配对堆就像简化形式的斐波那契堆。它还维护最小堆的属性,即父值小于其子节点值。它可以被认为是一个自调整二项式堆。
每个节点都有一个指向左孩子的指针,左孩子指向孩子的下一个兄弟节点。
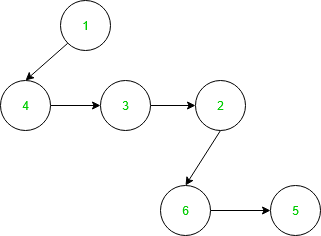
配对堆示例如下:
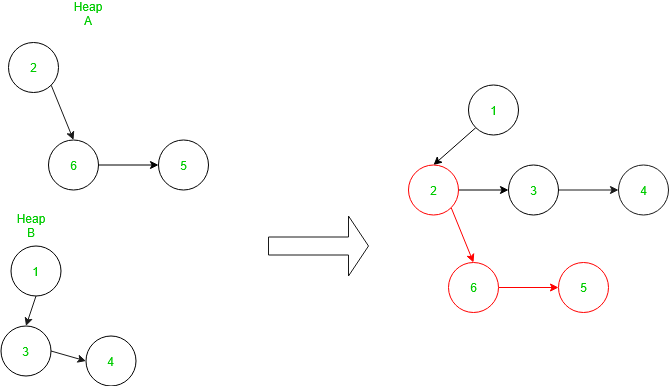
在配对堆中加入或合并
为了加入两个堆,首先,我们比较堆的根节点,如果第一个堆的根节点小于第二个堆的根节点,则第二个堆的根节点成为其根节点的左子节点第一个堆,反之亦然。这个过程的时间复杂度是 O(1)。
合并示例如下:
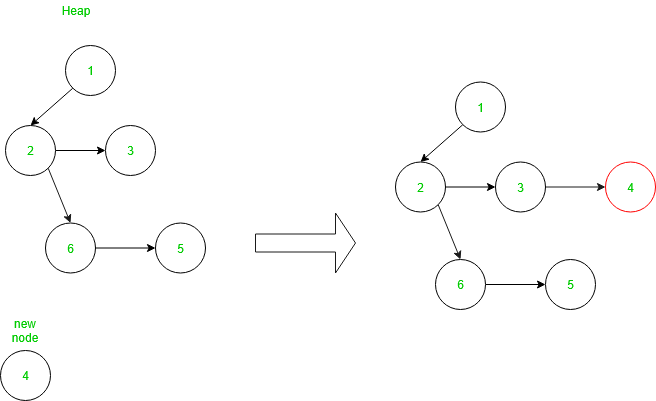
在配对堆中插入:
要在堆中插入新节点,请创建一个新节点并将其与现有堆合并,如上所述。因此,该函数的时间复杂度为 O(1)。
插入示例如下:
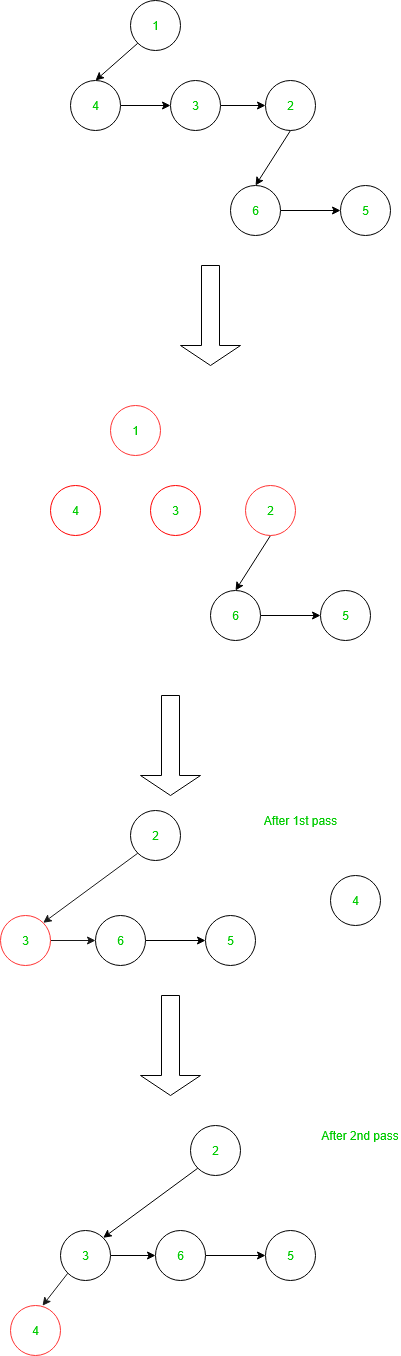
在配对堆中删除:
配对堆中的删除只发生在根节点。首先删除根、左孩子和左孩子的所有兄弟之间的链接。然后合并通过两次传递方法分离左孩子和所有兄弟姐妹获得的树子树并删除根节点。一次将分离的子树从左到右合并,然后从右到左合并子树,形成新的堆,不违反最小堆的条件。此过程需要 O(log n) 时间,其中 n 是节点数。
删除示例如下:
下面是上述方法的实现:
CPP14
#include
using namespace std;
// Heap structure
struct HeapNode {
int key;
HeapNode *leftChild;
HeapNode *nextSibling;
HeapNode():
leftChild(NULL), nextSibling(NULL) {}
// creates a new node
HeapNode(int key_, HeapNode *leftChild_, HeapNode *nextSibling_):
key(key_), leftChild(leftChild_), nextSibling(nextSibling_) {}
// Adds a child and sibling to the node
void addChild(HeapNode *node) {
if(leftChild == NULL)
leftChild = node;
else {
node->nextSibling = leftChild;
leftChild = node;
}
}
};
// Returns true if root of the tree
// is null otherwise returns false
bool Empty(HeapNode *node) {
return (node == NULL);
}
// Function to merge two heaps
HeapNode *Merge(HeapNode *A, HeapNode *B)
{
// If any of the two-nodes is null
// the return the not null node
if(A == NULL) return B;
if(B == NULL) return A;
// To maintain the min heap condition compare
// the nodes and node with minimum value become
// parent of the other node
if(A->key < B->key) {
A->addChild(B);
return A;
}
else {
B->addChild(A);
return B;
}
return NULL; // Unreachable
}
// Returns the root value of the heap
int Top(HeapNode *node) {
return node->key;
}
// Function to insert the new node in the heap
HeapNode *Insert(HeapNode *node, int key) {
return Merge(node, new HeapNode(key, NULL, NULL));
}
// This method is used when we want to delete root node
HeapNode *TwoPassMerge(HeapNode *node) {
if(node == NULL || node->nextSibling == NULL)
return node;
else {
HeapNode *A, *B, *newNode;
A = node;
B = node->nextSibling;
newNode = node->nextSibling->nextSibling;
A->nextSibling = NULL;
B->nextSibling = NULL;
return Merge(Merge(A, B), TwoPassMerge(newNode));
}
return NULL; // Unreachable
}
// Function to delete the root node in heap
HeapNode *Delete(HeapNode *node) {
return TwoPassMerge(node->leftChild);
}
struct PairingHeap {
HeapNode *root;
PairingHeap():
root(NULL) {}
bool Empty(void) {
return ::Empty(root);
}
int Top(void) {
return ::Top(root);
}
void Insert(int key) {
root = ::Insert(root, key);
}
void Delete(void) {
root = ::Delete(root);
}
void Join(PairingHeap other) {
root = ::Merge(root, other.root);
}
};
// Driver Code
int main(void) {
PairingHeap heap1, heap2;
heap2.Insert(5);
heap2.Insert(2);
heap2.Insert(6);
heap1.Insert(1);
heap1.Insert(3);
heap1.Insert(4);
heap1.Join(heap2);
cout << heap1.Top() << endl;
heap1.Delete();
cout << heap1.Top() << endl;
cout<< (heap1.Empty()?"True":"False");
return 0;
} 输出:
1
2
False时间复杂度:
插入: O(1)
合并: O(1)
删除: O(logN)
辅助空间:O(1)。
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。