->left = newNode(treeNode->key);
treeNode->left->left = left;
if(left != NULL)
left->left = copyLeftRightNode(left);
treeNode->left->right = copyLeftRightNode(treeNode->right);
return treeNode->left;
}
// This function sets random pointer in cloned tree as per original tree
// i.e. if node A's random pointer points to node B, then
// in cloned tree, cA wil point to cB (cA and cB are new node in cloned
// tree corresponding to node A and B in original tree)
void copyRandomNode(Node* treeNode, Node* cloneNode)
{
if (treeNode == NULL)
return;
if(treeNode->random != NULL)
cloneNode->random = treeNode->random->left;
else
cloneNode->random = NULL;
if(treeNode->left != NULL && cloneNode->left != NULL)
copyRandomNode(treeNode->left->left, cloneNode->left->left);
copyRandomNode(treeNode->right, cloneNode->right);
}
// This function will restore left pointers correctly in
// both original and cloned tree
void restoreTreeLeftNode(Node* treeNode, Node* cloneNode)
{
if (treeNode == NULL)
return;
if (cloneNode->left != NULL)
{
Node* cloneLeft = cloneNode->left->left;
treeNode->left = treeNode->left->left;
cloneNode->left = cloneLeft;
}
else
treeNode->left = NULL;
restoreTreeLeftNode(treeNode->left, cloneNode->left);
restoreTreeLeftNode(treeNode->right, cloneNode->right);
}
//This function makes the clone of given tree
Node* cloneTree(Node* treeNode)
{
if (treeNode == NULL)
return NULL;
Node* cloneNode = copyLeftRightNode(treeNode);
copyRandomNode(treeNode, cloneNode);
restoreTreeLeftNode(treeNode, cloneNode);
return cloneNode;
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
/* //Test No 1
Node *tree = newNode(1);
tree->left = newNode(2);
tree->right = newNode(3);
tree->left->left = newNode(4);
tree->left->right = newNode(5);
tree->random = tree->left->right;
tree->left->left->random = tree;
tree->left->right->random = tree->right;
// Test No 2
// Node *tree = NULL;
/*
// Test No 3
Node *tree = newNode(1);
// Test No 4
Node *tree = newNode(1);
tree->left = newNode(2);
tree->right = newNode(3);
tree->random = tree->right;
tree->left->random = tree;
Test No 5
Node *tree = newNode(1);
tree->left = newNode(2);
tree->right = newNode(3);
tree->left->left = newNode(4);
tree->left->right = newNode(5);
tree->right->left = newNode(6);
tree->right->right = newNode(7);
tree->random = tree->left;
*/
// Test No 6
Node *tree = newNode(10);
Node *n2 = newNode(6);
Node *n3 = newNode(12);
Node *n4 = newNode(5);
Node *n5 = newNode(8);
Node *n6 = newNode(11);
Node *n7 = newNode(13);
Node *n8 = newNode(7);
Node *n9 = newNode(9);
tree->left = n2;
tree->right = n3;
tree->random = n2;
n2->left = n4;
n2->right = n5;
n2->random = n8;
n3->left = n6;
n3->right = n7;
n3->random = n5;
n4->random = n9;
n5->left = n8;
n5->right = n9;
n5->random = tree;
n6->random = n9;
n9->random = n8;
/* Test No 7
Node *tree = newNode(1);
tree->left = newNode(2);
tree->right = newNode(3);
tree->left->random = tree;
tree->right->random = tree->left;
*/
cout << "Inorder traversal of original binary tree is: \n";
printInorder(tree);
Node *clone = cloneTree(tree);
cout << "\n\nInorder traversal of cloned binary tree is: \n";
printInorder(clone);
return 0;
}
Inorder traversal of original binary tree is:
[5 9], [6 7], [7 NULL], [8 10], [9 7], [10 6], [11 9], [12 8], [13 NULL],
Inorder traversal of cloned binary tree is:
[5 9], [6 7], [7 NULL], [8 10], [9 7], [10 6], [11 9], [12 8], [13 NULL], 如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。