Java中的 ConcurrentLinkedQueue 示例
Java中的ConcurrentLinkedQueue类是Java集合框架的一部分。它属于Java.util.concurrent包。它是在 JDK 1.5 中引入的。它用于在 LinkedList 的帮助下同时实现 Queue。它是 Queue 的无界线程安全实现,它以 FIFO(先进先出)的方式在 Queue 的尾部插入元素。它可以在多个线程之间共享无界队列时使用。此类不允许空元素。迭代器是弱一致的。此类及其迭代器实现了Queue和Iterator接口的所有可选方法。
类层次结构:
java.lang.Object
↳ java.util.AbstractCollection
↳ java.util.AbstractQueue
↳ Class ConcurrentLinkedQueue 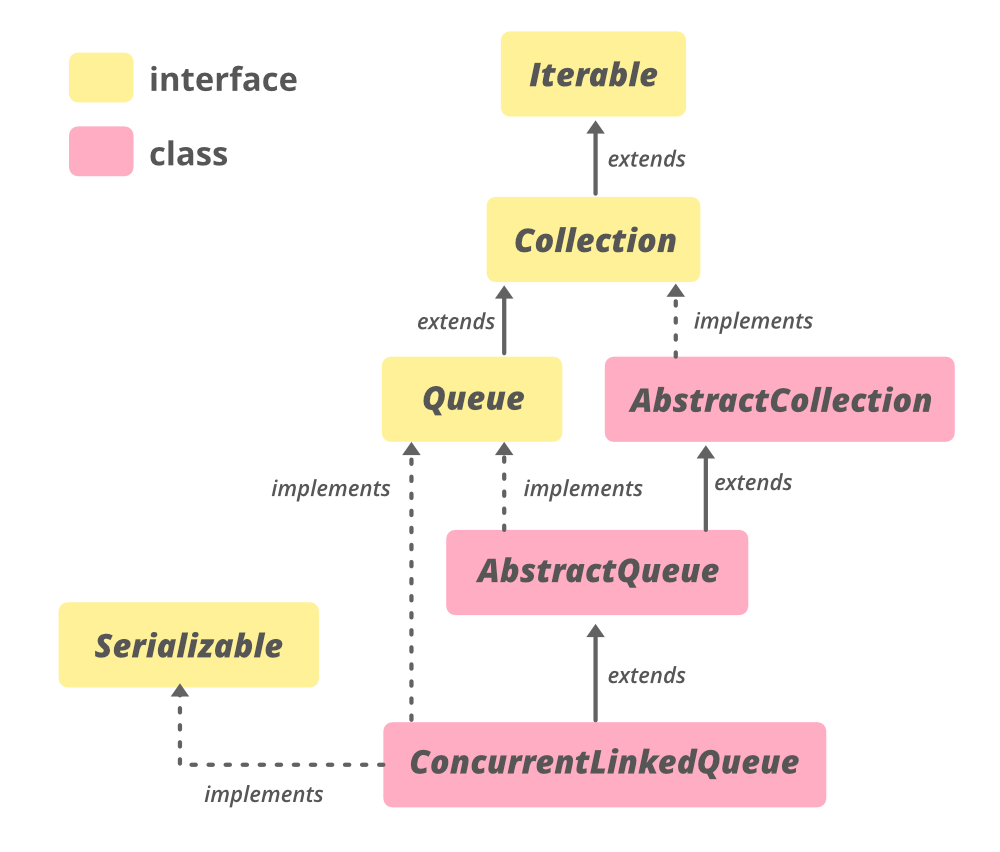
宣言:
public class ConcurrentLinkedQueue
这里, E是这个集合维护的元素的类型。
ConcurrentLinkedQueue 的构造函数
要构造 ConcurrentLinkedQueue,我们需要从Java.util.ConcurrentLinkedQueue导入它。
1. ConcurrentLinkedQueue() :该构造函数用于构造一个空队列。
ConcurrentLinkedQueue
2. ConcurrentLinkedQueue(Collection
ConcurrentLinkedQueue
下面是一个示例程序,用于说明Java中的 ConcurrentLinkedQueue:
示例 1:
Java
// Java program to demonstrate ConcurrentLinkedQueue
import java.util.concurrent.*;
class ConcurrentLinkedQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Create a ConcurrentLinkedQueue
// using ConcurrentLinkedQueue() constructor
ConcurrentLinkedQueue
clq = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue();
clq.add(12);
clq.add(70);
clq.add(1009);
clq.add(475);
// Displaying the existing LinkedQueue
System.out.println("ConcurrentLinkedQueue: "
+ clq);
// Create a ConcurrentLinkedQueue
// using ConcurrentLinkedQueue(Collection c)
// constructor
ConcurrentLinkedQueue
clq1 = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue(clq);
// Displaying the existing LinkedQueue
System.out.println("ConcurrentLinkedQueue1: "
+ clq1);
}
} Java
// Java code to illustrate
// methods of ConcurrentLinkedQueue
import java.util.concurrent.*;
class ConcurrentLinkedQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Create a ConcurrentLinkedQueue
// using ConcurrentLinkedQueue()
// constructor
ConcurrentLinkedQueue
clq = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue();
clq.add(12);
clq.add(70);
clq.add(1009);
clq.add(475);
// Displaying the existing ConcurrentLinkedQueue
System.out.println("ConcurrentLinkedQueue: "
+ clq);
// Displaying the first element
// using peek() method
System.out.println("First Element is: "
+ clq.peek());
// Remove and display the first element
// using poll() method
System.out.println("Head Element is: "
+ clq.poll());
// Displaying the existing ConcurrentLinkedQueue
System.out.println("ConcurrentLinkedQueue: "
+ clq);
// Get the size using size() method
System.out.println("Size: "
+ clq.size());
}
} Java
// Java Program Demonstrate adding
// elements to ConcurrentLinkedQueue
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.util.*;
public class AddingElementsExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Create an instance of ConcurrentLinkedQueue
ConcurrentLinkedQueue queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue();
// Add String to queue using add method
queue.add("Kolkata");
queue.add("Patna");
queue.add("Delhi");
queue.add("Jammu");
// Displaying the existing ConcurrentLinkedQueue
System.out.println("ConcurrentLinkedQueue: " + queue);
// create a ArrayList of Strings
ArrayList arraylist = new ArrayList();
// add String to ArrayList
arraylist.add("Sanjeet");
arraylist.add("Rabi");
arraylist.add("Debasis");
arraylist.add("Raunak");
arraylist.add("Mahesh");
// Displaying the existing Collection
System.out.println("Collection to be added: " + arraylist);
// apply addAll() method and passed
// the arraylist as parameter
boolean response = queue.addAll(arraylist);
// Displaying the existing ConcurrentLinkedQueue
System.out.println("Collection added: " + response);
// Displaying the existing ConcurrentLinkedQueue
System.out.println("ConcurrentLinkedQueue: " + queue);
}
} Java
// Java Program Demonstrate removing
// elements from ConcurrentLinkedQueue
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class RemovingElementsExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Create an instance of ConcurrentLinkedQueue
ConcurrentLinkedQueue queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue();
// Add Numbers to queue using add(e) method
queue.add(4353);
queue.add(7824);
queue.add(78249);
queue.add(8724);
// Displaying the existing ConcurrentLinkedQueue
System.out.println("ConcurrentLinkedQueue: " + queue);
// apply remove() for Number 78249
boolean response = queue.remove(78249);
// print results
System.out.println("Removing Number 78249 successful: " + response);
// Displaying the existing ConcurrentLinkedQueue
System.out.println("Updated ConcurrentLinkedQueue: " + queue);
}
} Java
// Java Program Demonstrate Iterating
// over ConcurrentLinkedQueue
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.util.*;
public class TraversingExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Create an instance of ConcurrentLinkedQueue
ConcurrentLinkedQueue queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue();
// Add String to queue using add(e) method
queue.add("Aman");
queue.add("Amar");
queue.add("Sanjeet");
queue.add("Rabi");
// Displaying the existing ConcurrentLinkedQueue
System.out.println("ConcurrentLinkedQueue : " + queue);
// Call iterator() method
Iterator iterator = queue.iterator();
// Print elements of iterator
System.out.println("\nThe String Values of iterator are:");
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
} Java
// Java Program Demonstrate accessing
// elements of ConcurrentLinkedQueue
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class AccessingElementsExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IllegalStateException
{
// Create an instance of ConcurrentLinkedQueue
ConcurrentLinkedQueue Q = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>();
// Add numbers to end of Queue
Q.add(7855642);
Q.add(35658786);
Q.add(5278367);
Q.add(74381793);
// print queue
System.out.println("Queue: " + Q);
// print head
System.out.println("Queue's head: " + Q.element());
// print head
System.out.println("Queue's head: " + Q.peek());
}
} ConcurrentLinkedQueue: [12, 70, 1009, 475]
ConcurrentLinkedQueue1: [12, 70, 1009, 475]示例 2:
Java
// Java code to illustrate
// methods of ConcurrentLinkedQueue
import java.util.concurrent.*;
class ConcurrentLinkedQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Create a ConcurrentLinkedQueue
// using ConcurrentLinkedQueue()
// constructor
ConcurrentLinkedQueue
clq = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue();
clq.add(12);
clq.add(70);
clq.add(1009);
clq.add(475);
// Displaying the existing ConcurrentLinkedQueue
System.out.println("ConcurrentLinkedQueue: "
+ clq);
// Displaying the first element
// using peek() method
System.out.println("First Element is: "
+ clq.peek());
// Remove and display the first element
// using poll() method
System.out.println("Head Element is: "
+ clq.poll());
// Displaying the existing ConcurrentLinkedQueue
System.out.println("ConcurrentLinkedQueue: "
+ clq);
// Get the size using size() method
System.out.println("Size: "
+ clq.size());
}
}
ConcurrentLinkedQueue: [12, 70, 1009, 475]
First Element is: 12
Head Element is: 12
ConcurrentLinkedQueue: [70, 1009, 475]
Size: 3基本操作
1.添加元素
ConcurrentLinkedQueue 提供了两种添加元素的方法。
- add() 它插入元素,作为参数传递到这个 ConcurrentLinkedQueue 的尾部。如果插入成功,此方法返回 True。 ConcurrentLinkedQueue 是无界的,所以这个方法永远不会抛出 IllegalStateException 或返回 false。
- addAll() 它插入集合的所有元素,在 ConcurrentLinkedQueue 的末尾作为参数传递。元素的插入与集合的迭代器返回的顺序相同。
Java
// Java Program Demonstrate adding
// elements to ConcurrentLinkedQueue
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.util.*;
public class AddingElementsExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Create an instance of ConcurrentLinkedQueue
ConcurrentLinkedQueue queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue();
// Add String to queue using add method
queue.add("Kolkata");
queue.add("Patna");
queue.add("Delhi");
queue.add("Jammu");
// Displaying the existing ConcurrentLinkedQueue
System.out.println("ConcurrentLinkedQueue: " + queue);
// create a ArrayList of Strings
ArrayList arraylist = new ArrayList();
// add String to ArrayList
arraylist.add("Sanjeet");
arraylist.add("Rabi");
arraylist.add("Debasis");
arraylist.add("Raunak");
arraylist.add("Mahesh");
// Displaying the existing Collection
System.out.println("Collection to be added: " + arraylist);
// apply addAll() method and passed
// the arraylist as parameter
boolean response = queue.addAll(arraylist);
// Displaying the existing ConcurrentLinkedQueue
System.out.println("Collection added: " + response);
// Displaying the existing ConcurrentLinkedQueue
System.out.println("ConcurrentLinkedQueue: " + queue);
}
}
ConcurrentLinkedQueue: [Kolkata, Patna, Delhi, Jammu]
Collection to be added: [Sanjeet, Rabi, Debasis, Raunak, Mahesh]
Collection added: true
ConcurrentLinkedQueue: [Kolkata, Patna, Delhi, Jammu, Sanjeet, Rabi, Debasis, Raunak, Mahesh]2. 移除元素
ConcurrentLinkedQueue 的 remove(Object o) 方法用于删除指定元素的单个实例(如果存在)。它删除一个元素e ,使得 o.equals(e)。如果此 ConcurrentLinkedQueue 包含指定的元素,则返回 true,否则返回 false。
Java
// Java Program Demonstrate removing
// elements from ConcurrentLinkedQueue
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class RemovingElementsExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Create an instance of ConcurrentLinkedQueue
ConcurrentLinkedQueue queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue();
// Add Numbers to queue using add(e) method
queue.add(4353);
queue.add(7824);
queue.add(78249);
queue.add(8724);
// Displaying the existing ConcurrentLinkedQueue
System.out.println("ConcurrentLinkedQueue: " + queue);
// apply remove() for Number 78249
boolean response = queue.remove(78249);
// print results
System.out.println("Removing Number 78249 successful: " + response);
// Displaying the existing ConcurrentLinkedQueue
System.out.println("Updated ConcurrentLinkedQueue: " + queue);
}
}
ConcurrentLinkedQueue: [4353, 7824, 78249, 8724]
Removing Number 78249 successful: true
Updated ConcurrentLinkedQueue: [4353, 7824, 8724]3. 迭代元素
ConcurrentLinkedQueue 的 iterator() 方法用于以适当的顺序返回与此 ConcurrentLinkedQueue 相同元素的迭代器。此方法返回的元素包含从 first(head) 到 last(tail) 顺序的元素。返回的迭代器是弱一致的。
Java
// Java Program Demonstrate Iterating
// over ConcurrentLinkedQueue
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.util.*;
public class TraversingExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Create an instance of ConcurrentLinkedQueue
ConcurrentLinkedQueue queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue();
// Add String to queue using add(e) method
queue.add("Aman");
queue.add("Amar");
queue.add("Sanjeet");
queue.add("Rabi");
// Displaying the existing ConcurrentLinkedQueue
System.out.println("ConcurrentLinkedQueue : " + queue);
// Call iterator() method
Iterator iterator = queue.iterator();
// Print elements of iterator
System.out.println("\nThe String Values of iterator are:");
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
}
ConcurrentLinkedQueue : [Aman, Amar, Sanjeet, Rabi]
The String Values of iterator are:
Aman
Amar
Sanjeet
Rabi4. 访问元素
Queue提供的 peek() 和 element() 方法用于访问 ConcurrentLinkedQueue 的元素。
element()方法与peek( ) 方法的不同之处仅在于如果此队列为空,它将引发异常。
Java
// Java Program Demonstrate accessing
// elements of ConcurrentLinkedQueue
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class AccessingElementsExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IllegalStateException
{
// Create an instance of ConcurrentLinkedQueue
ConcurrentLinkedQueue Q = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>();
// Add numbers to end of Queue
Q.add(7855642);
Q.add(35658786);
Q.add(5278367);
Q.add(74381793);
// print queue
System.out.println("Queue: " + Q);
// print head
System.out.println("Queue's head: " + Q.element());
// print head
System.out.println("Queue's head: " + Q.peek());
}
}
Queue: [7855642, 35658786, 5278367, 74381793]
Queue's head: 7855642
Queue's head: 7855642ConcurrentLinkedQueue 的方法
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| add(E e) | Inserts the specified element at the tail of this queue. |
| addAll(Collection c) | Appends all of the elements in the specified collection to the end of this queue, in the order that they are returned by the specified collection’s iterator. |
| contains(Object o) | Returns true if this queue contains the specified element. |
| forEach(Consumer action) | Performs the given action for each element of the Iterable until all elements have been processed or the action throws an exception. |
| isEmpty() | Returns true if this queue contains no elements. |
| iterator() | Returns an iterator over the elements in this queue in the proper sequence. |
| offer(E e) | Inserts the specified element at the tail of this queue. |
| remove(Object o) | Removes a single instance of the specified element from this queue, if it is present. |
| removeAll(Collection c) | Removes all of this collection’s elements that are also contained in the specified collection (optional operation). |
| removeIf(Predicate filter) | Removes all of the elements of this collection that satisfy the given predicate. |
| retainAll(Collection c) | Retains only the elements in this collection that are contained in the specified collection (optional operation). |
| size() | Returns the number of elements in this queue. |
| spliterator() | Returns a Spliterator over the elements in this queue. |
| toArray() | Returns an array containing all of the elements in this queue, in the proper sequence. |
| toArray(T[] a) | Returns an array containing all of the elements in this queue, in proper sequence; the runtime type of the returned array is that of the specified array. |
在类Java.util.AbstractQueue 中声明的方法
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| clear() | Removes all the elements from this queue. |
| element() | Retrieves, but does not remove, the head of this queue. |
| remove() | Retrieves and removes the head of this queue. |
在类Java.util.AbstractCollection 中声明的方法
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| containsAll(Collection c) | Returns true if this collection contains all of the elements in the specified collection. |
| toString() | Returns a string representation of this collection. |
在接口Java.util.Collection 中声明的方法
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| clear() | Removes all of the elements from this collection (optional operation). |
| containsAll(Collection c) | Returns true if this collection contains all of the elements in the specified collection. |
| equals(Object o) | Compares the specified object with this collection for equality. |
| hashCode() | Returns the hash code value for this collection. |
| parallelStream() | Returns a possibly parallel Stream with this collection as its source. |
| stream() | Returns a sequential Stream with this collection as its source. |
| toArray(IntFunction | Returns an array containing all of the elements in this collection, using the provided generator function to allocate the returned array. |
在接口Java .util.Queue 中声明的方法
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| element() | Retrieves, but does not remove, the head of this queue. |
| peek() | Retrieves, but does not remove, the head of this queue, or returns null if this queue is empty. |
| poll() | Retrieves and removes the head of this queue, or returns null if this queue is empty. |
| remove() | Retrieves and removes the head of this queue. |
参考: Java : Java