Java Executor Framework 中的 FixedSizeThreadPoolExecutor
在固定线程池中,池中的线程数取决于任务的类型。对于 CPU 密集型任务,例如加密、实现哈希算法,线程数取决于内核数。因此,每个线程都在其核心上运行,一旦完成任务,它就会从队列中选择下一个任务。此外,可能有多个应用程序正在运行,因此并非所有内核都可以访问。
对于涉及过多 DB 调用或 HTTP 调用的 IO 密集型任务,如果线程较少,则可能有太多线程等待这些 IO 调用完成。因此,CPU 时间被浪费了,因此拥有更多线程是有意义的。通过这种方式,很少有线程利用 CPU 时间进行一些处理/计算,并且很少有线程可能等待 DB/HTTP 调用完成。
方法一:标准方法
在Java,当您想以异步方式运行任务时,您可以生成线程并使线程执行任务。为此,我们有一个实现 Runnable 接口的类。然后我们将 Runnable 的一个实例传递给执行任务的线程。
例子
Java
// Java Program to Test Threads
// Importing required packages
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Main class
// to test the threads
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating 5 threads and passing an instance
// of Runnable implementation
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
// Creating object of Thread class
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
// Printing and display the current thread
// using curentThread() and getName() method
System.out.println(
"Printing document by thread : "
+ Thread.currentThread().getName());
// Try block to check for exceptions
try {
// Making current threads to sleep
// for 1 second
Thread.sleep(1000L);
}
// Catch block to handle th exceptions
catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Print the line number where exception
// occurred
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
// Starting the threads using start() method
thread.start();
}
}
}Java
// Java Program to demonstrate FixedThreadPoolExecutor
// Importing required libraries
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an object of ExecutorService for
// asking the executor service to create a thread
// pool with fixed number of threads
ExecutorService service
= Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
// Creating 5 threads using loops
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
// Submitting task to service's execute method
service.execute(() -> {
// Printing and display the current thread
// using curentThread() and getName() method
System.out.println(
"Printing document by thread : "
+ Thread.currentThread().getName());
// Try block to check for exceptions
try {
// Making threads to sleep for 1 second
// using the sleep() method
Thread.sleep(1000L);
}
// Catch block to handle the exceptions
catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Print and display the line number
// where the exception occurred
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
// In order to avoid further coming execution of
// tasks shutdown() method is used
service.shutdown();
}
}Note: The order of executing the task changes with each run.
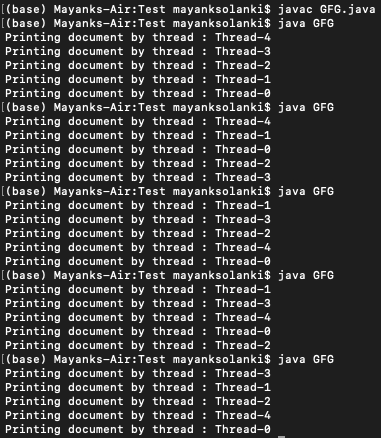
输出说明:
这里在主线程中产生了 5 个线程,每个线程都给出了一个 Runnable 实现的实例。当我们说thread.start() 时,可运行实现的 run 方法被调用并执行任务。
方法二:
到目前为止,我们已经讨论了上述方法,并经历了每次运行的输出波动。有必要制定另一种方法,因为作为开发人员,我们需要处理线程的创建和管理,当应用程序中有很多线程时,这会变得很乏味。为此,我们有 ExecutorService 框架,它有助于管理线程。作为开发者,我们选择执行器服务必须创建的线程池类型,并将线程管理的责任委托给执行器服务。在 Fixed Size 线程池执行器中,我们在池中创建固定数量的线程并将任务提交给执行器服务。提交的任务被存储在阻塞队列中,每个线程从阻塞队列中挑选一个任务并执行它,然后继续执行下一个任务。阻塞队列以这样一种方式实现,它可以处理并发操作,尤其是当多个线程试图从队列中提取相同的任务时。
例子:
Java
// Java Program to demonstrate FixedThreadPoolExecutor
// Importing required libraries
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an object of ExecutorService for
// asking the executor service to create a thread
// pool with fixed number of threads
ExecutorService service
= Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
// Creating 5 threads using loops
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
// Submitting task to service's execute method
service.execute(() -> {
// Printing and display the current thread
// using curentThread() and getName() method
System.out.println(
"Printing document by thread : "
+ Thread.currentThread().getName());
// Try block to check for exceptions
try {
// Making threads to sleep for 1 second
// using the sleep() method
Thread.sleep(1000L);
}
// Catch block to handle the exceptions
catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Print and display the line number
// where the exception occurred
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
// In order to avoid further coming execution of
// tasks shutdown() method is used
service.shutdown();
}
}
输出:
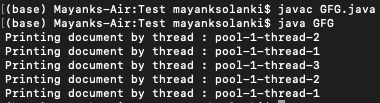
输出说明:
这里我们创建了一个包含 3 个线程的线程池,我们将 5 个任务提交给了 executor 服务。该执行器服务负责执行由线程池中的线程提交的任务。执行器服务负责创建线程池。所以这里的线程名称是 pool-X-thread-Y。